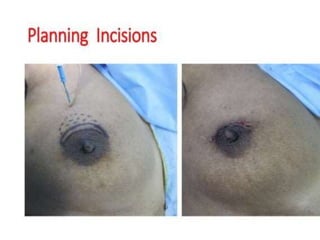
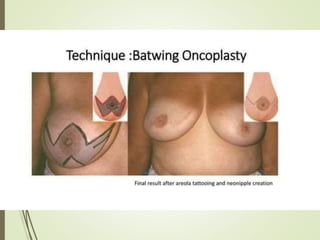
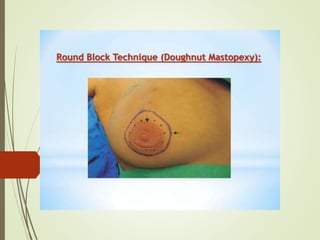
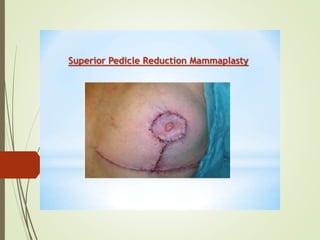
This document discusses various breast reconstruction procedures after mastectomy. It describes breast-conserving surgeries like reduction, mastopexy, and flap techniques. Breast reconstruction can involve implants, tissue expanders, or flaps from the abdomen, back, thighs, or buttocks. The timing of reconstruction can be immediate, delayed, or delayed-immediate. Post-operative monitoring includes fluorescent angiography or near-infrared spectroscopy to check flap vascularity. Nipple reconstruction may also be performed along with tattooing.