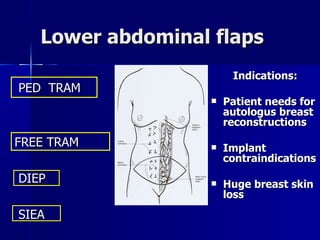
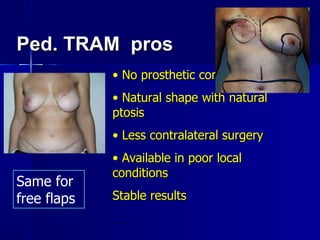
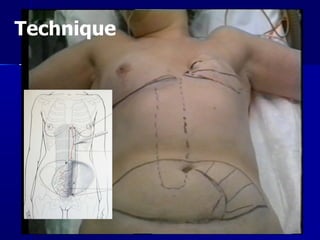
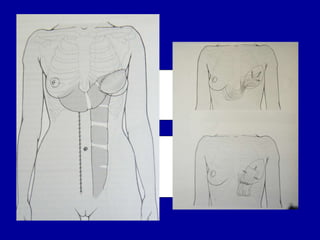
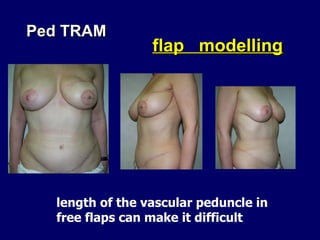
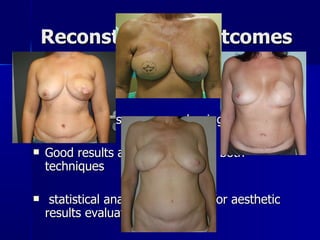
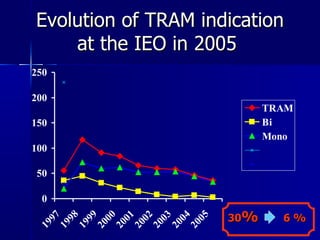
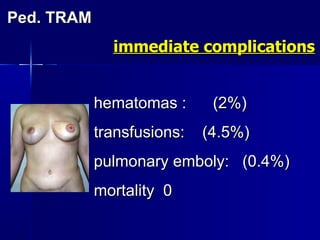
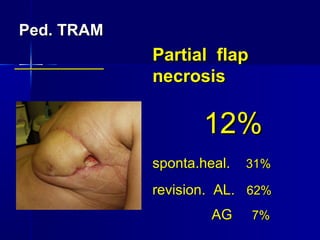
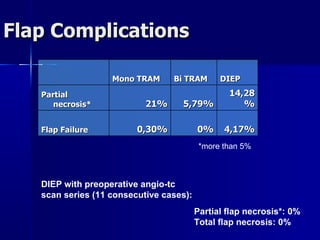
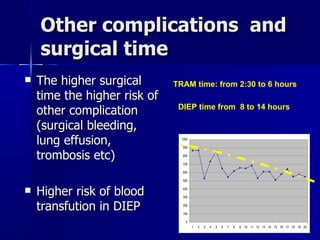
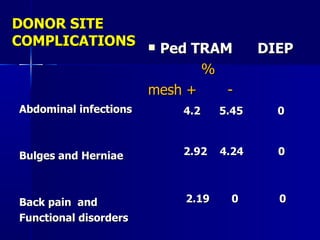
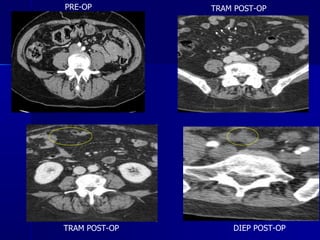
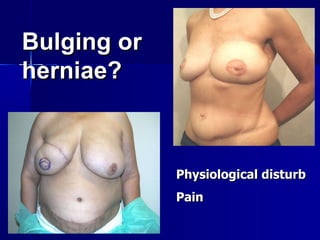
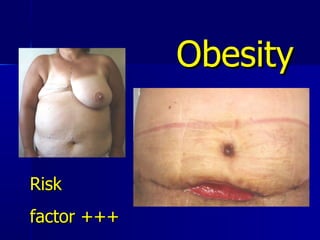
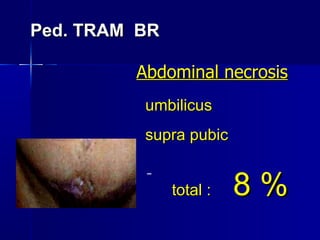
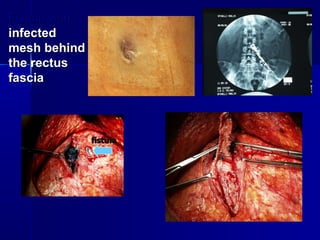
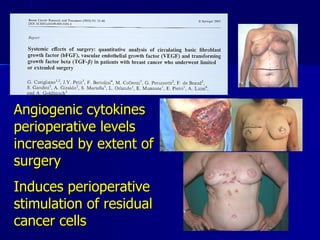
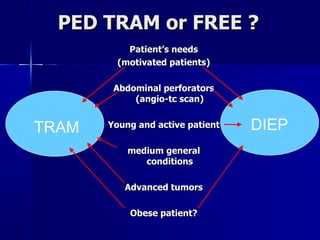
The document compares pedicled transverse rectus abdominis myocutaneous (TRAM) flaps and deep inferior epigastric perforator (DIEP) flaps for breast reconstruction. TRAM flaps have faster procedures and lower total flap failure rates, while DIEP flaps have fewer donor site complications and preserve abdominal wall function with less partial flap necrosis. Either technique can achieve good aesthetic outcomes, but DIEP may have fewer complications due to shorter operating times and less disruption of the abdominal wall. Patient factors like perforator anatomy, tumor status, and obesity should be considered to determine the best flap for each individual.