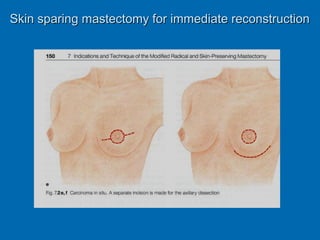
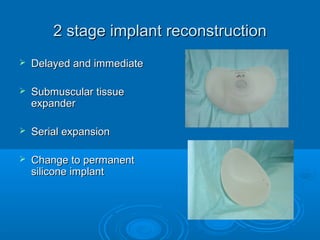
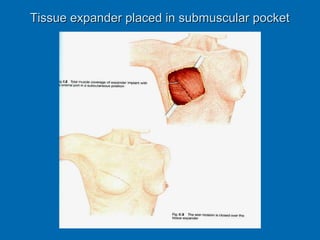
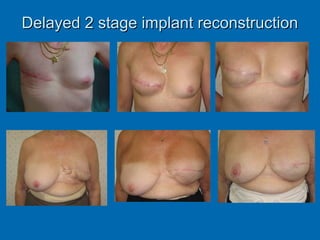
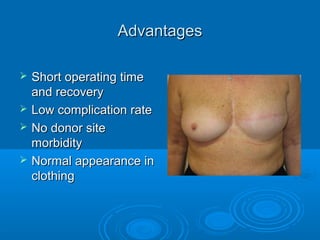
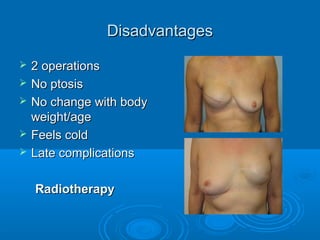
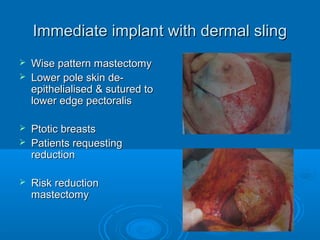
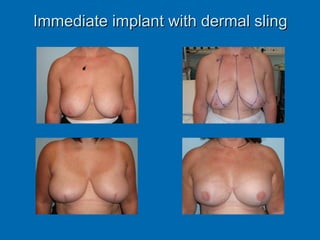
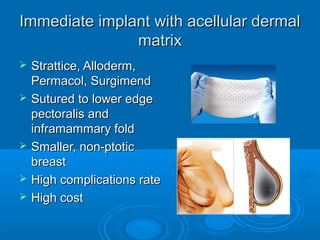
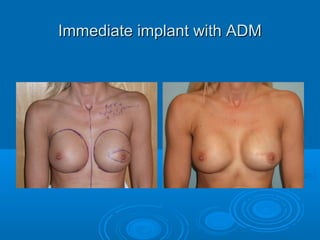
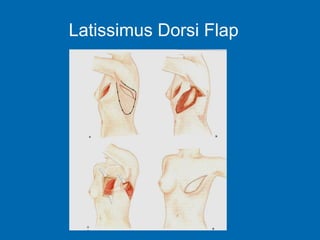
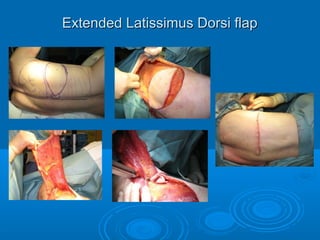
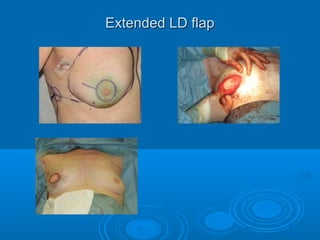
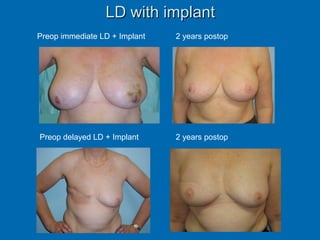
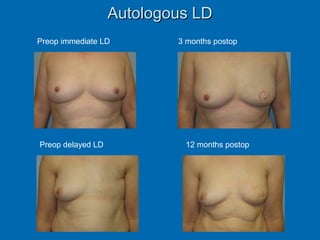
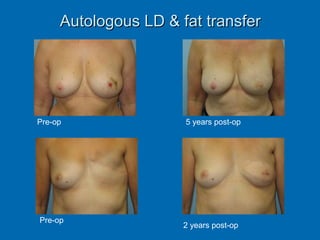
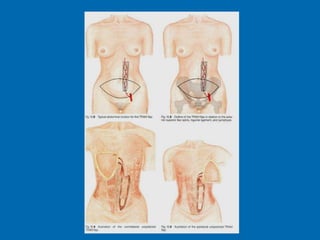
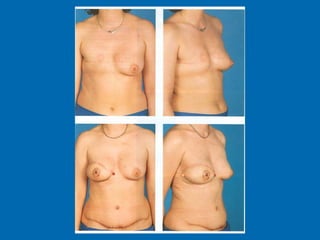
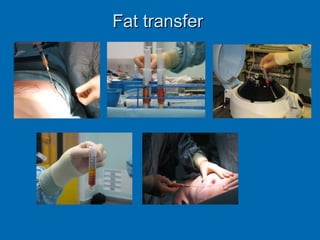
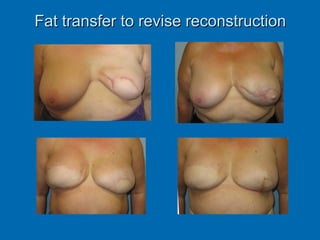
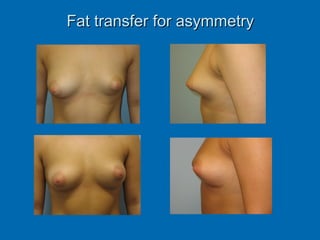
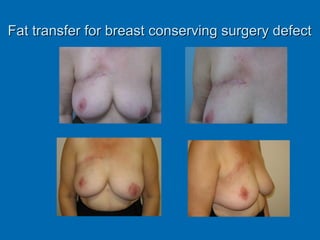
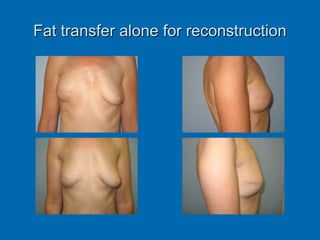
Breast reconstruction can be done immediately during mastectomy or delayed after adjuvant therapy completion. Immediate reconstruction provides better cosmetic outcomes and early psychological benefits, while delayed allows more time for consideration and ensures therapy is done. Techniques include expanders/implants, latissimus dorsi flaps, TRAM/DIEP flaps, and fat grafting. Each option has pros and cons like operating time, recovery duration, and risks of complications or donor site morbidity that require considering patient factors and desires. A multidisciplinary team can help personalize the optimal reconstructive approach.