1. Flap reconstruction in breast cancer involves using tissue from another part of the body to reconstruct the breast after mastectomy.
2. The main types of flaps are implant-based reconstruction, autologous tissue reconstruction using the patient's own tissue, and a combination of implant and autologous tissue.
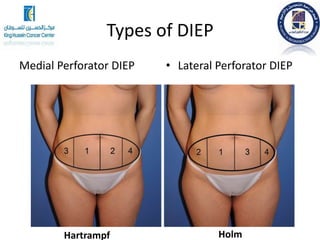
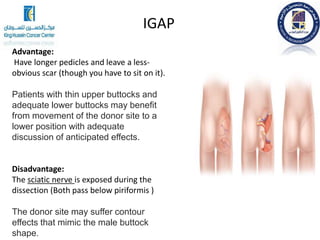
3. Specific autologous tissue flaps discussed include the latissimus dorsi flap which uses back muscle and skin, and TRAM flaps which use abdominal tissue. Each flap has benefits and risks that depend on the individual patient's situation and goals.



























































![Relevant Anatomy
If Single Pedicle
• Only tissues directly over or immediately
adjacent to the muscle have adequate vascularity.
• If more tissues are needed, consider other
procedures (midabdominal TRAM, delay
procedure, double pedicle TRAM, super-charged
TRAM, free TRAM flap, deep inferior epigastric
perforator [DIEP] flap).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/flapreconstruction-final-201224070759/85/Flap-reconstruction-61-320.jpg)