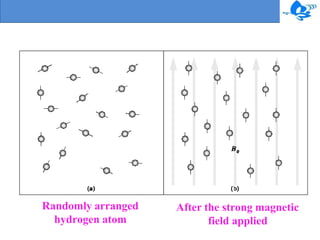
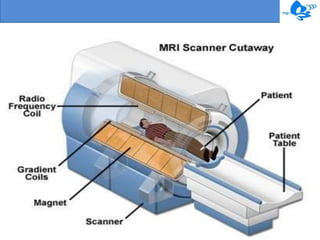
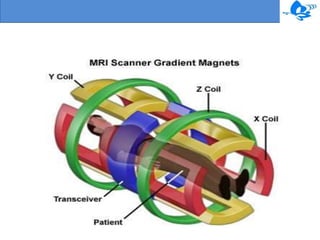
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique that uses magnetism, radio waves, and a computer to produce detailed images of organs and tissues in the body. The first MRI exam took 5 hours to produce one image in 1997, but modern MRI machines can generate highly detailed images of soft tissues using powerful magnetic fields and radiofrequency coils. While MRI is useful for imaging soft tissues and does not use ionizing radiation, it has some disadvantages such as high costs, loud noises during scans, and its incompatibility with certain medical devices.