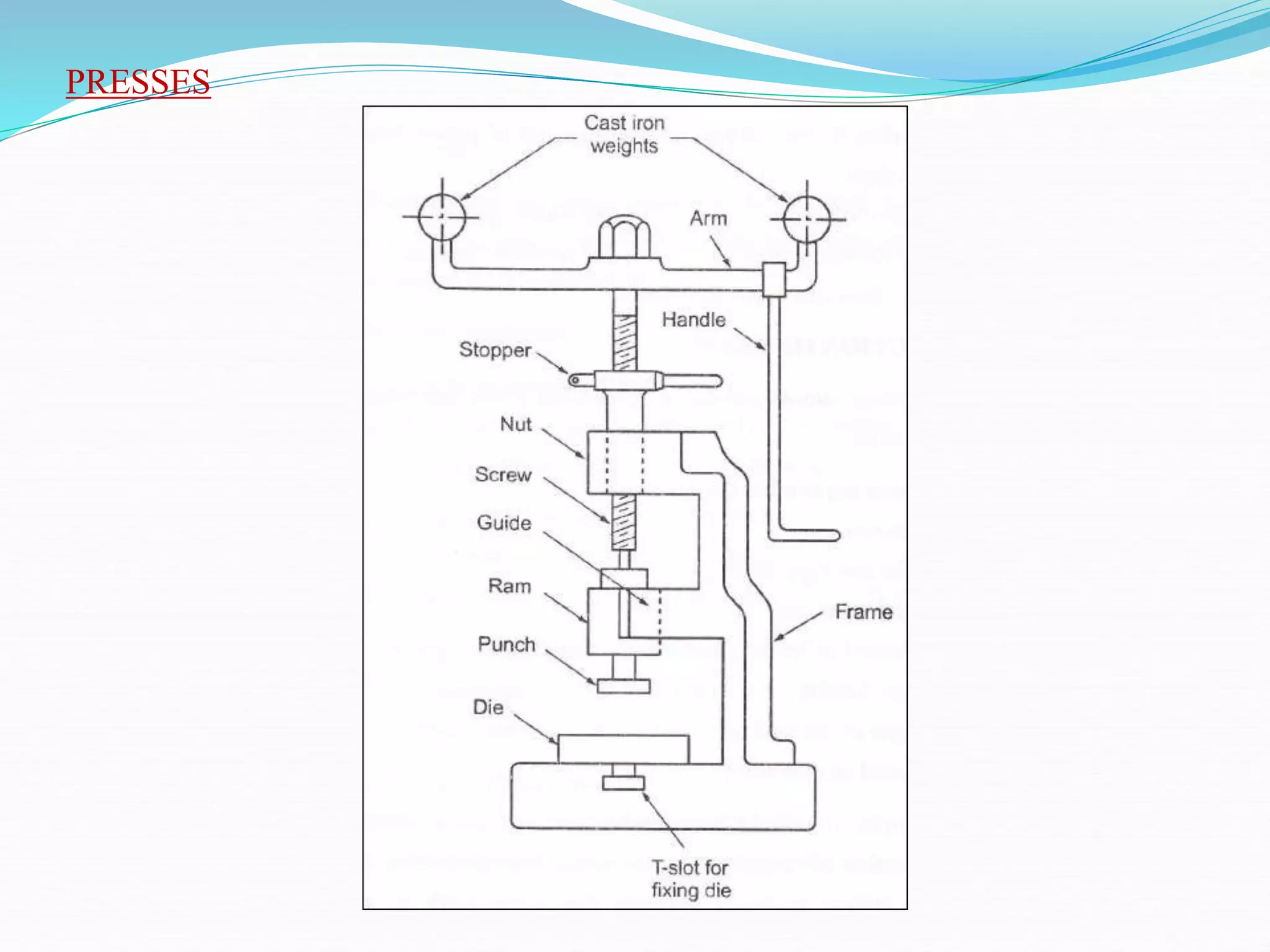
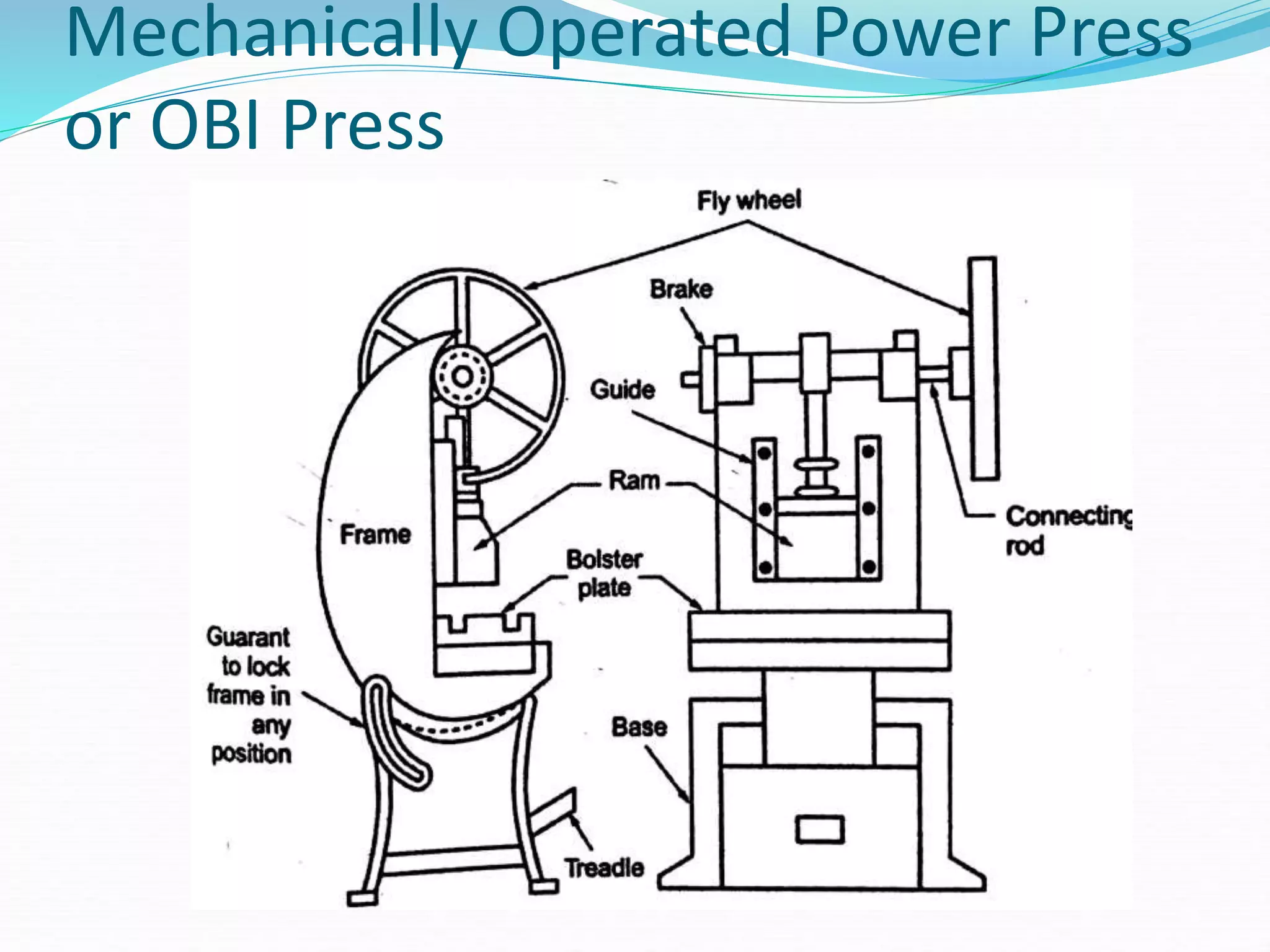
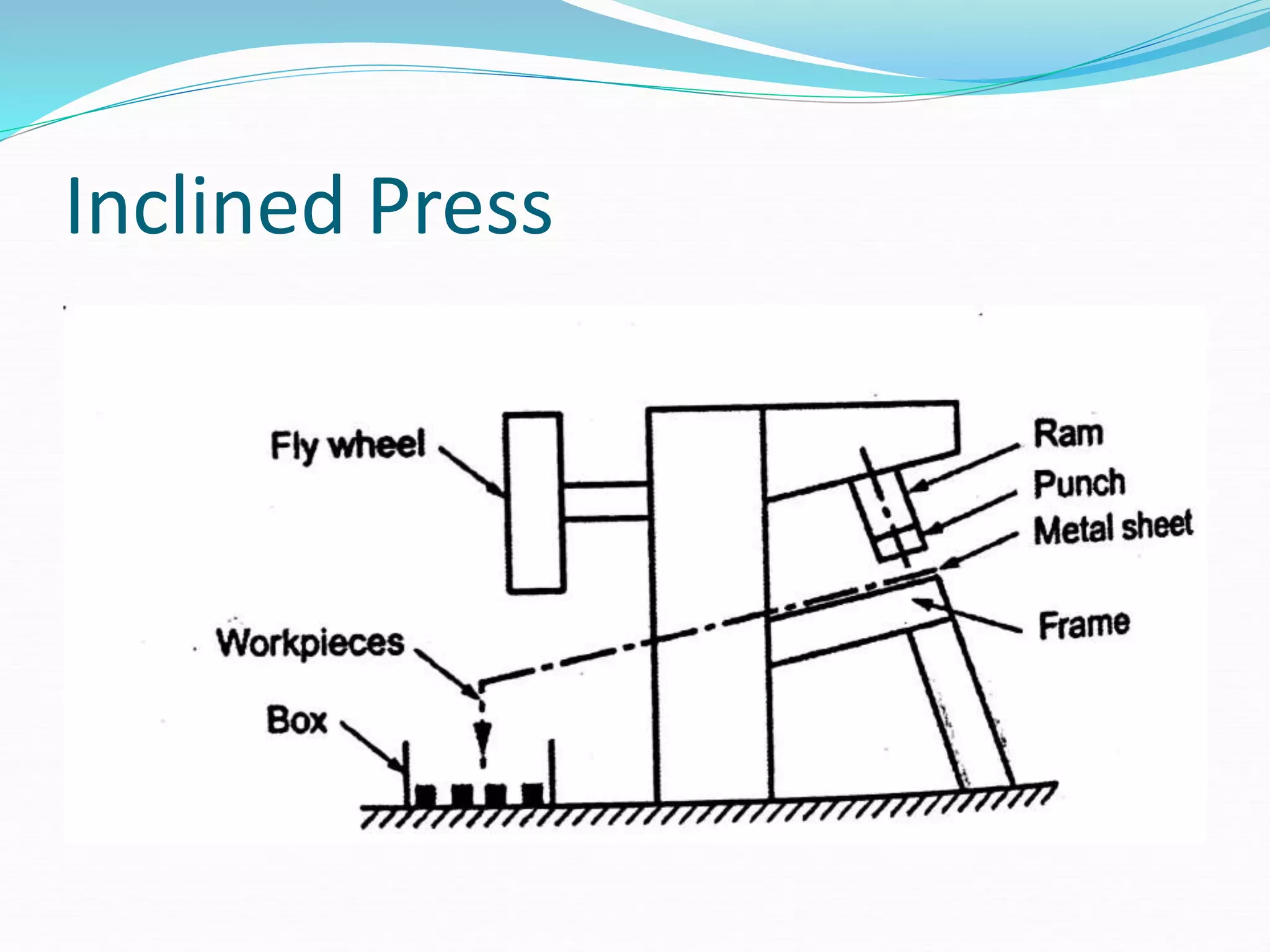
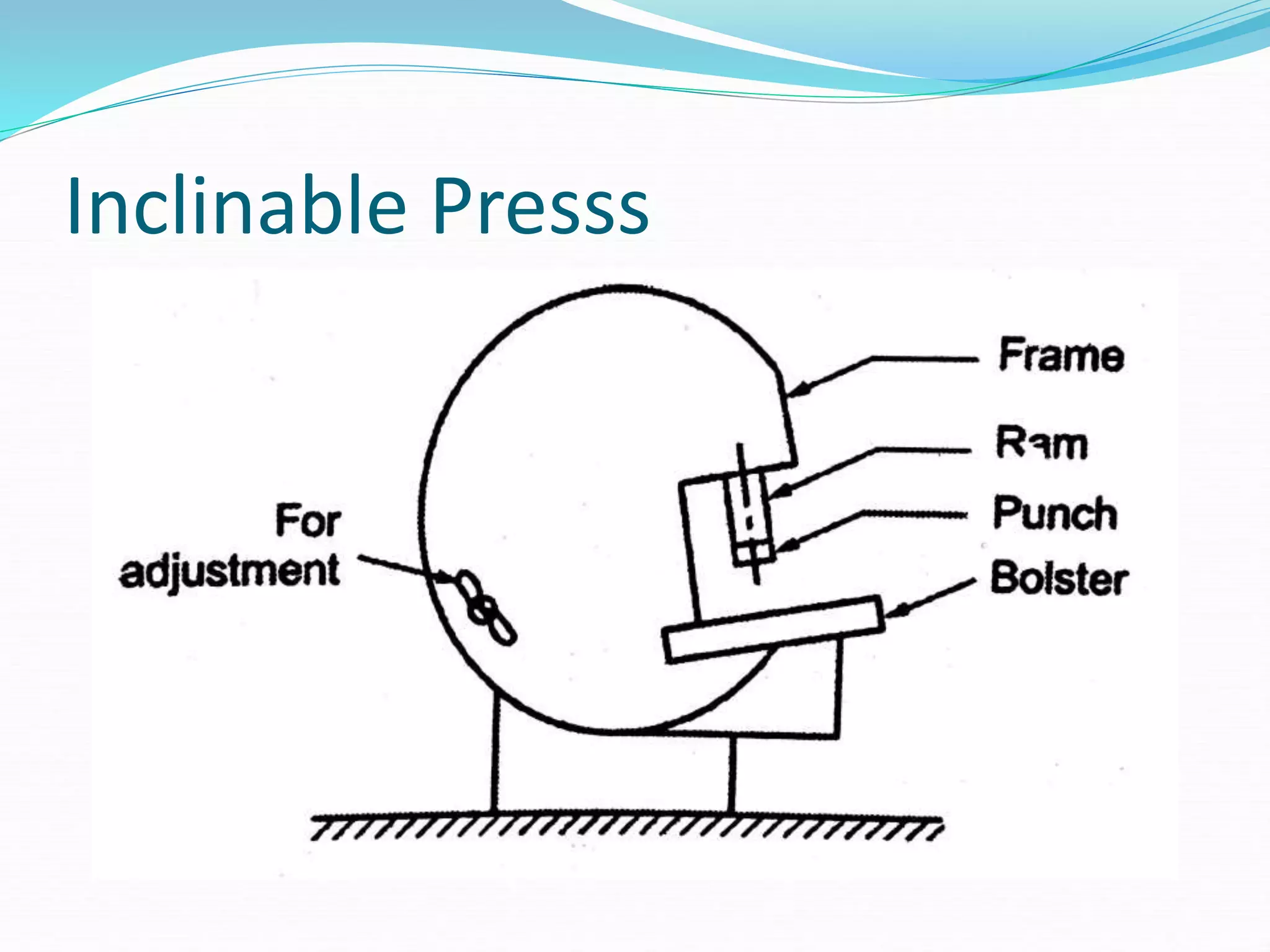
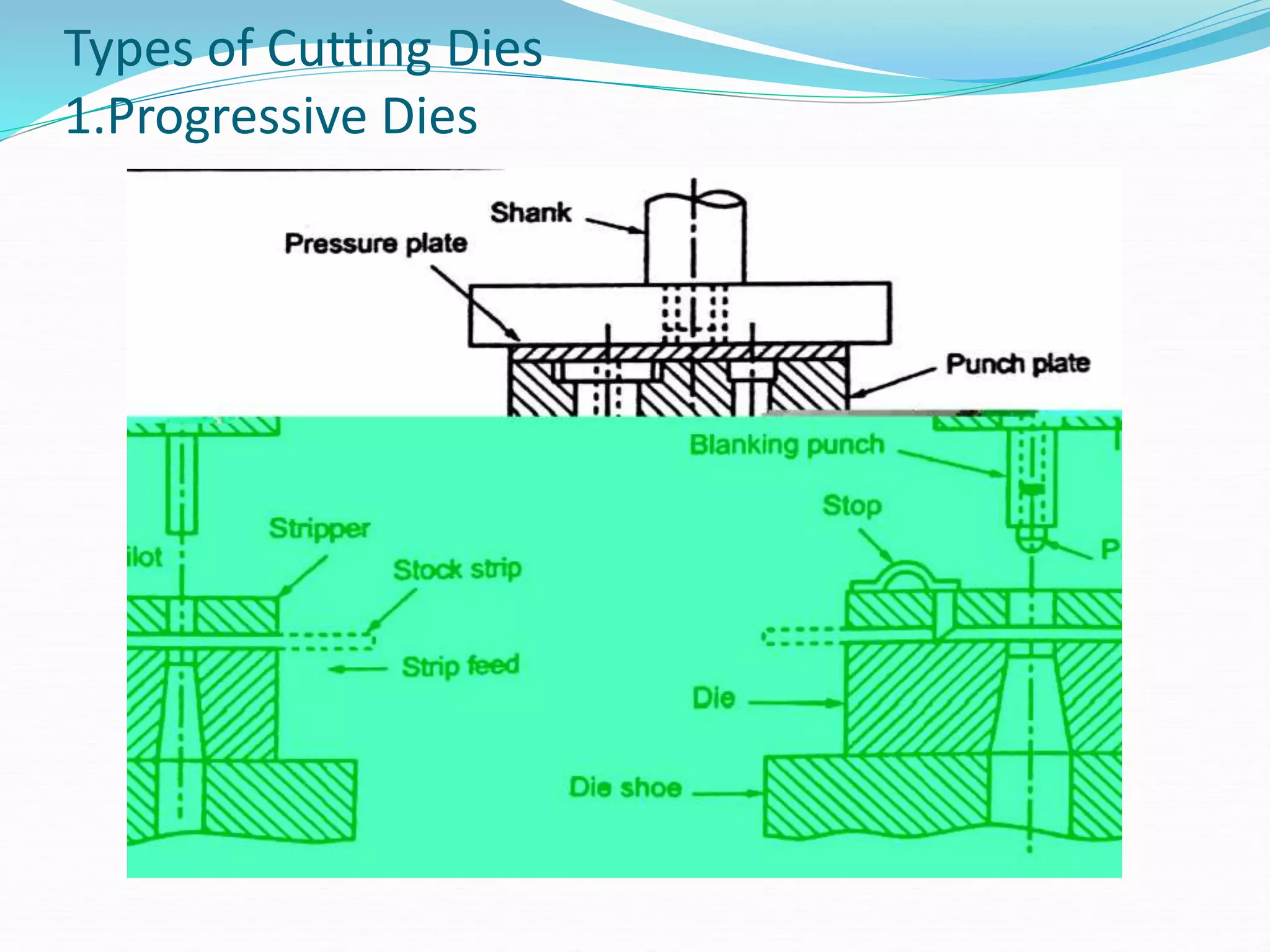
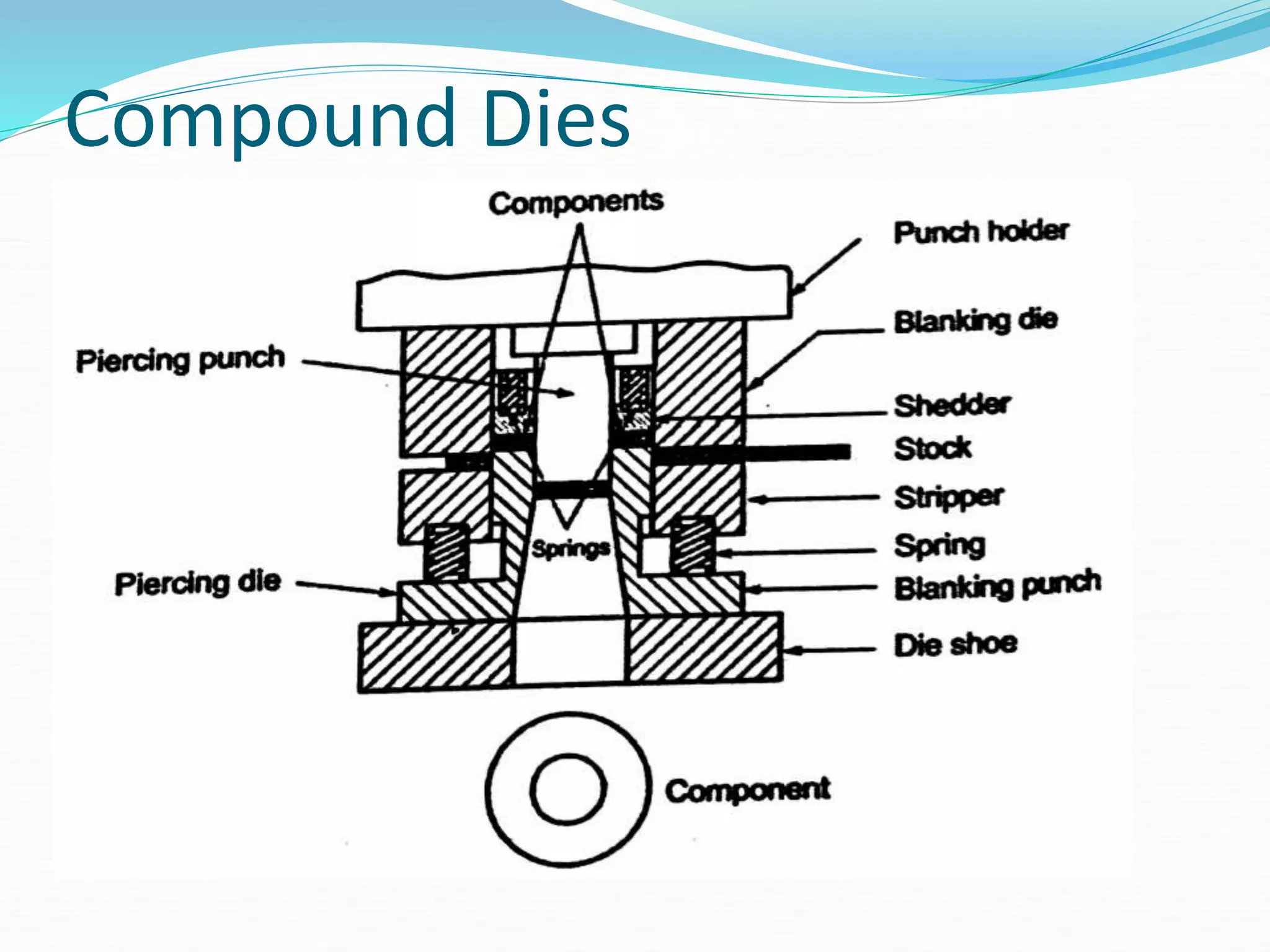
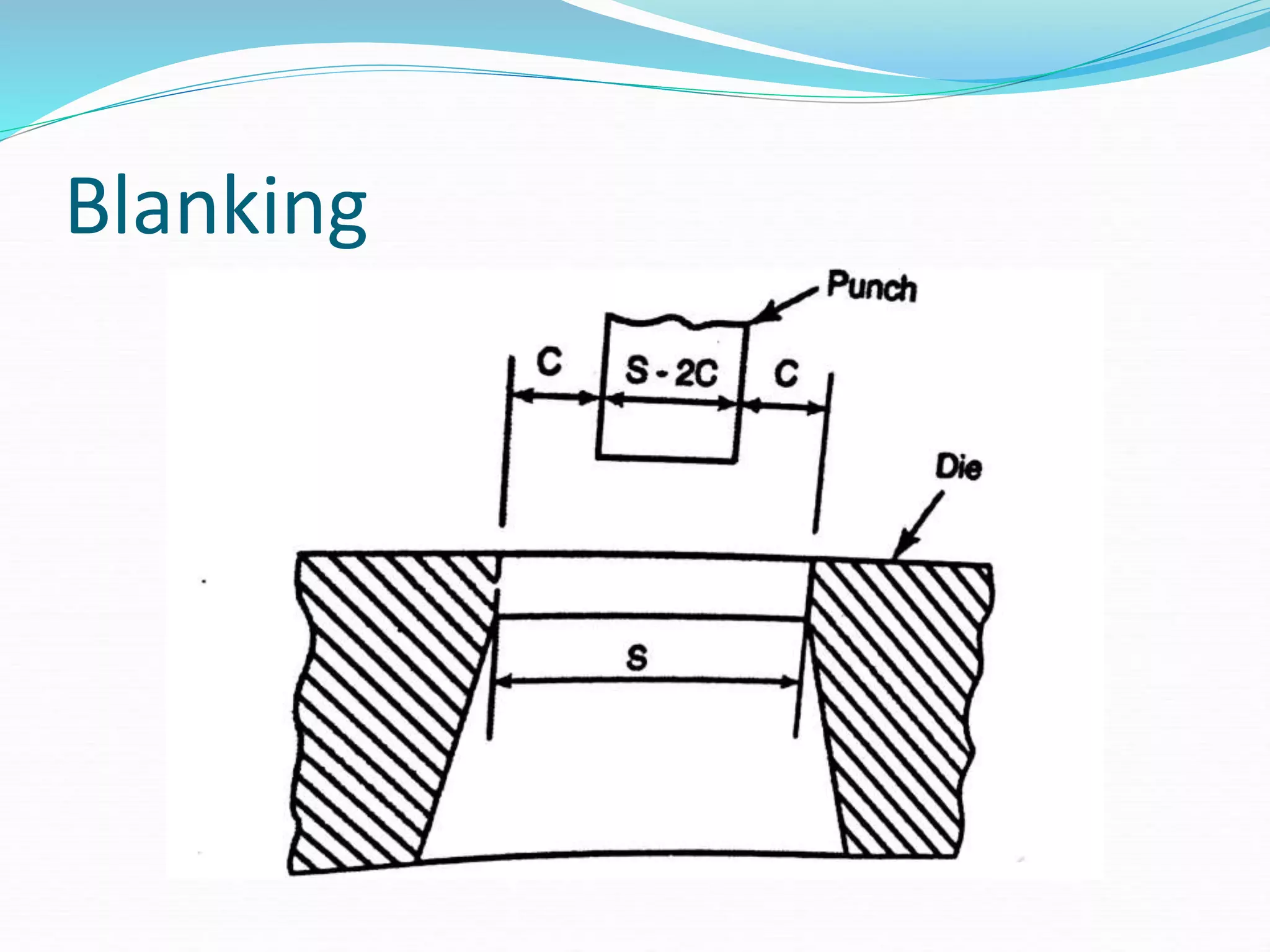
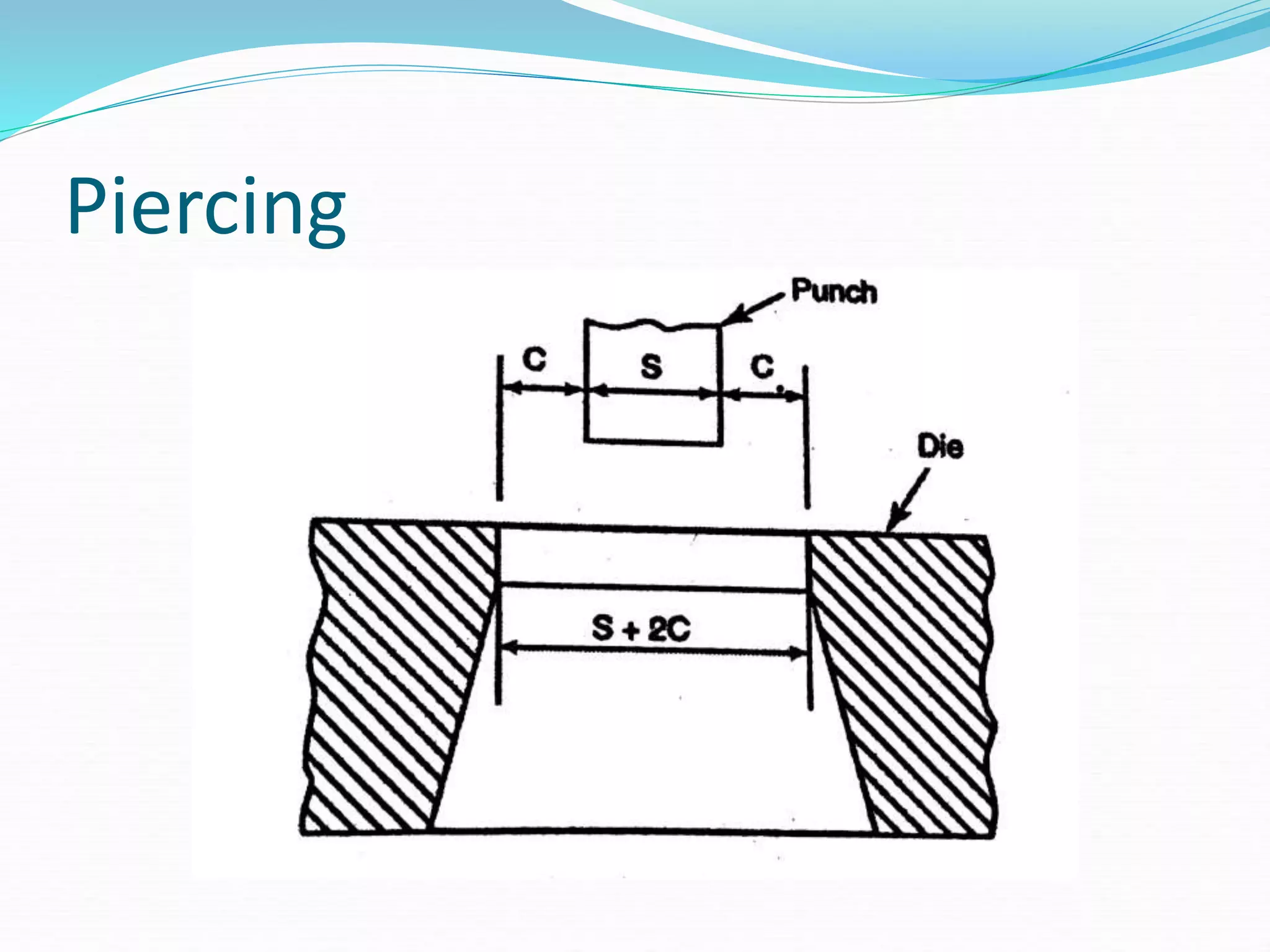
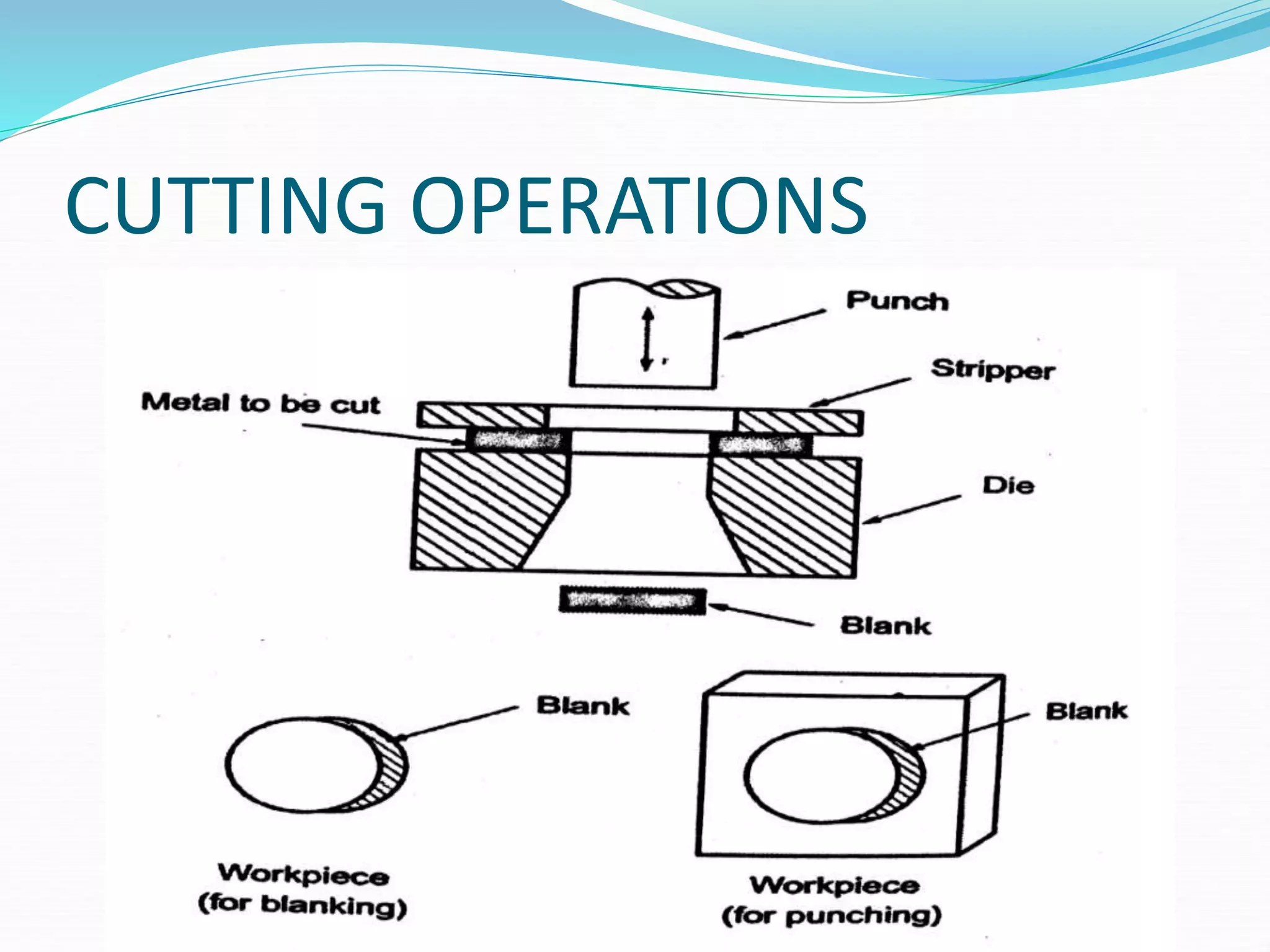
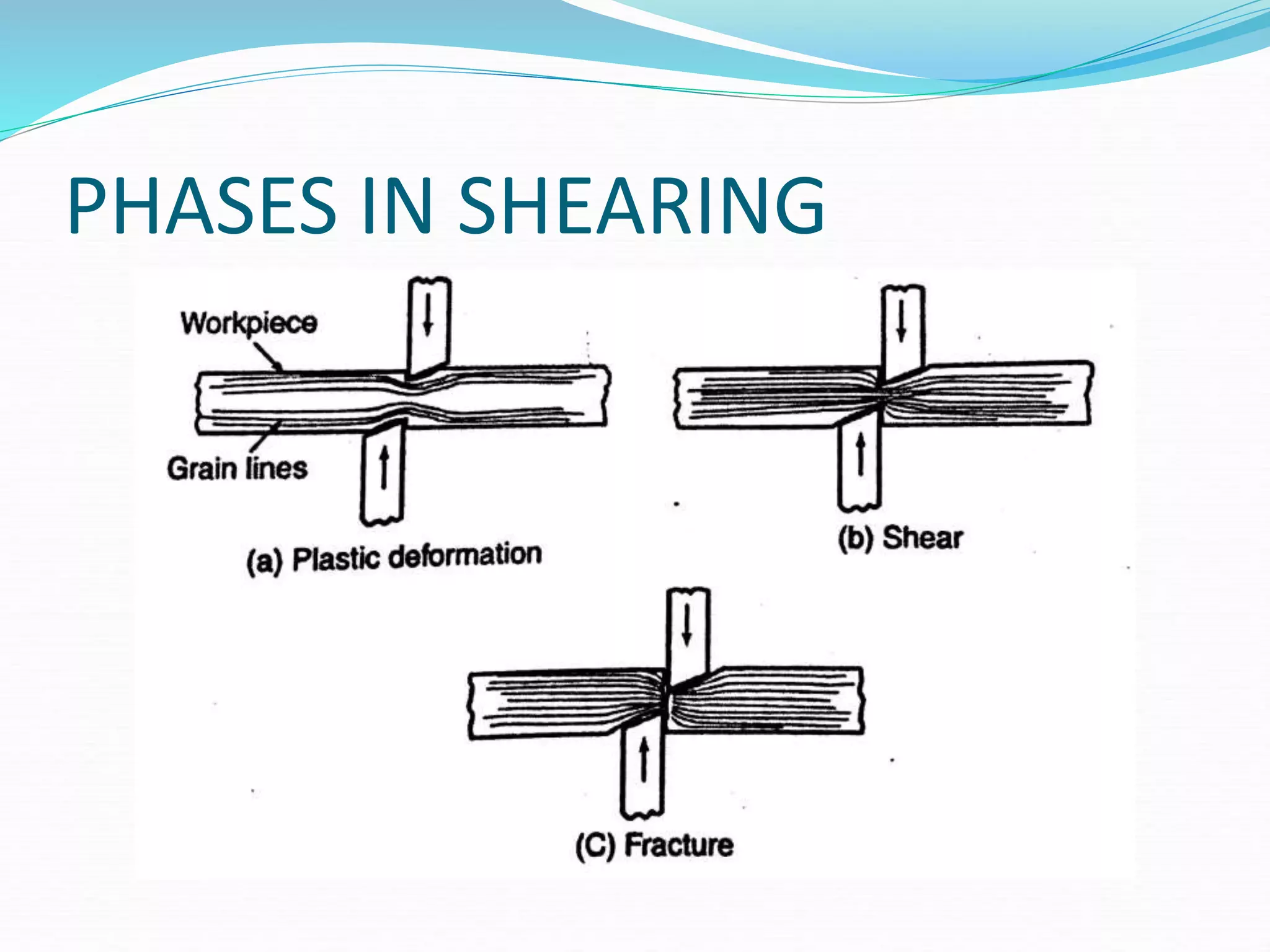
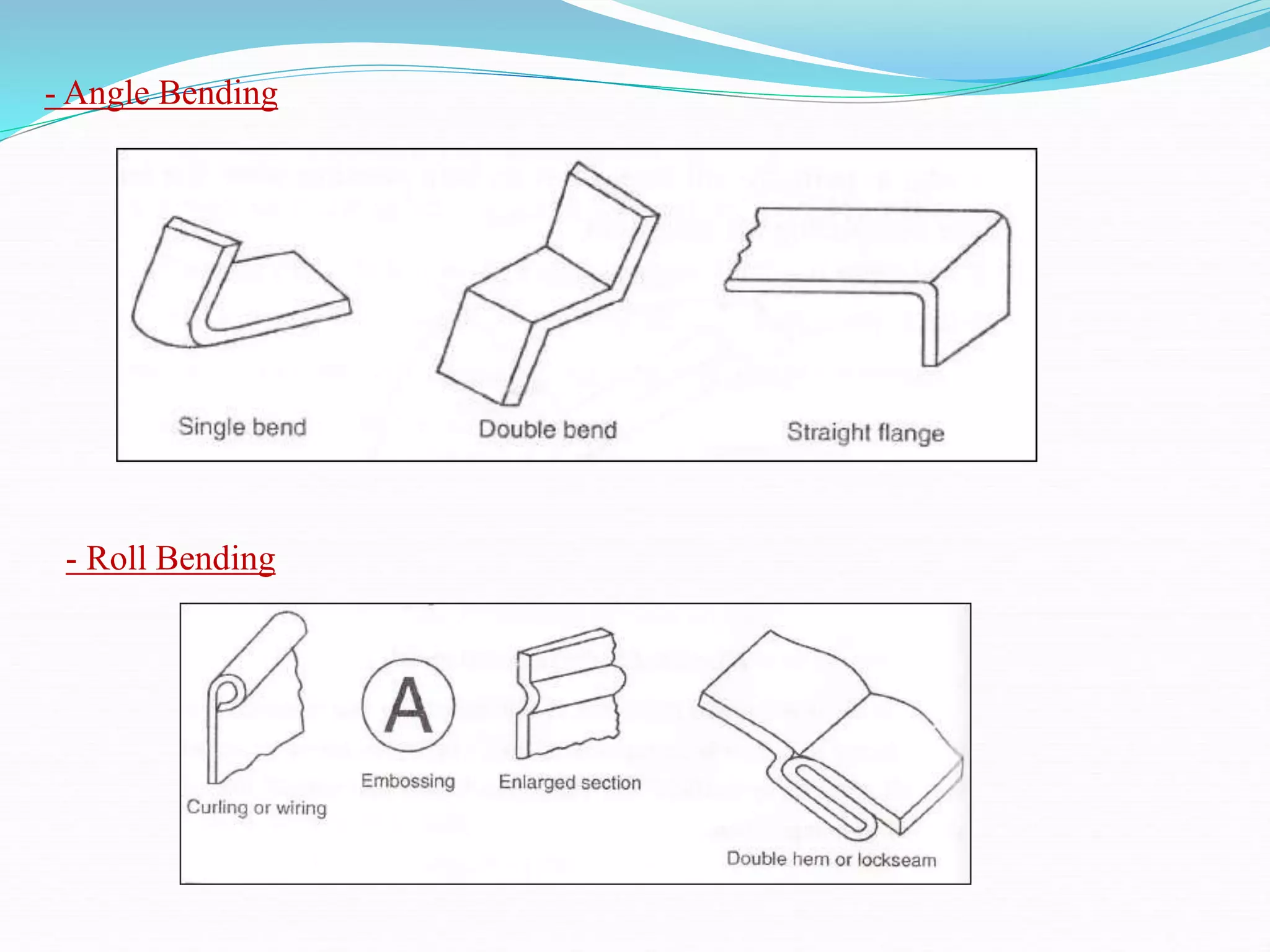
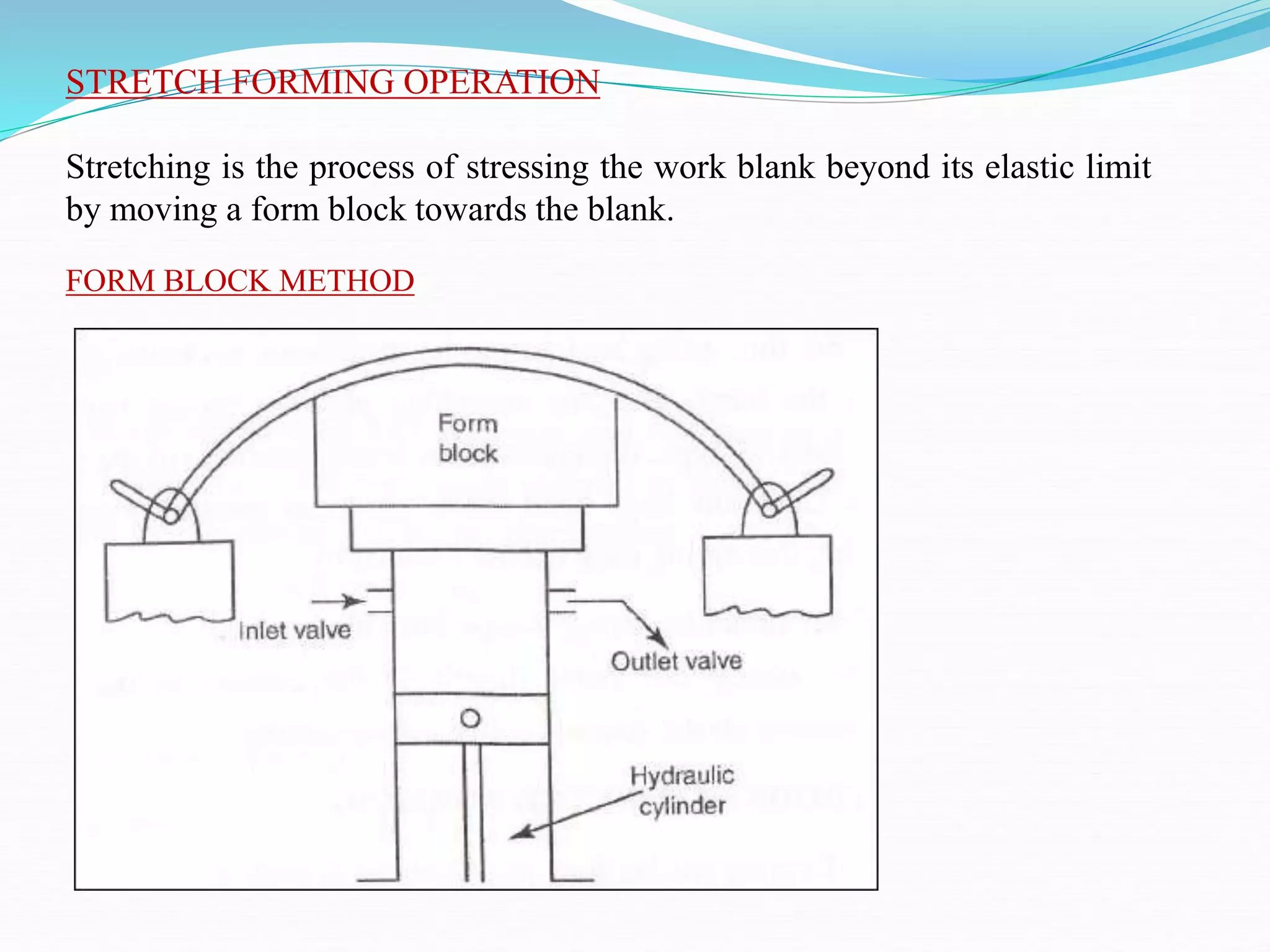
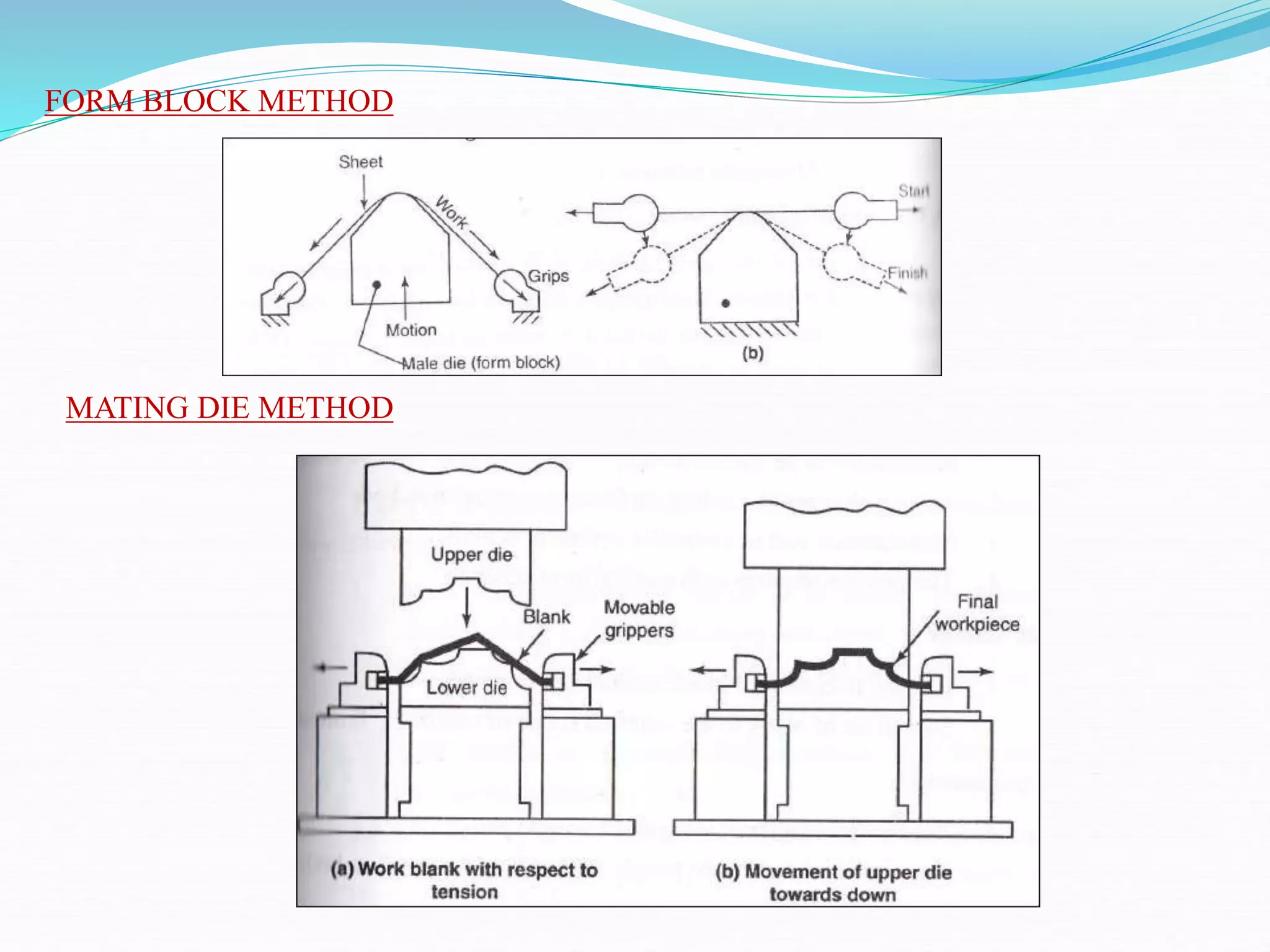
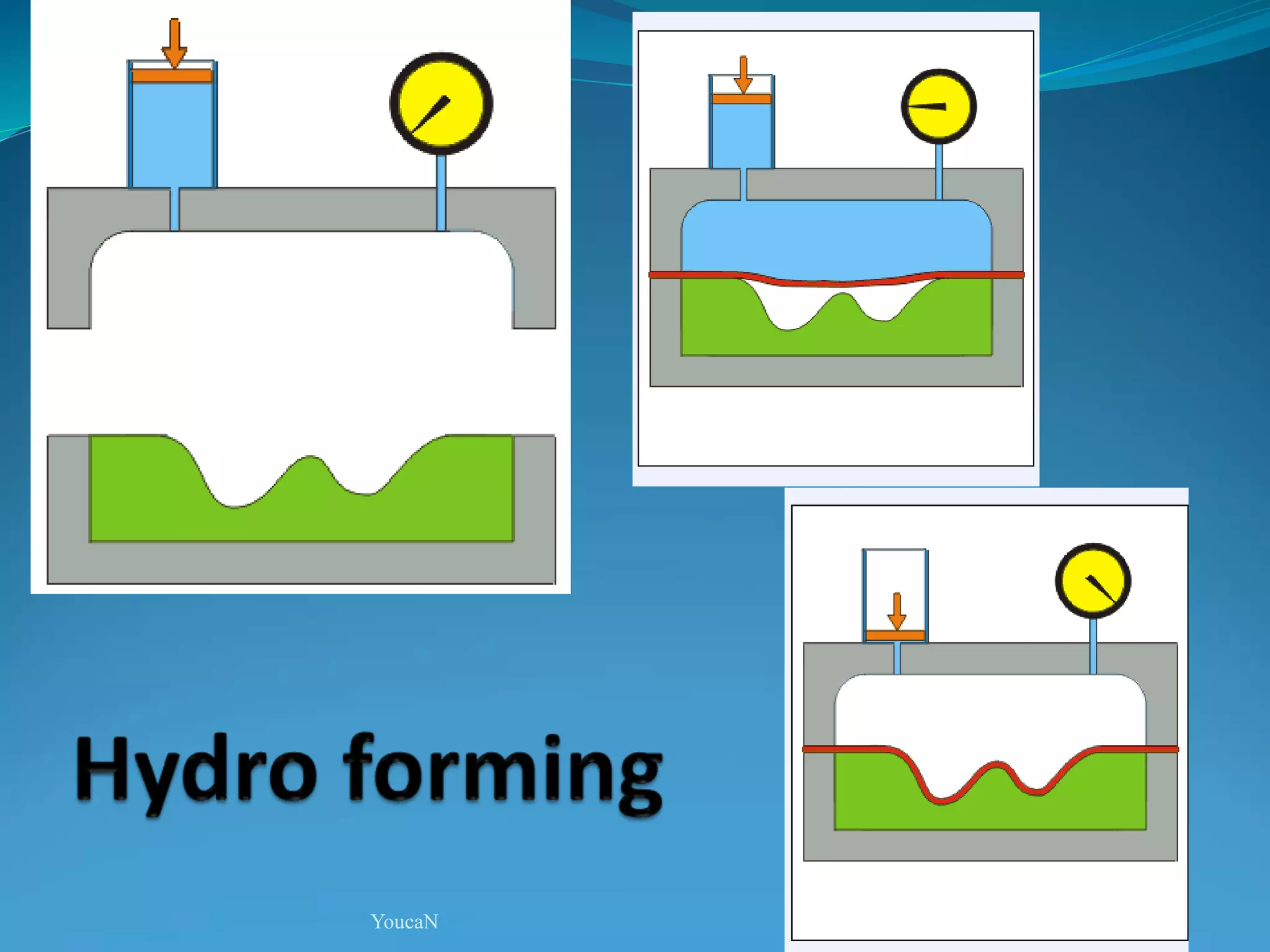
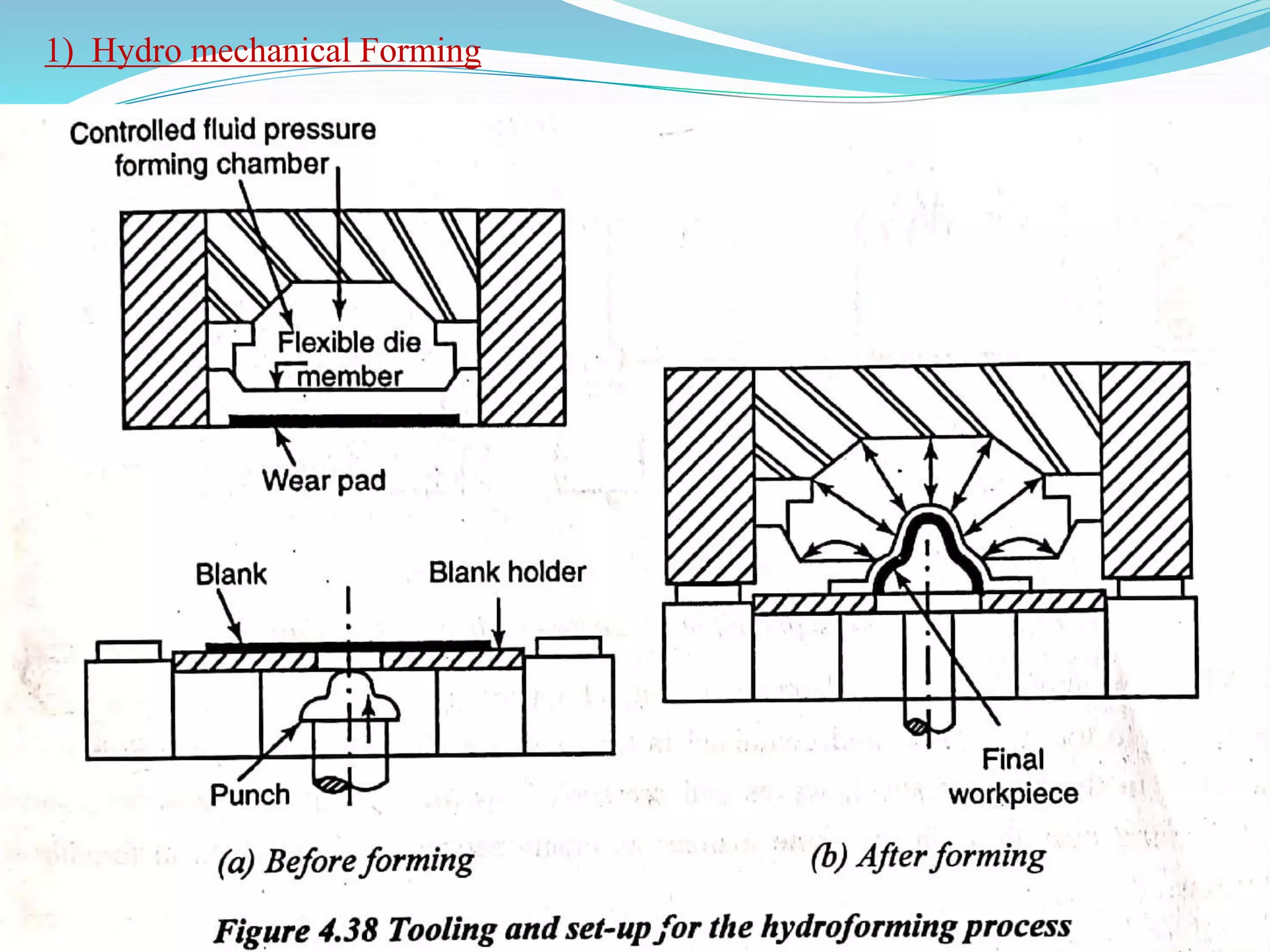
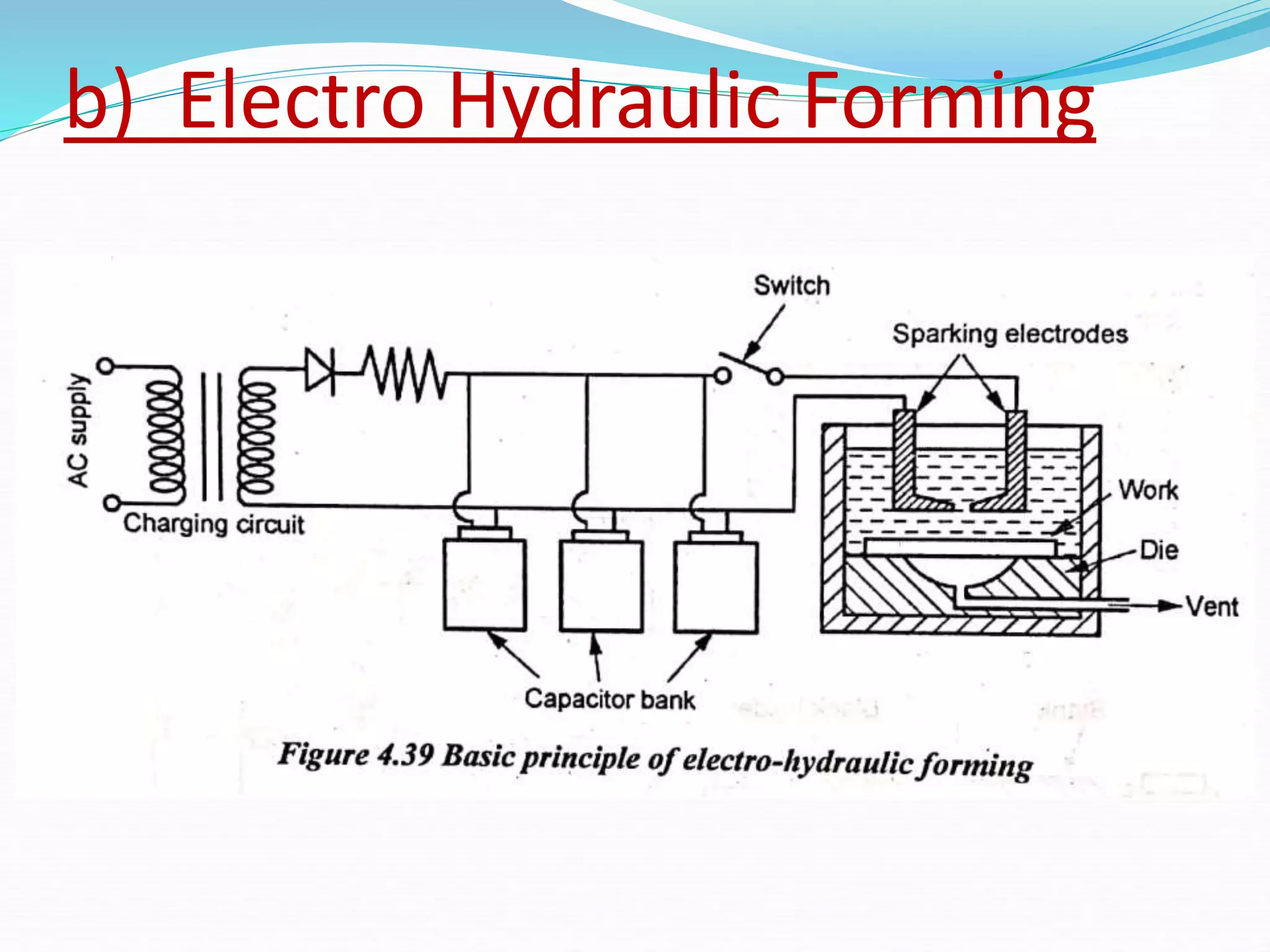
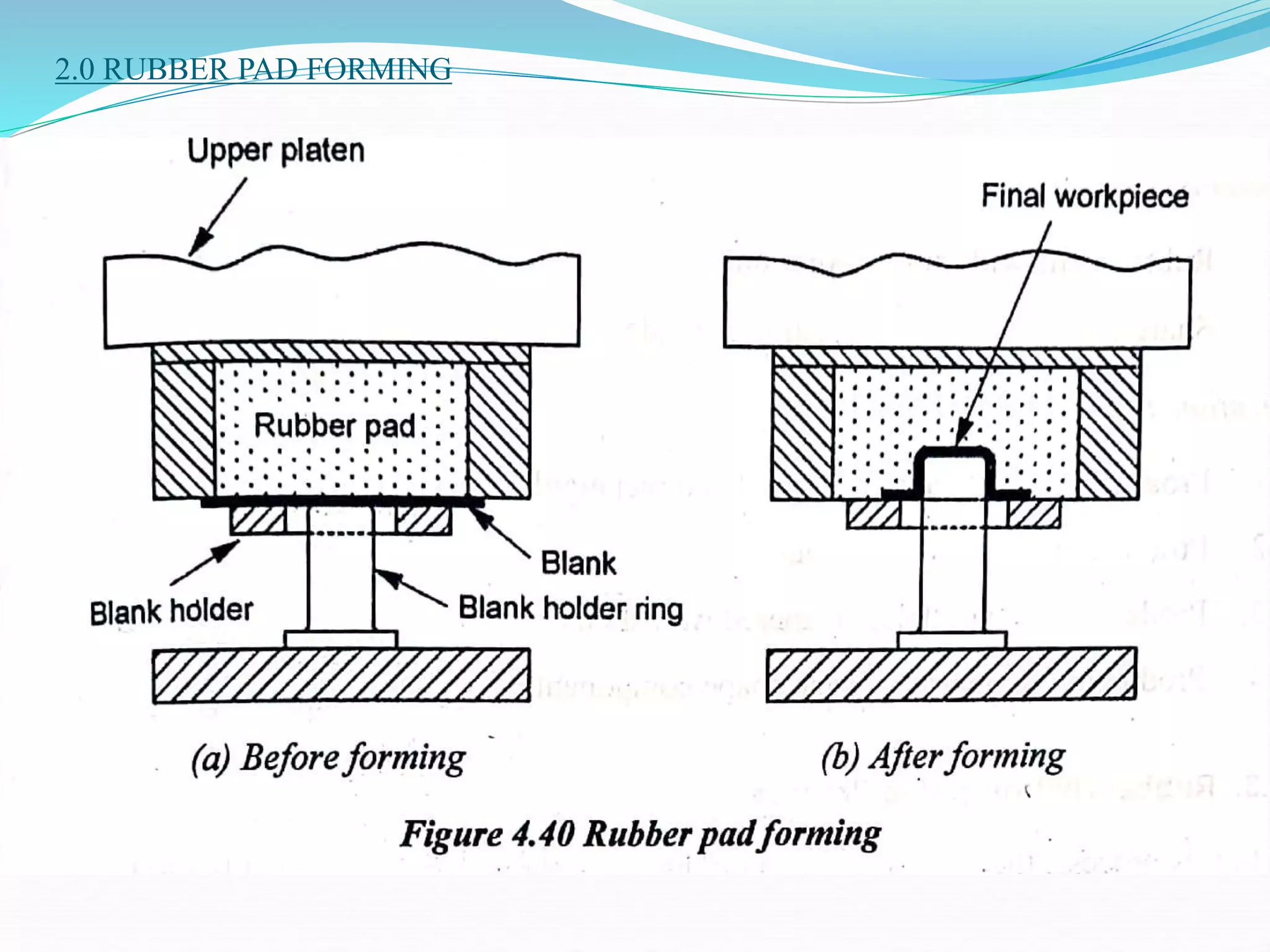
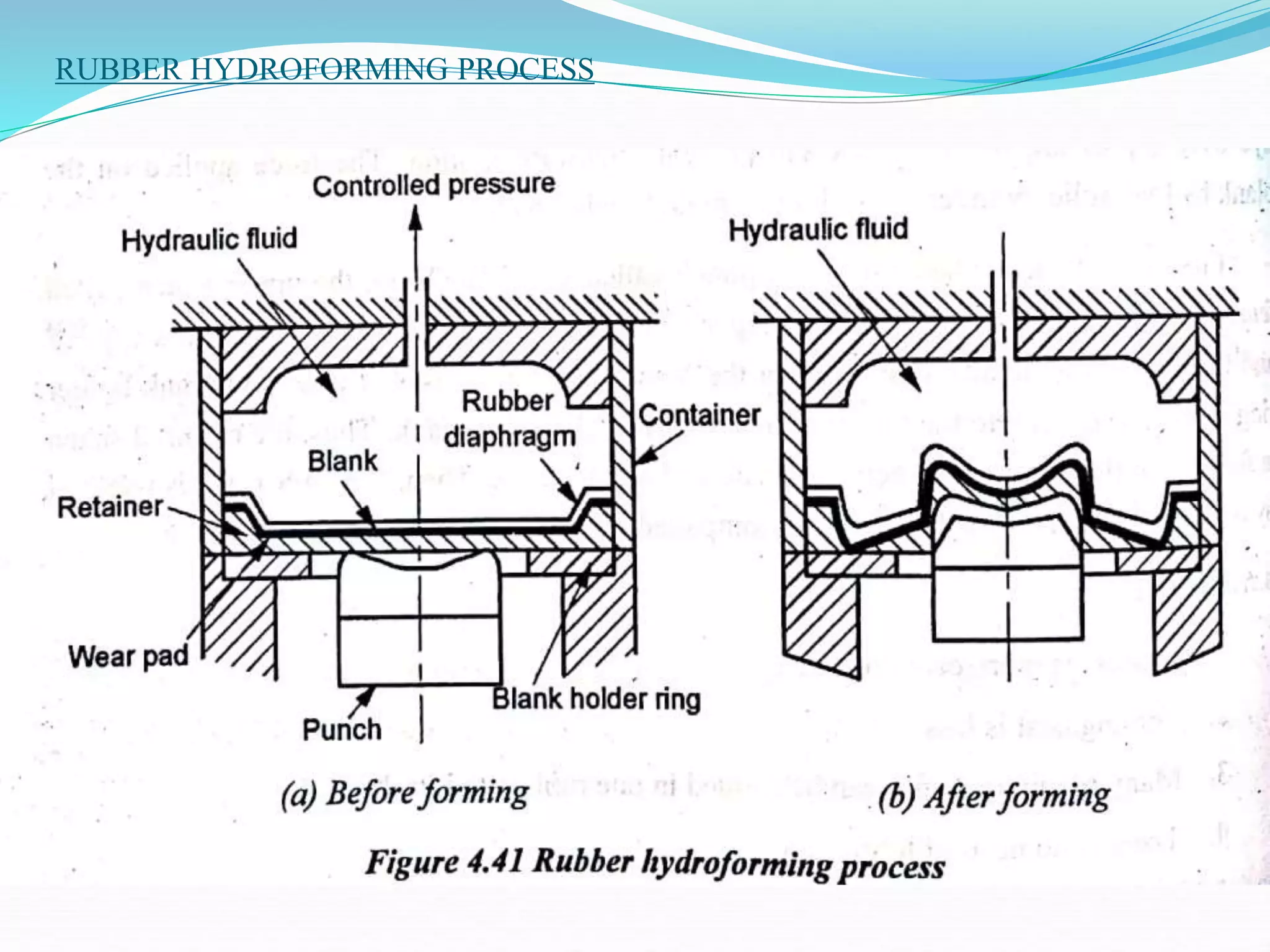
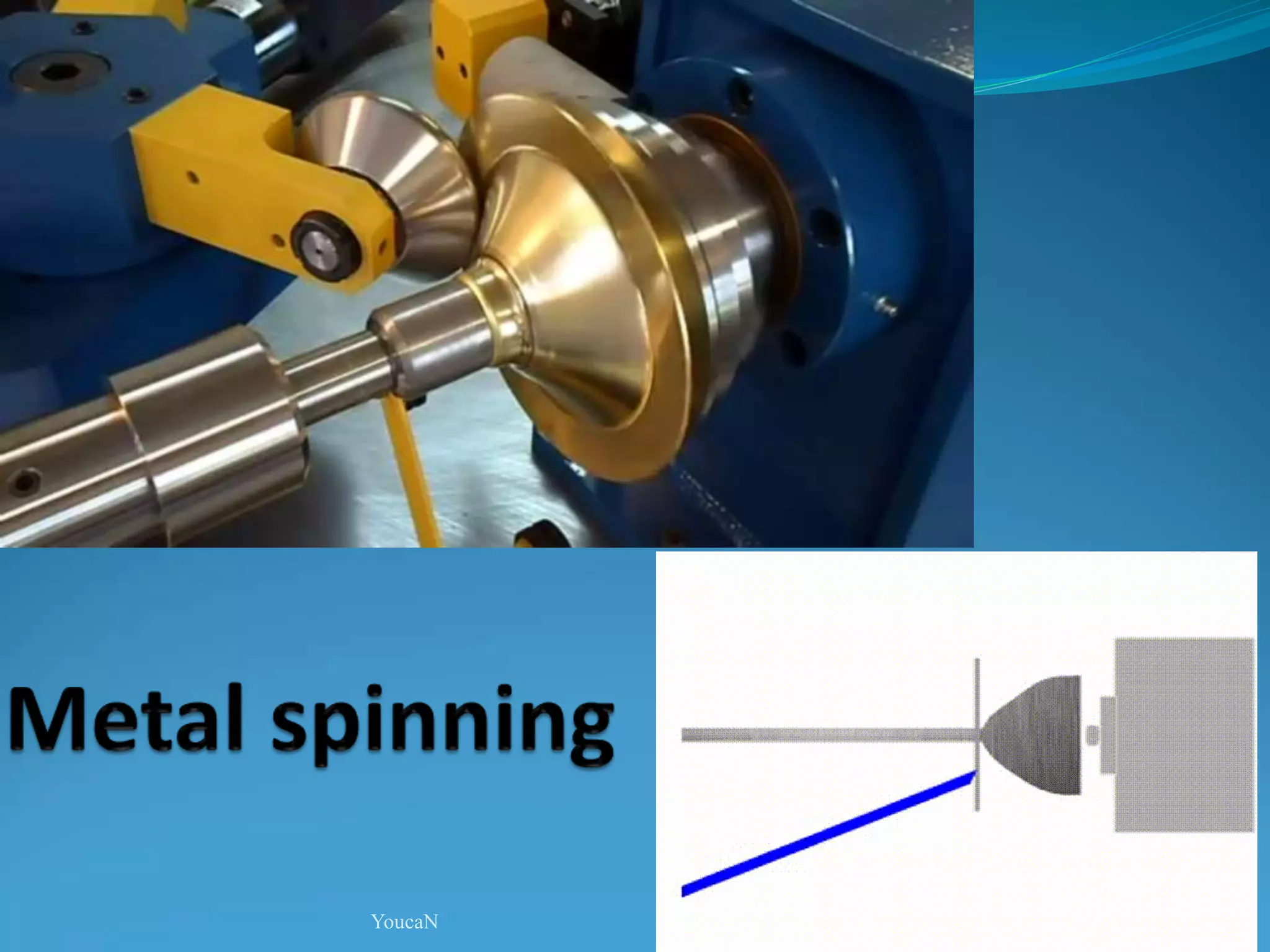
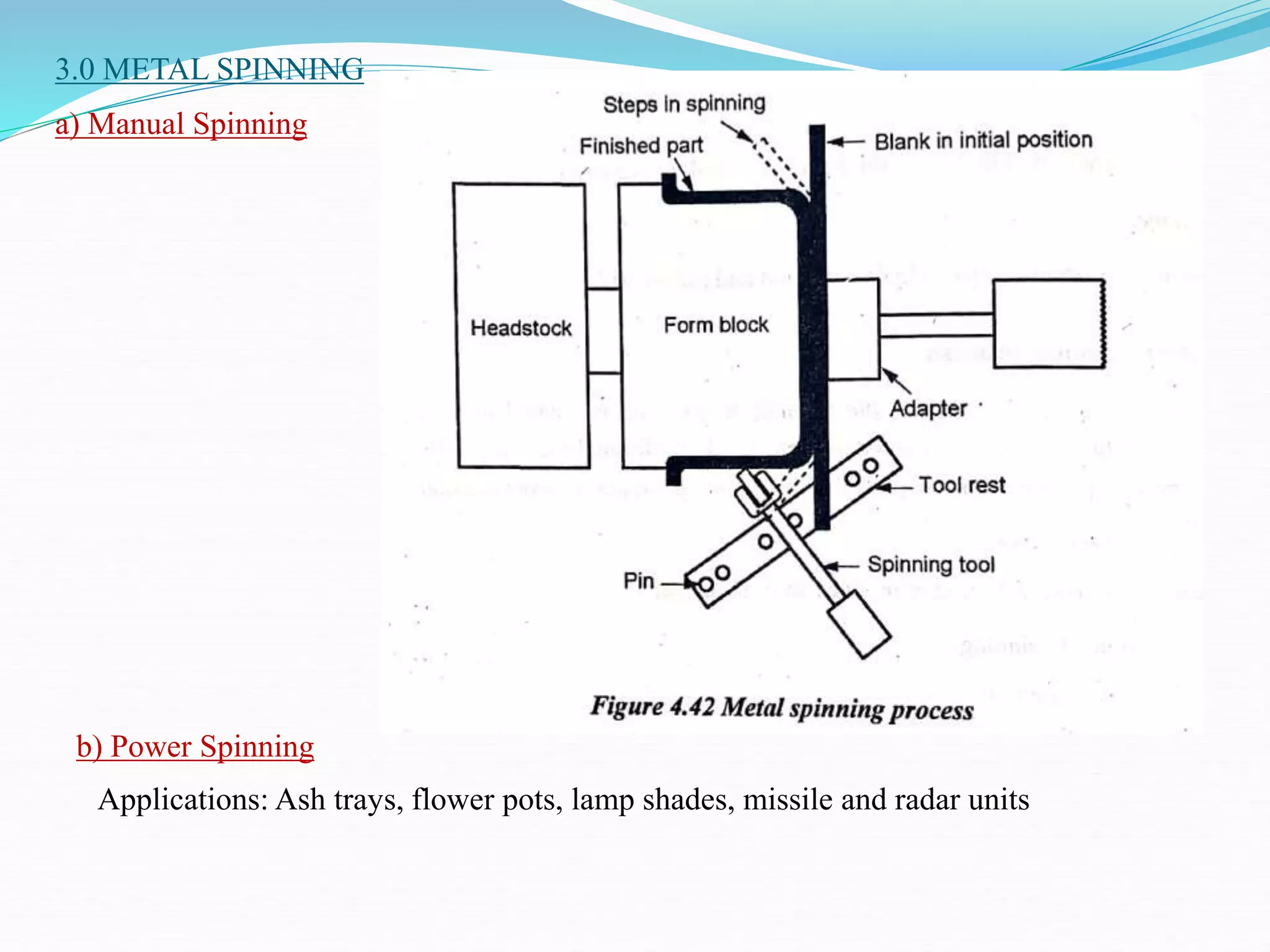
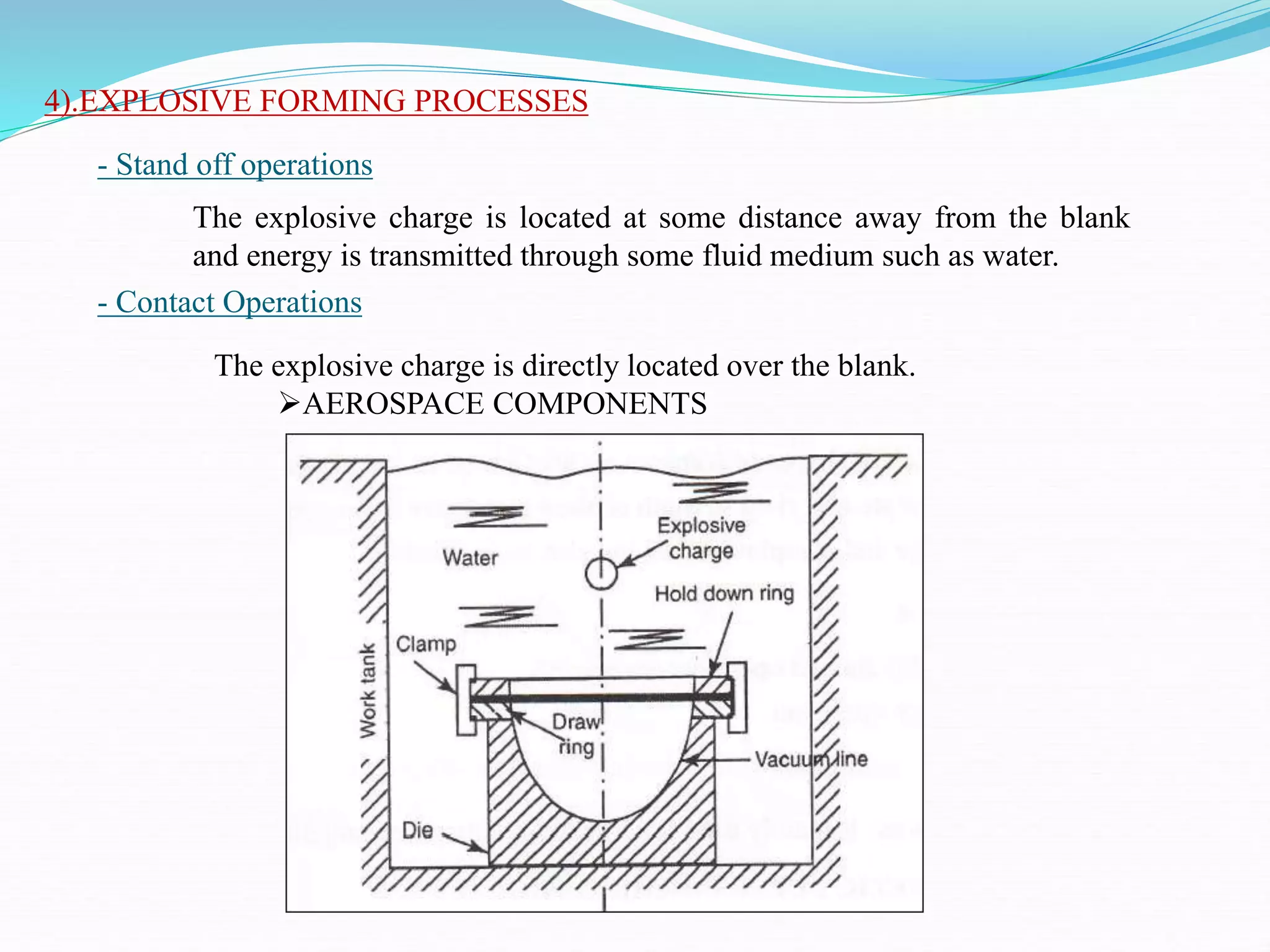
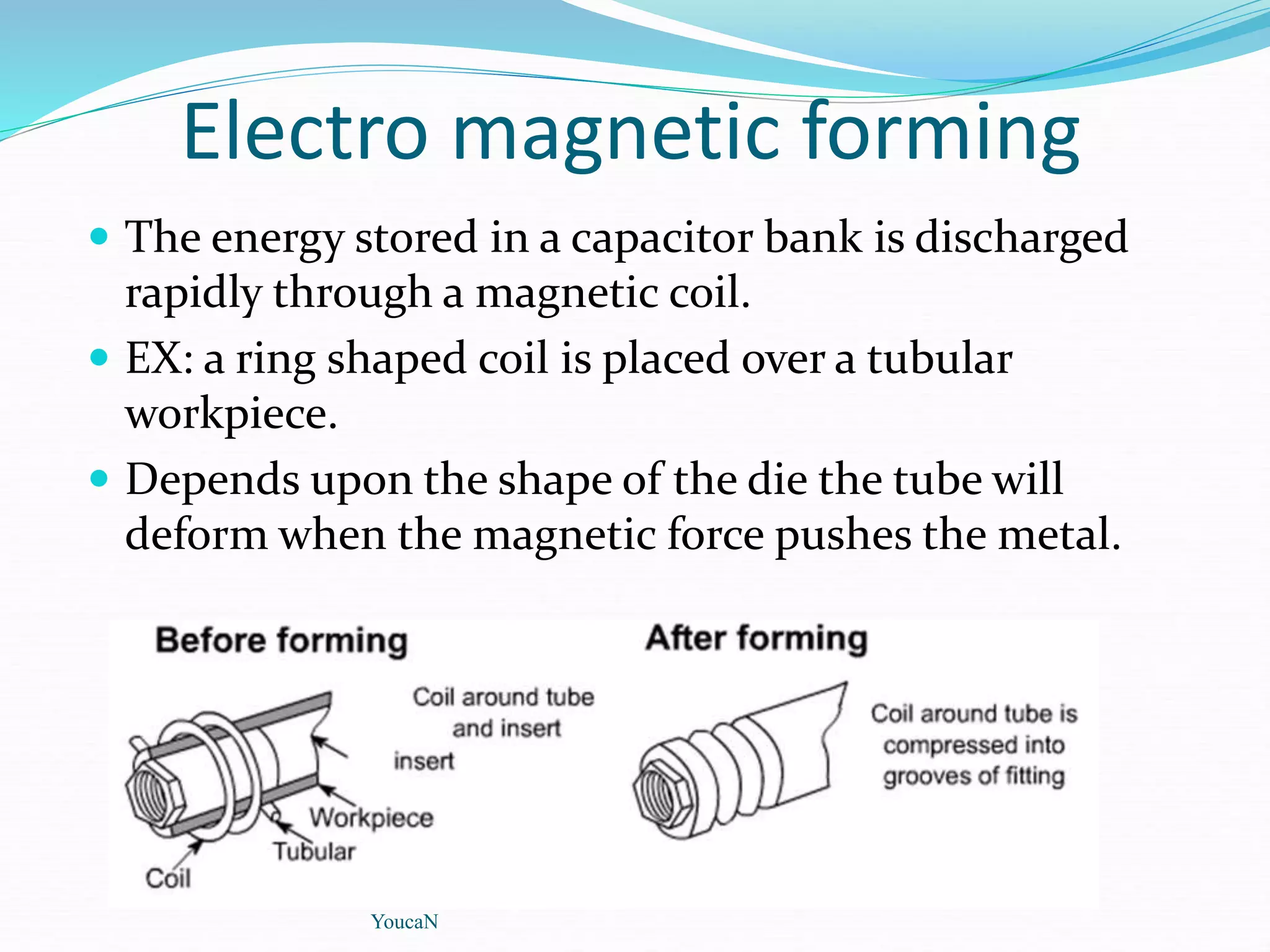
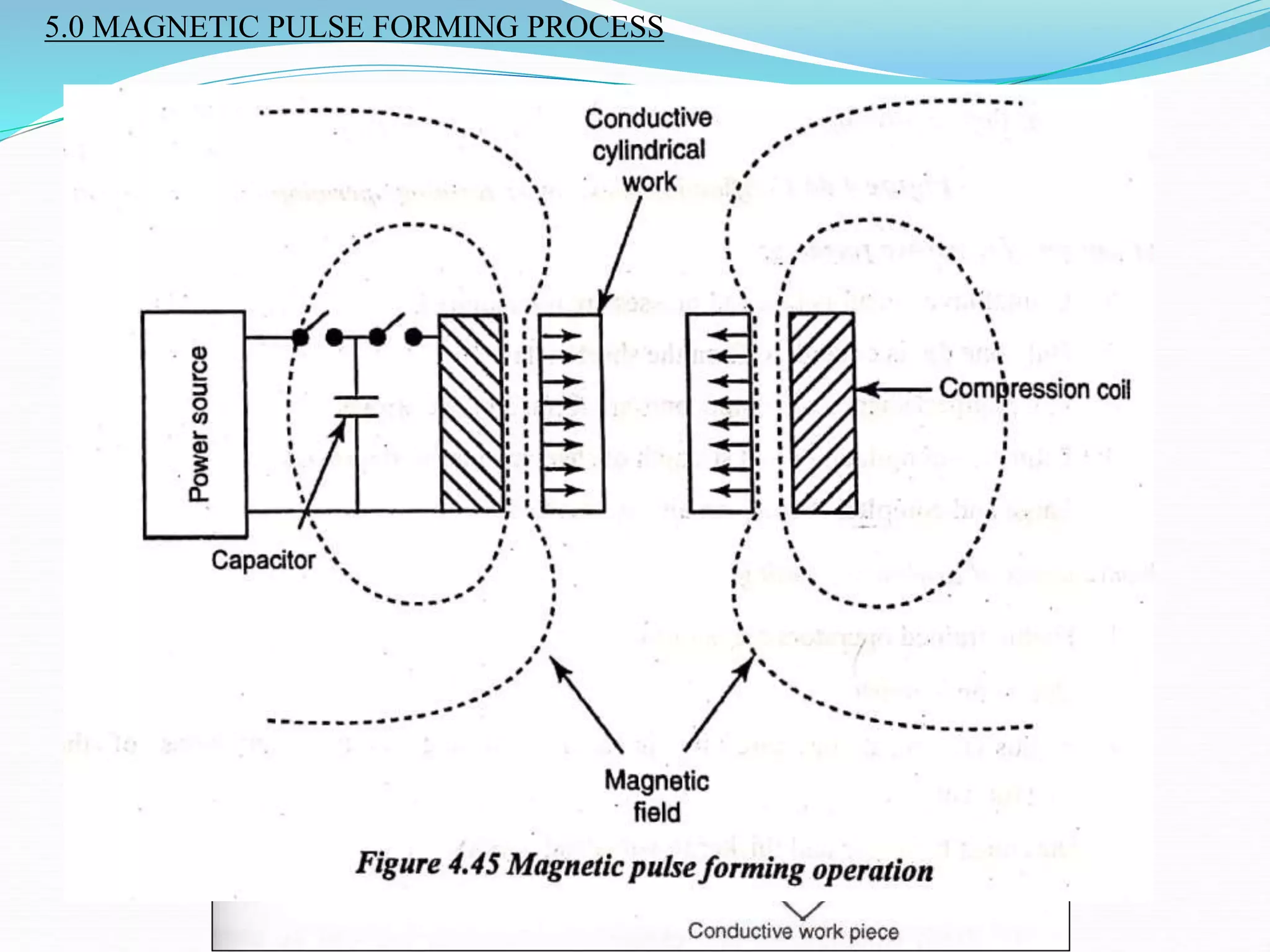
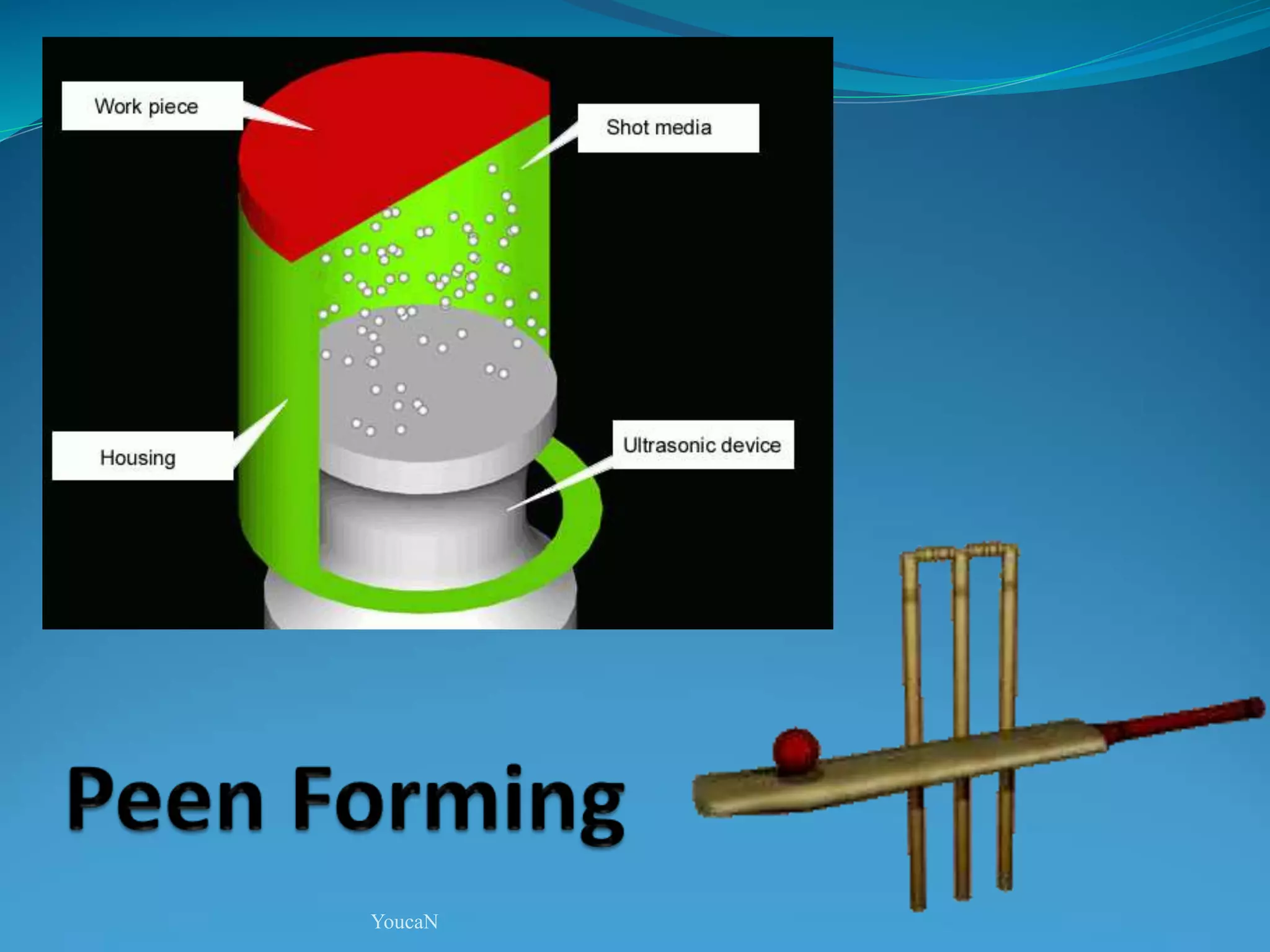
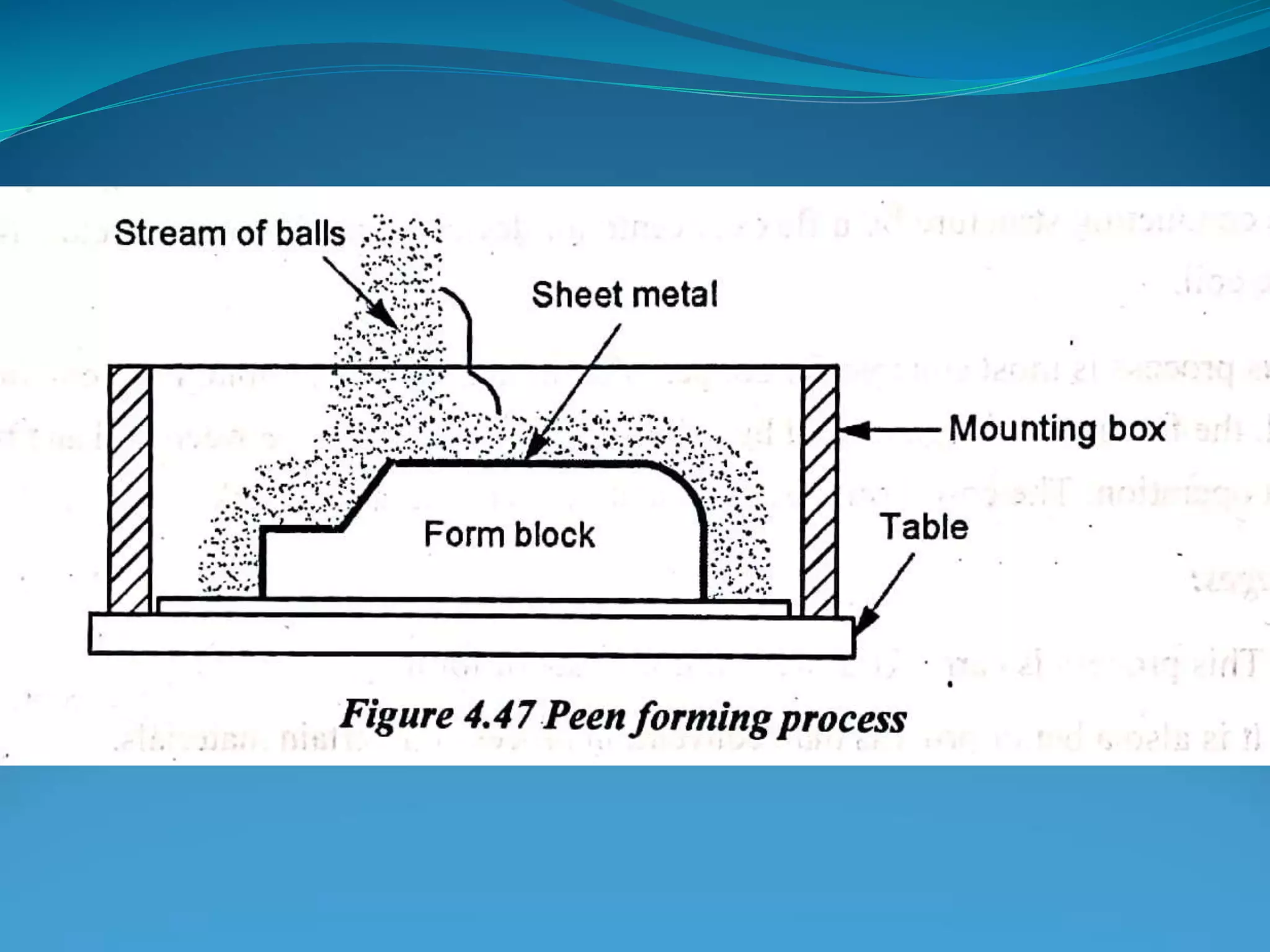
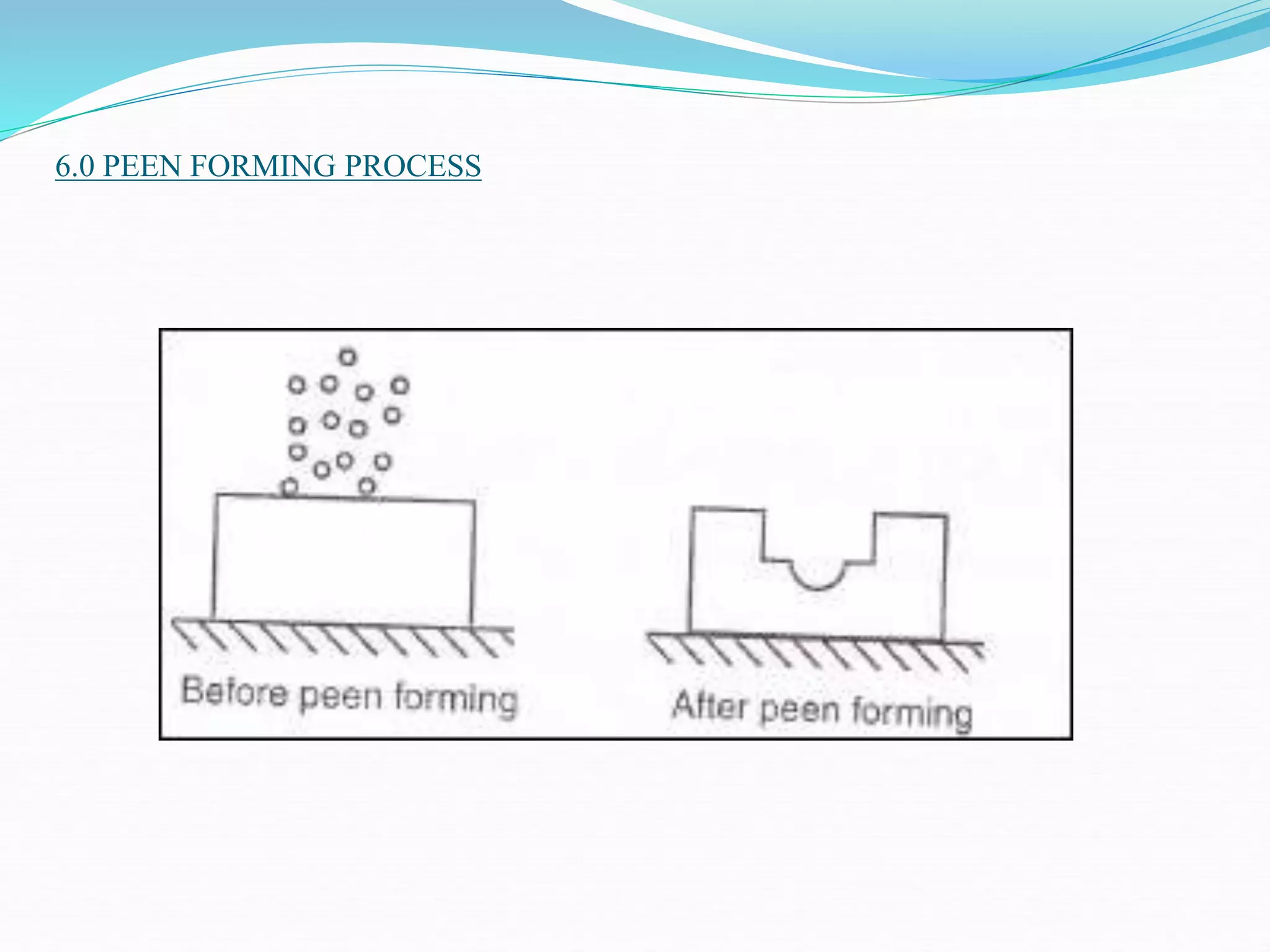
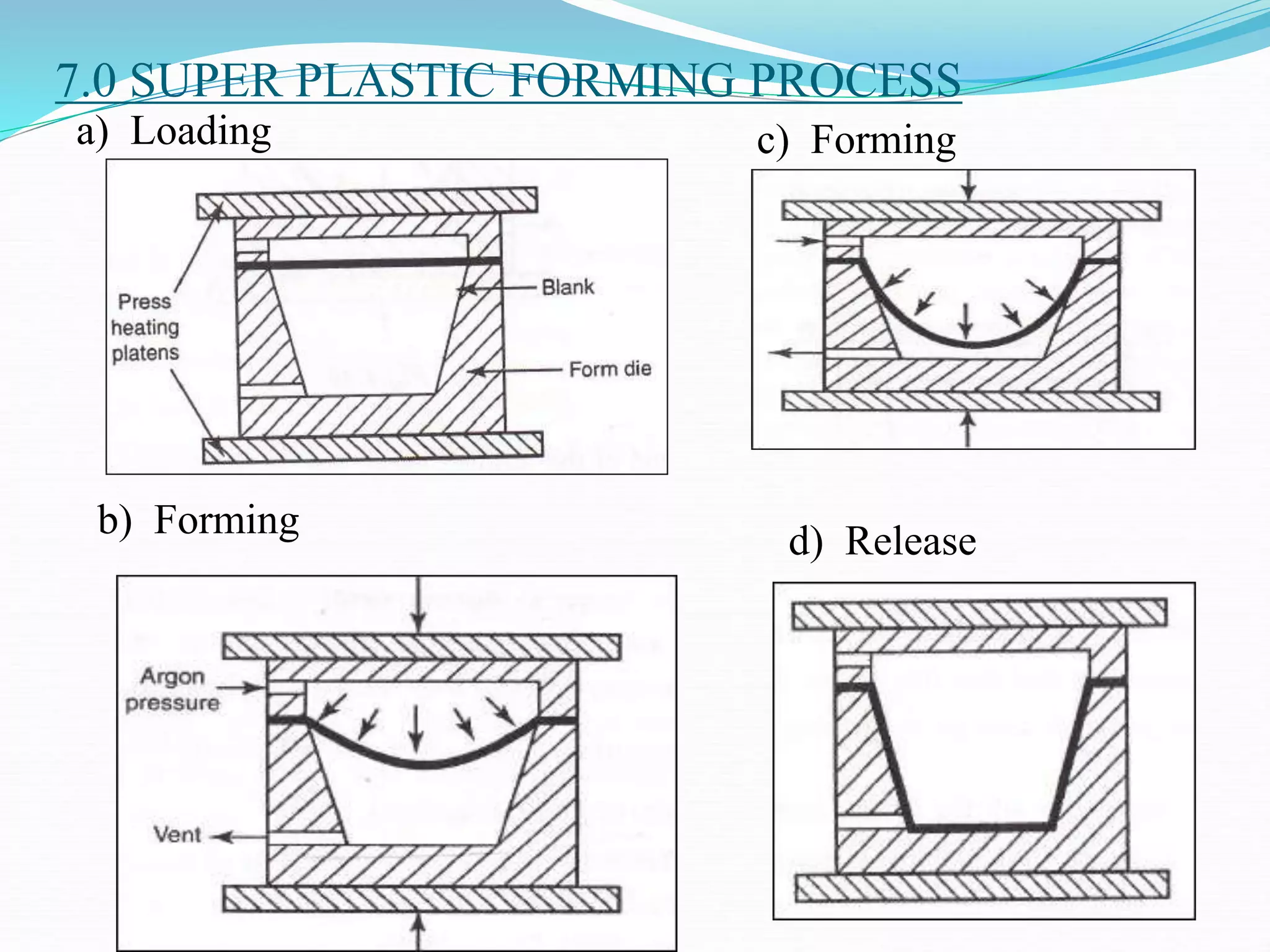
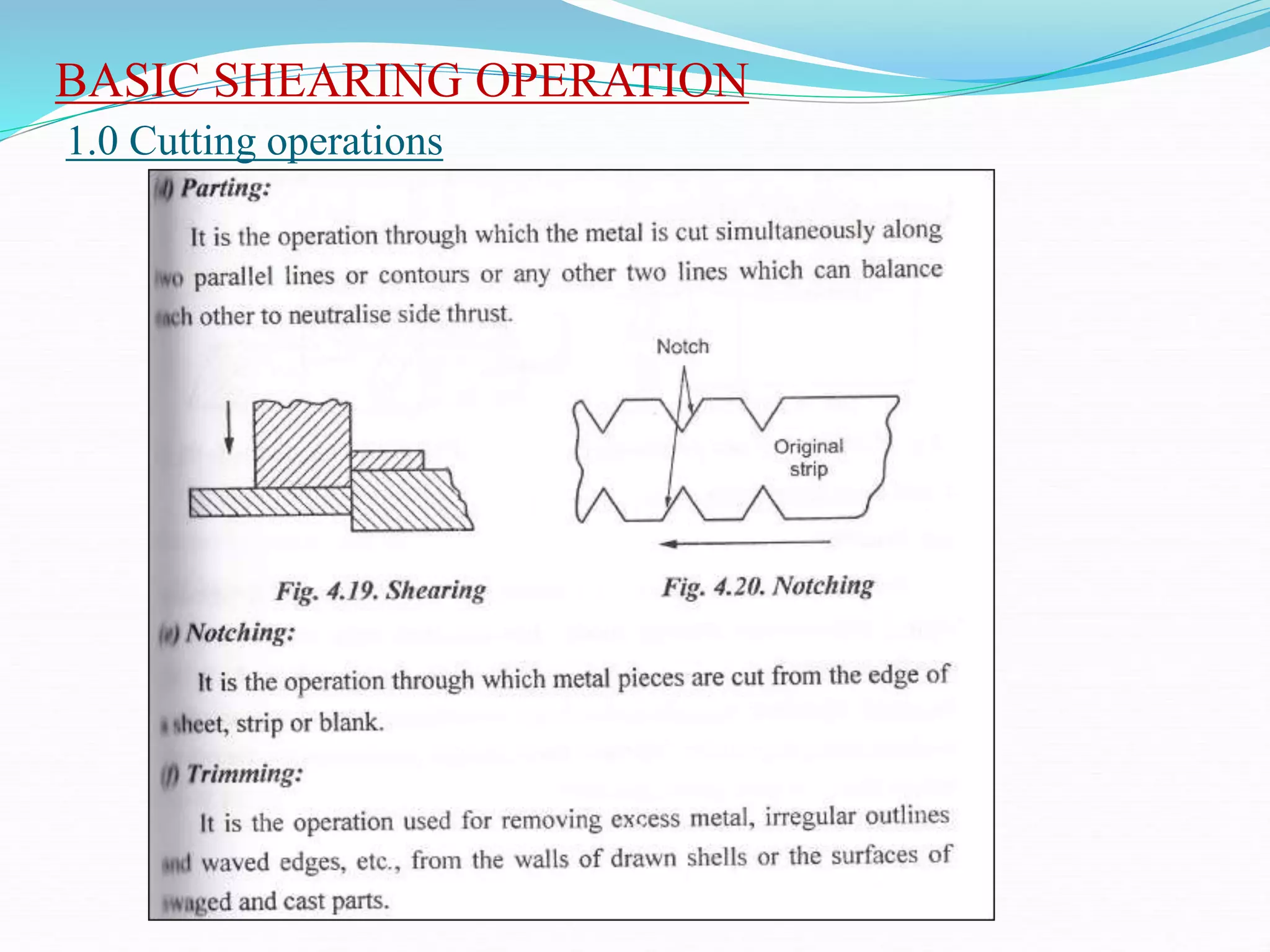
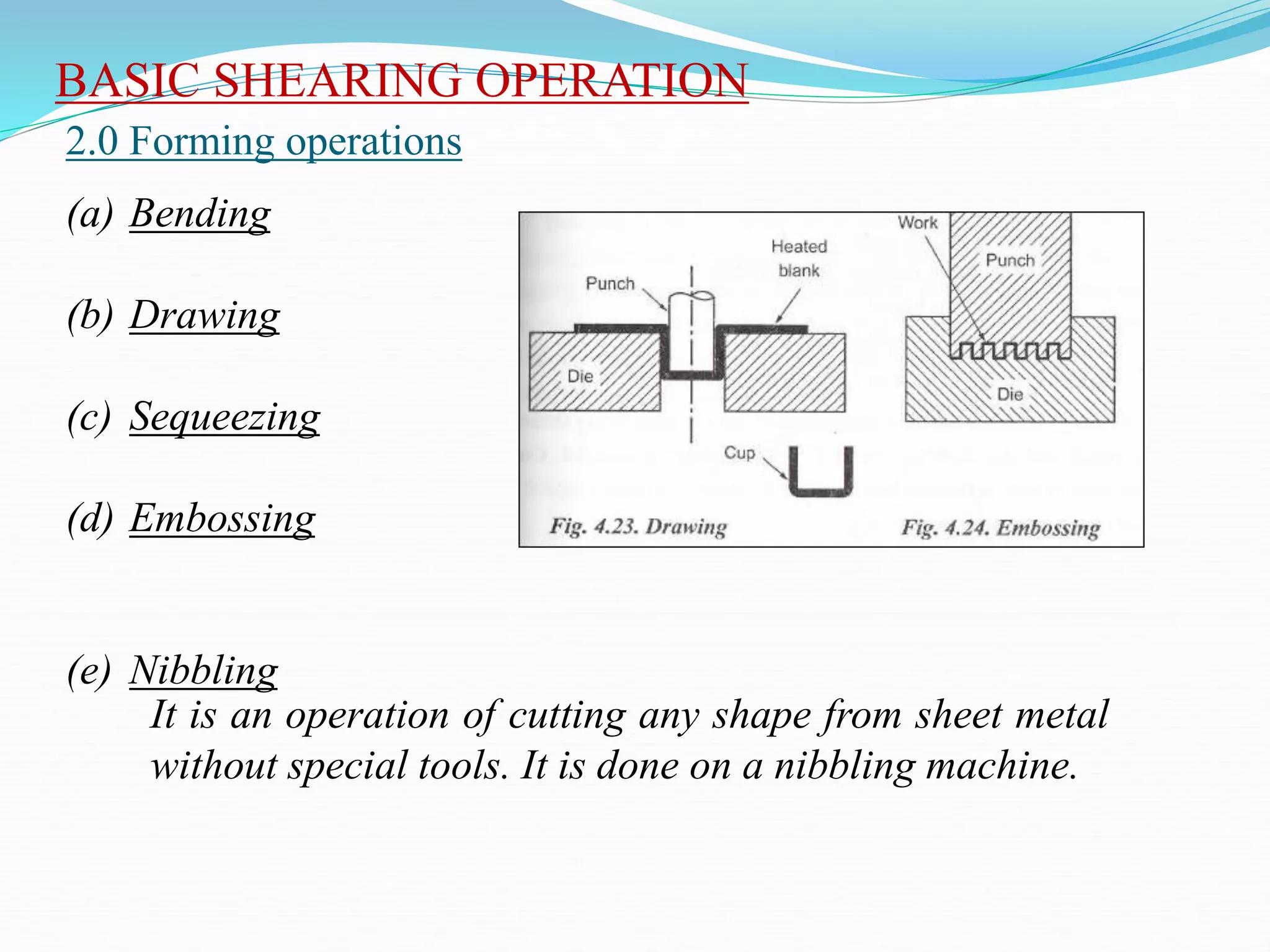
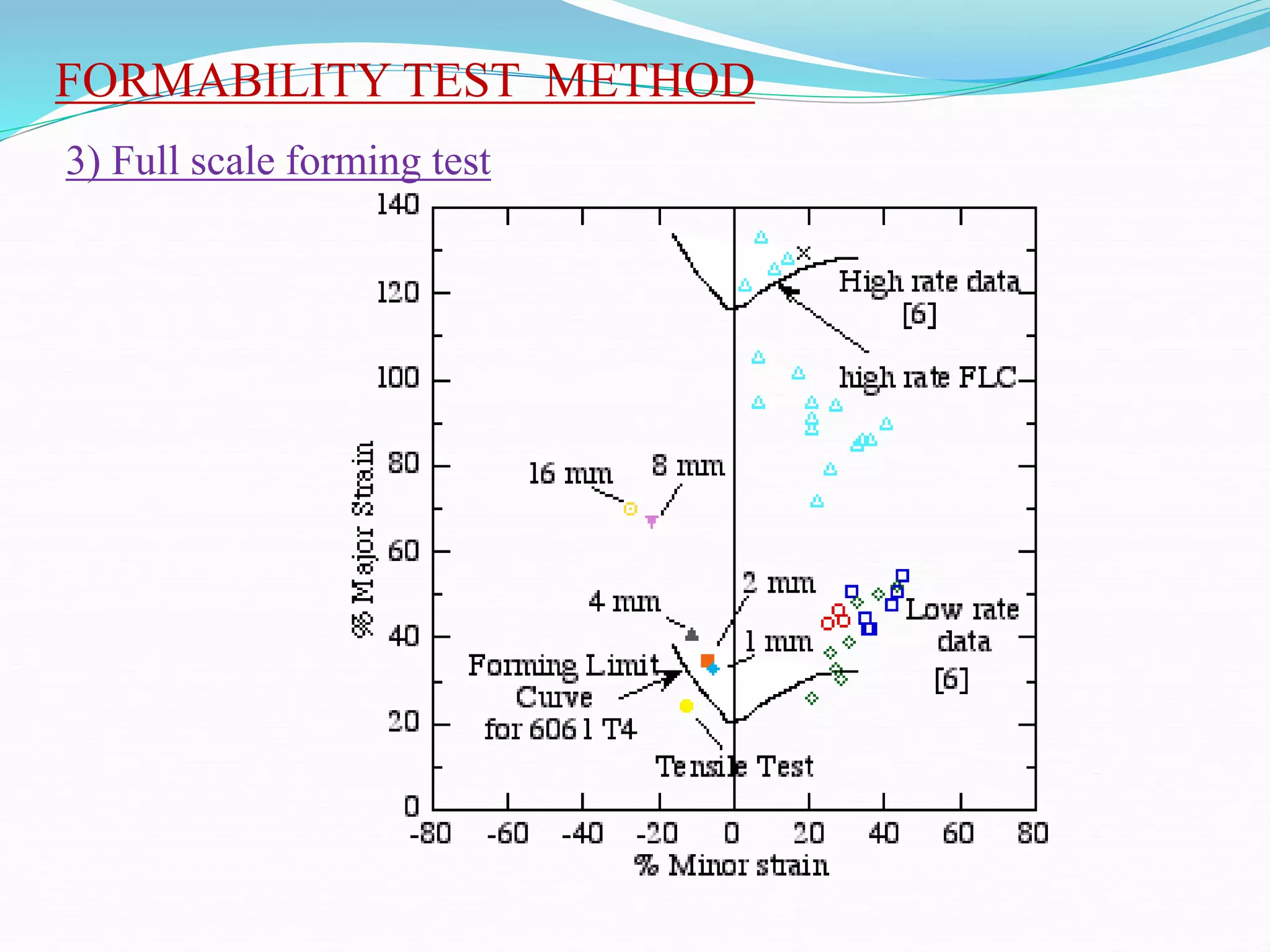
This document discusses various sheet metal processes and forming operations. It describes common sheet metal materials and characteristics. Various presses and cutting dies are discussed for operations like blanking, piercing, and bending. Specific forming processes like drawing, stretching, spinning, hydroforming and magnetic pulse forming are explained. Tests for assessing formability of sheet metals are also summarized.