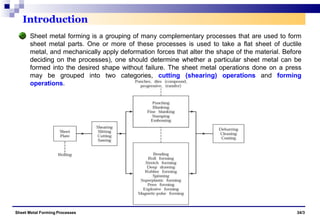
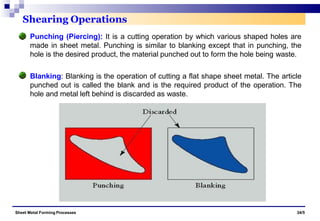
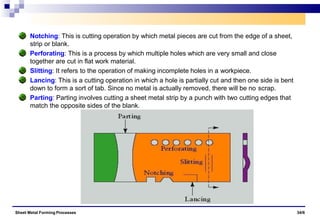
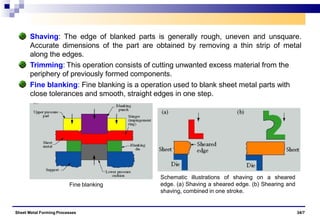
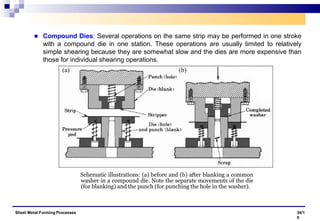
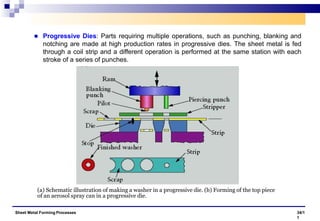
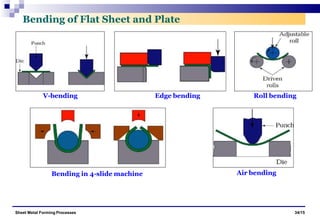
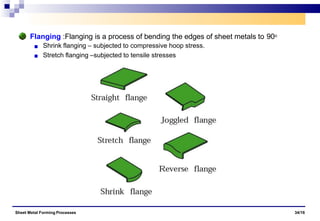
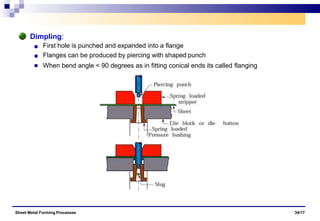
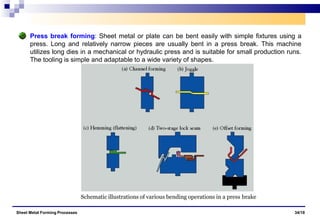
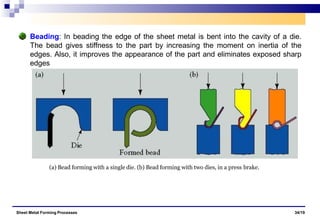
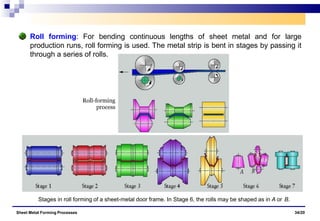
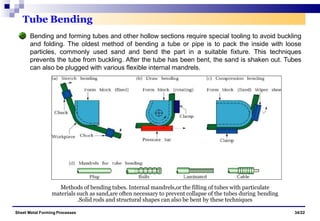
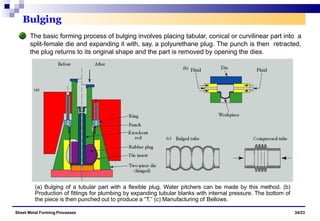
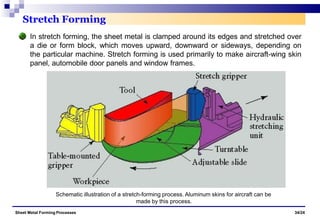
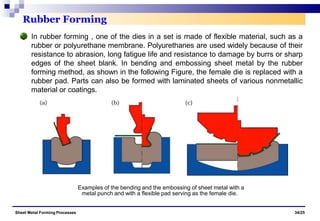
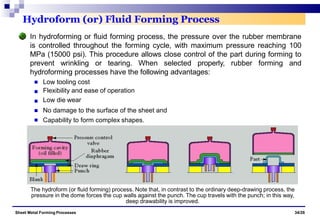
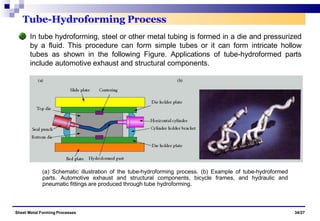
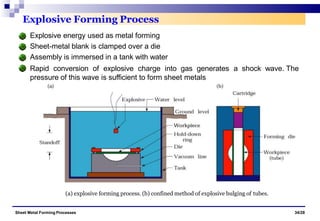
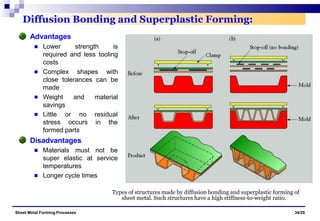
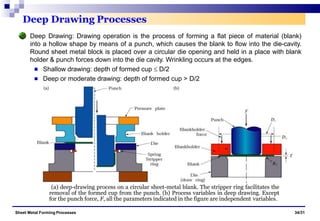
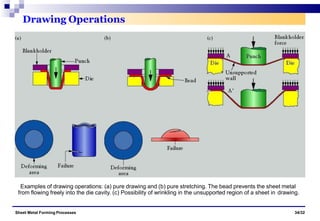
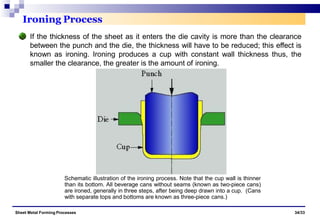
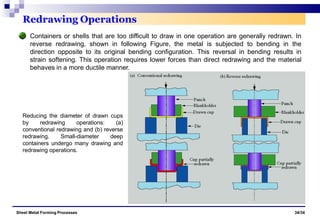
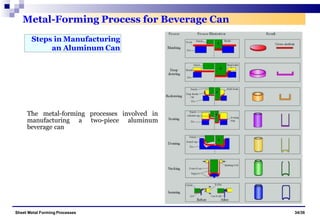
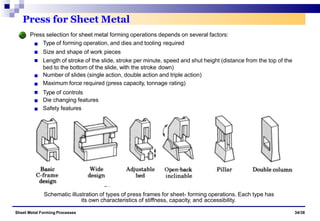
The document discusses various sheet metal forming processes. It describes cutting (shearing) operations such as punching, blanking, notching, etc. that stress the metal beyond its ultimate strength. It also discusses forming operations such as bending, drawing, squeezing, etc. that stress the metal below its ultimate strength. Various bending operations like V-bending, roll bending, and bead forming are also covered. The document discusses shearing and compound dies used for cutting operations. It also describes progressive, transfer, and hydroforming dies used for complex forming operations.