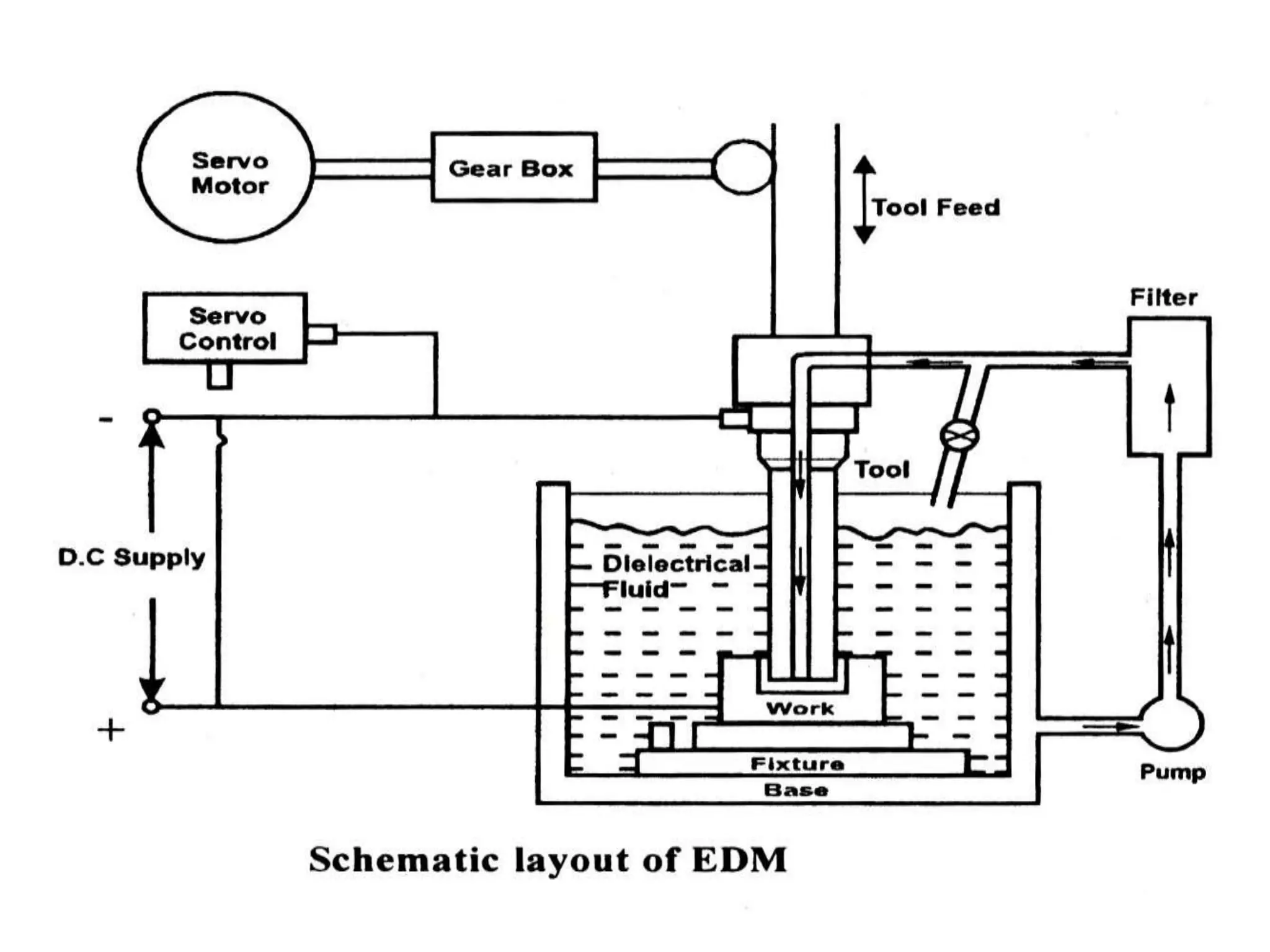
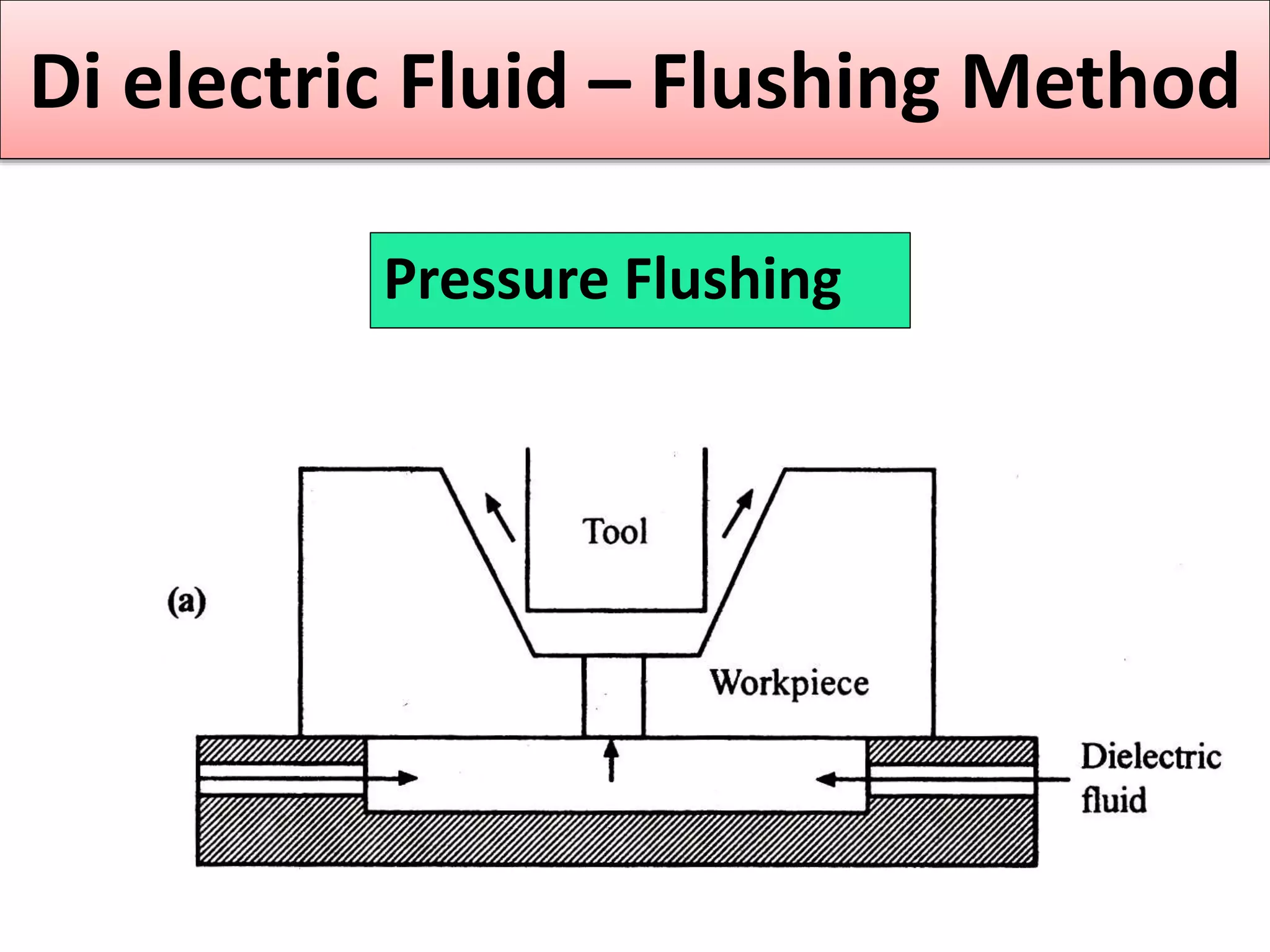
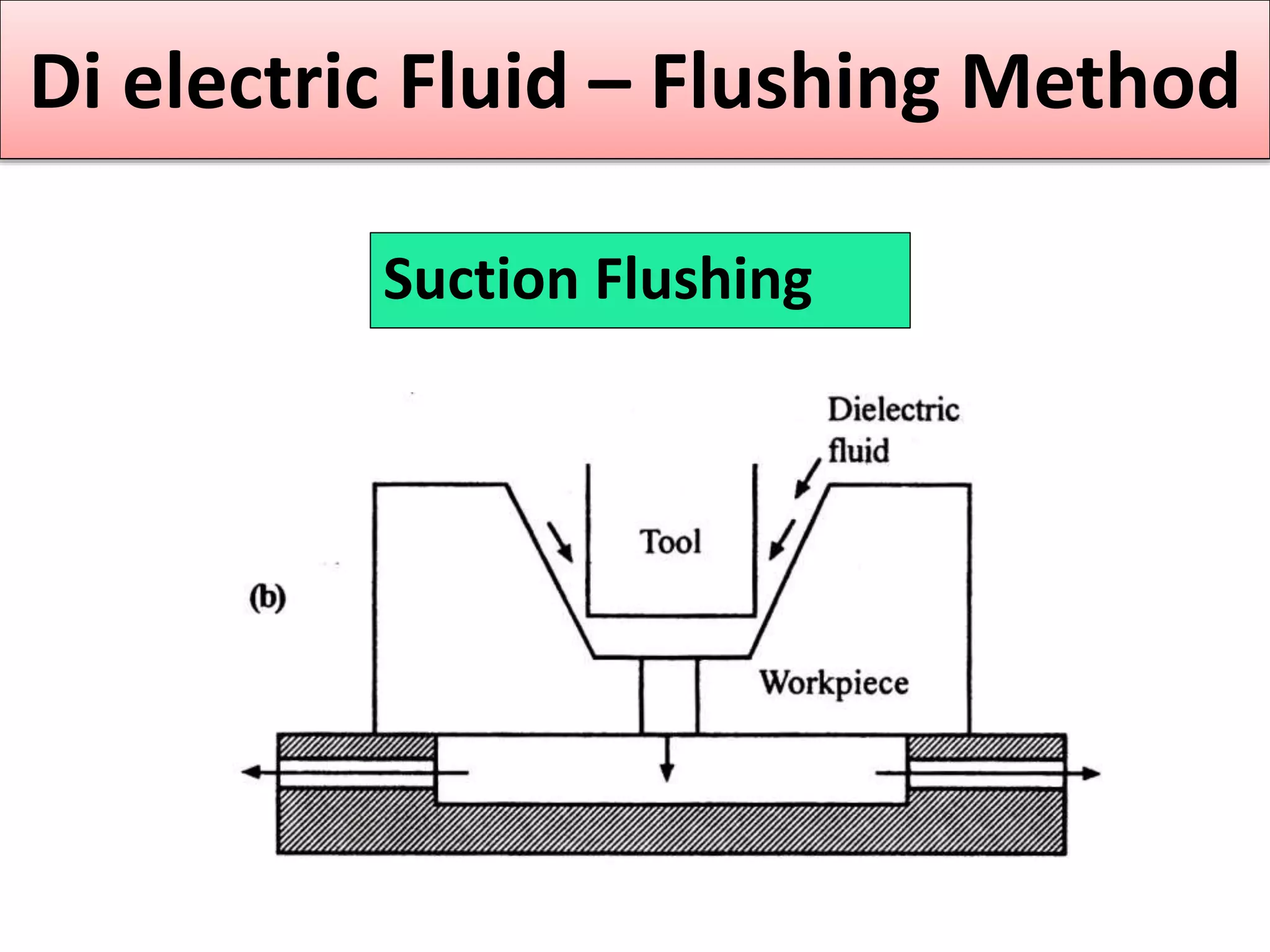
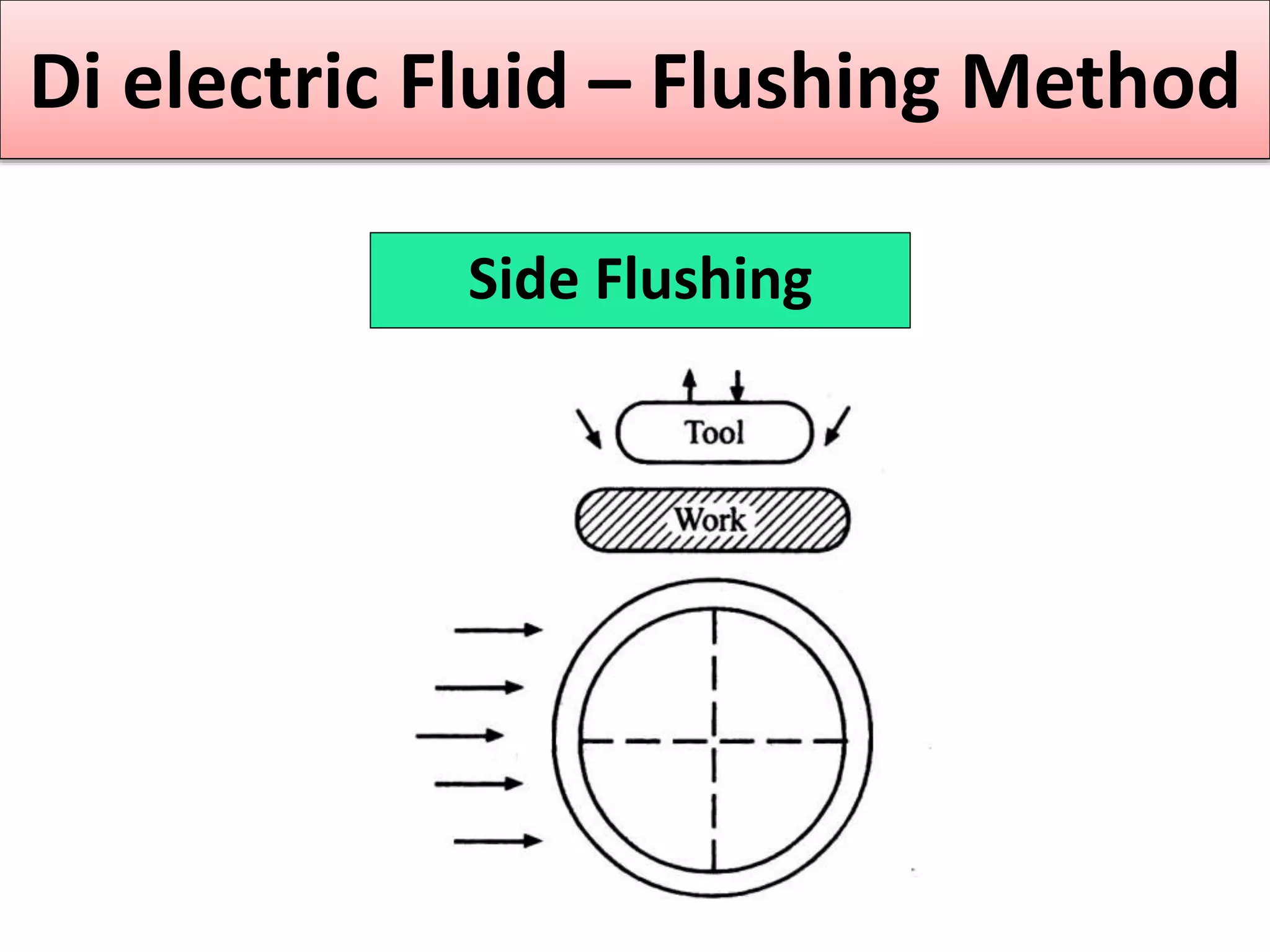
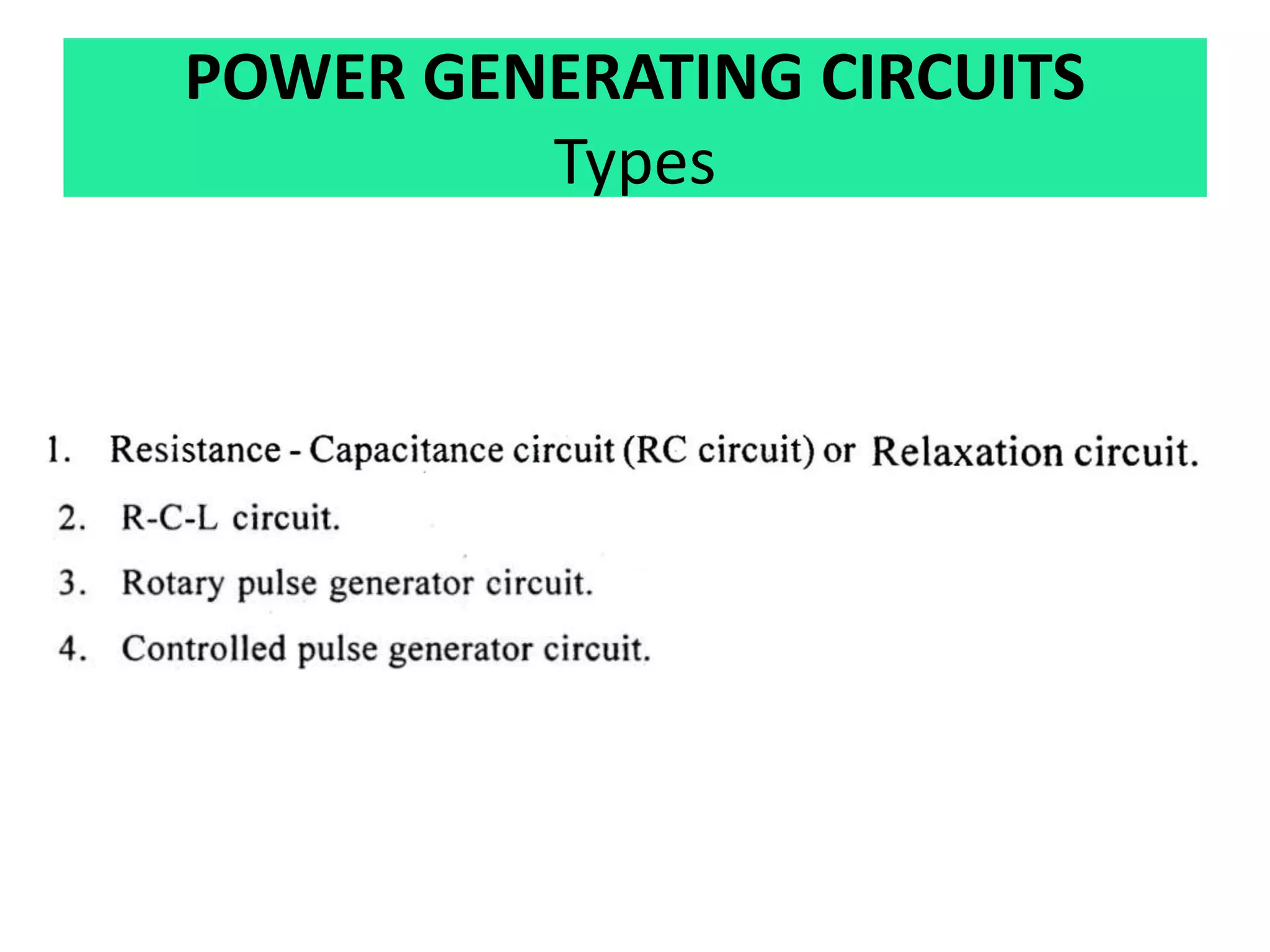
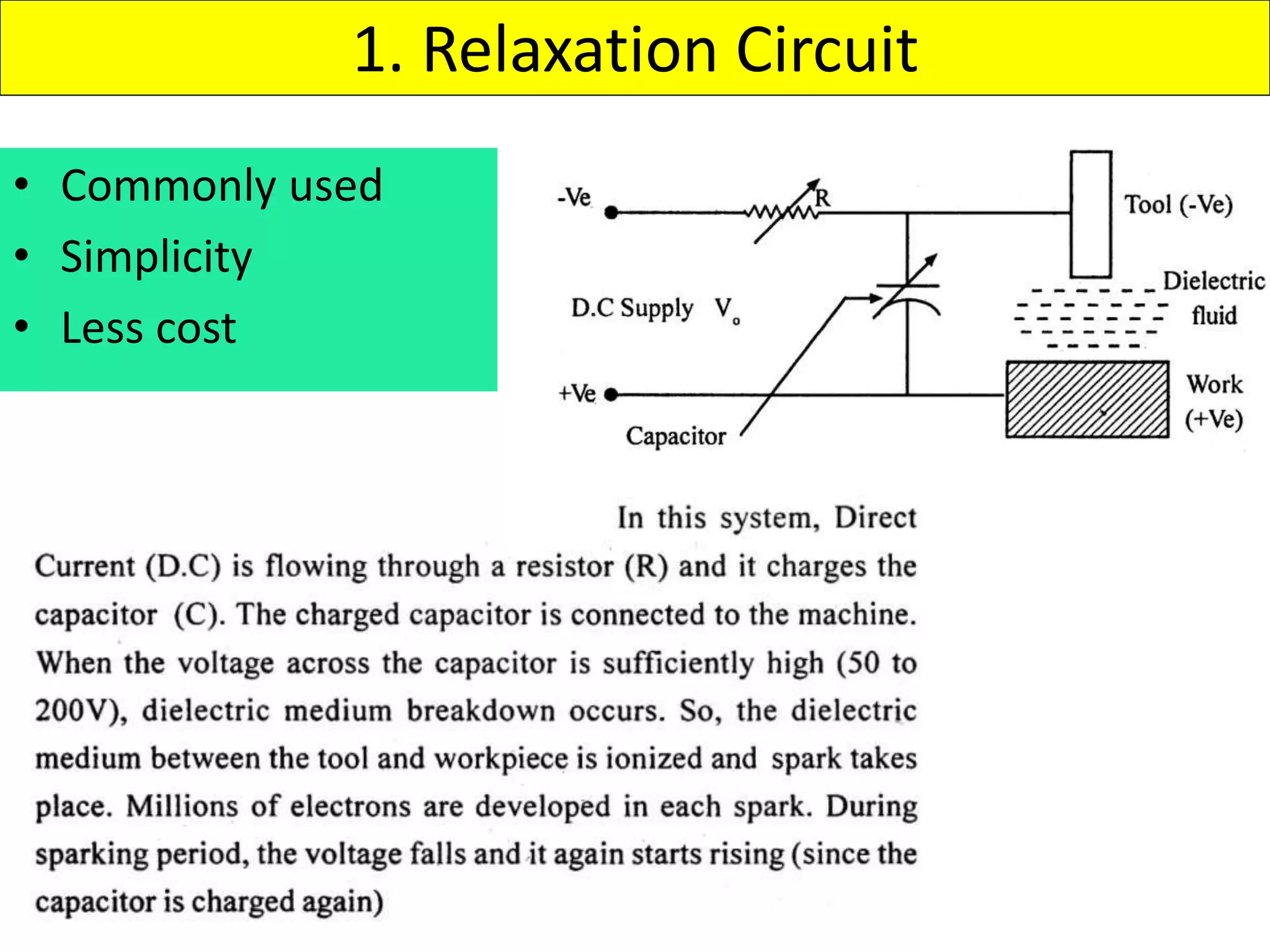
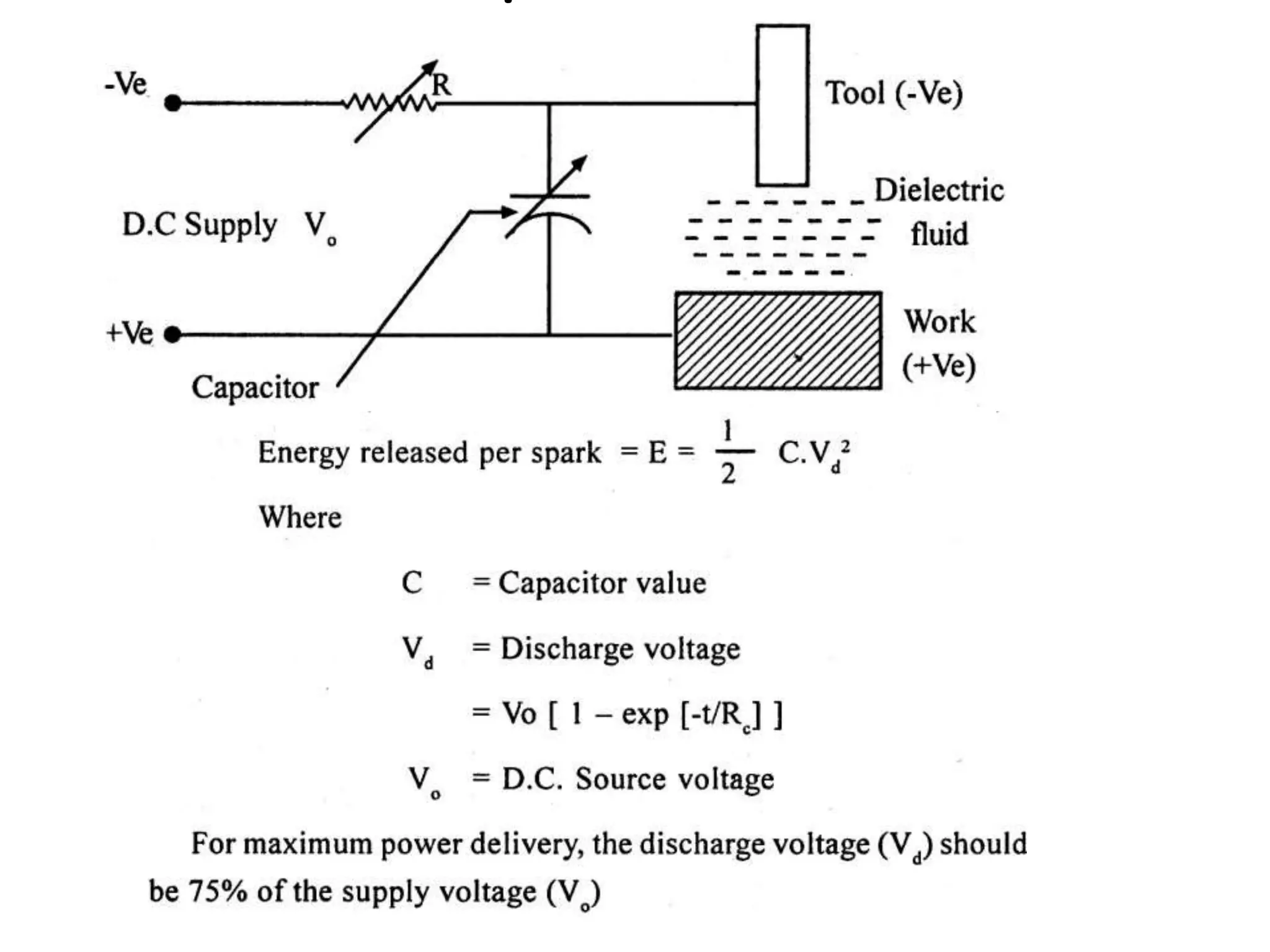
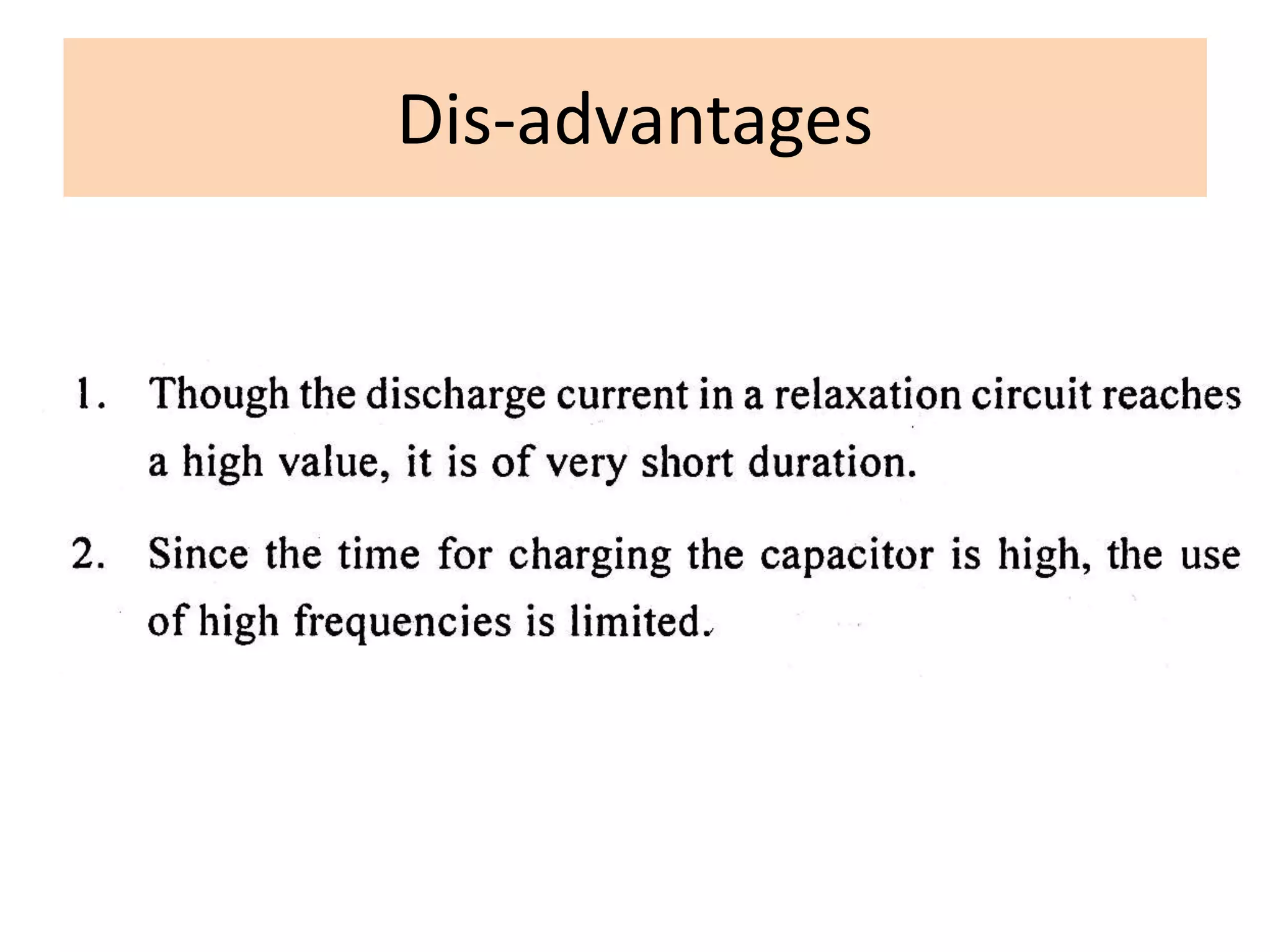
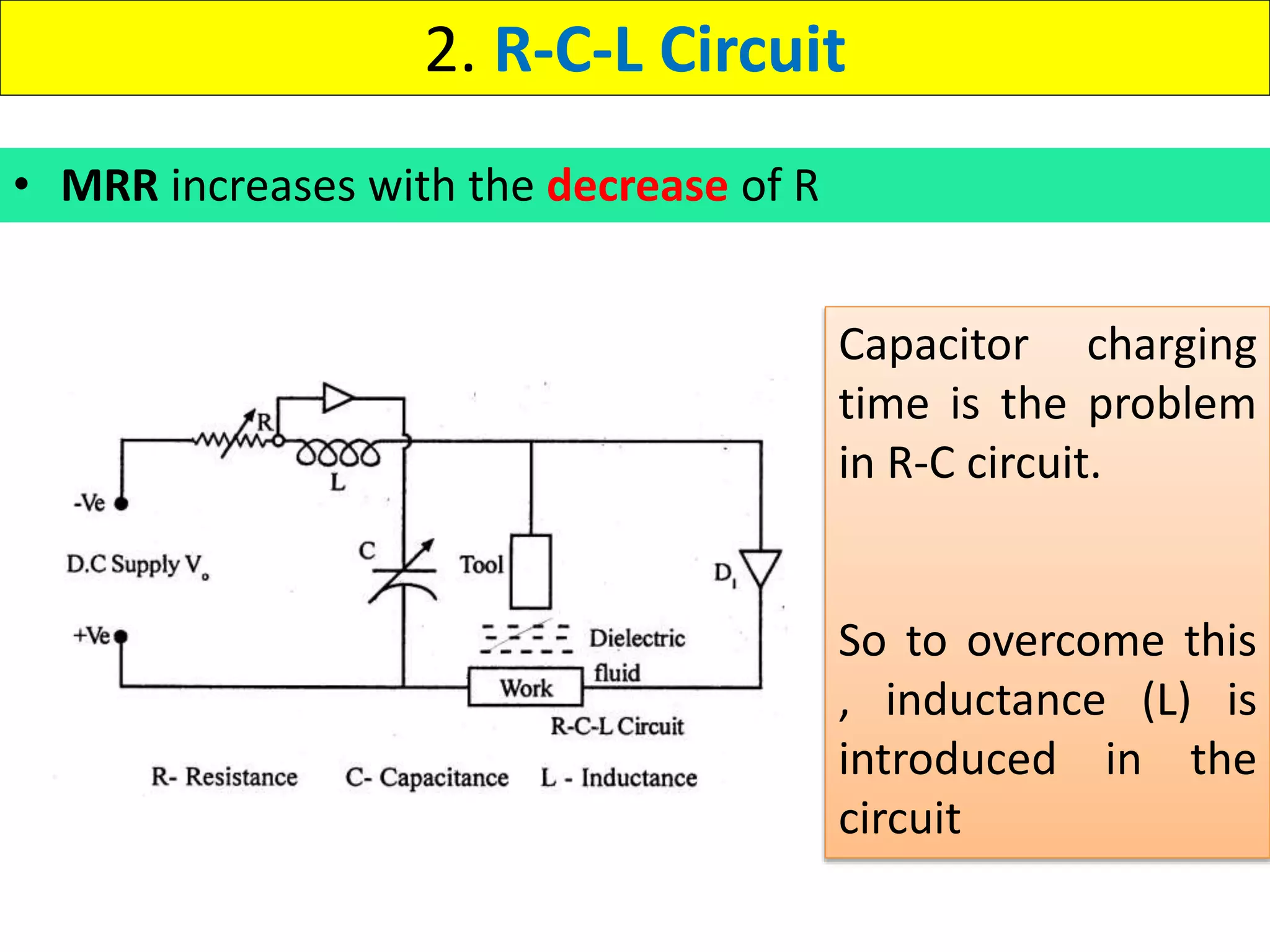
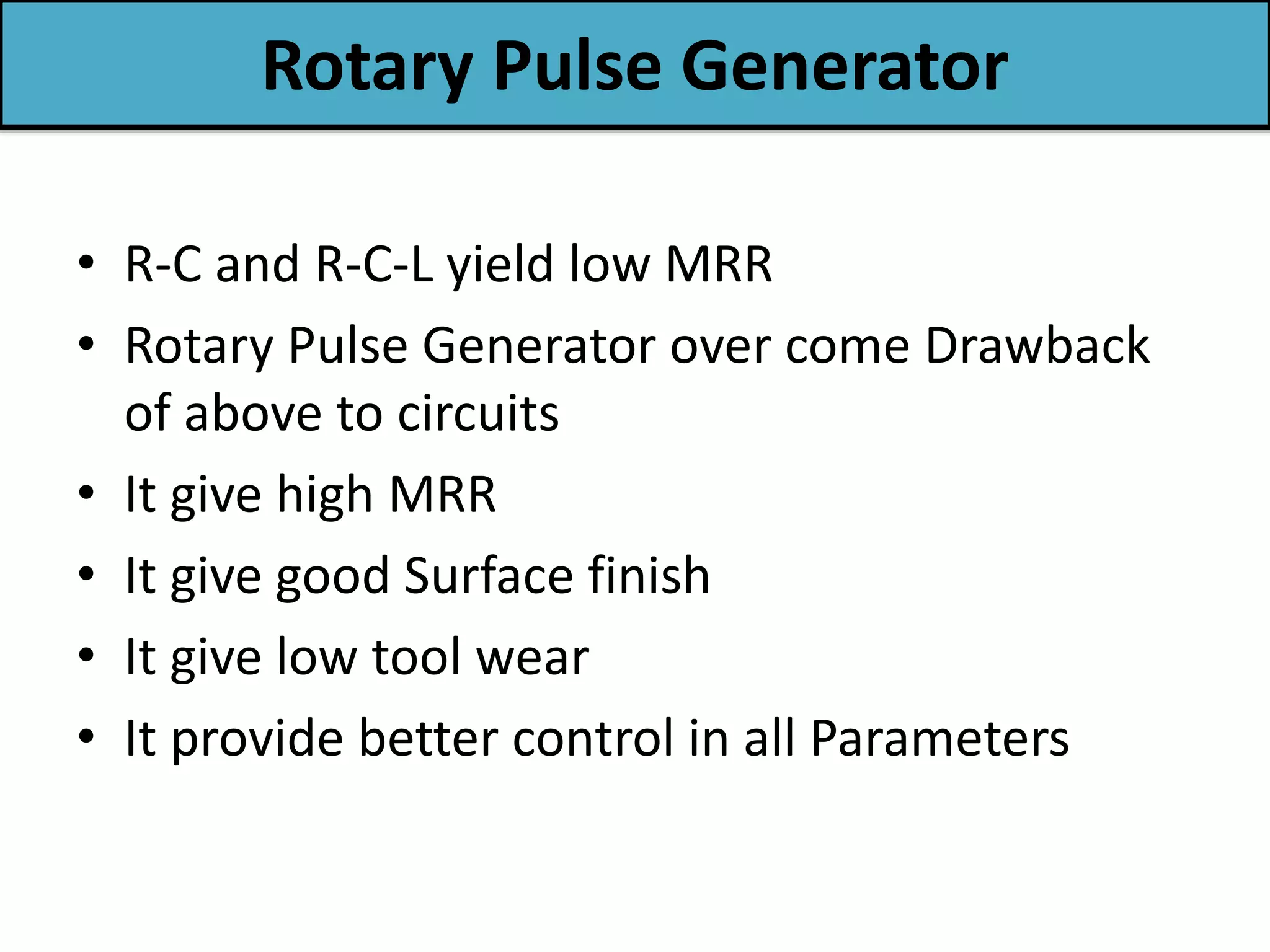
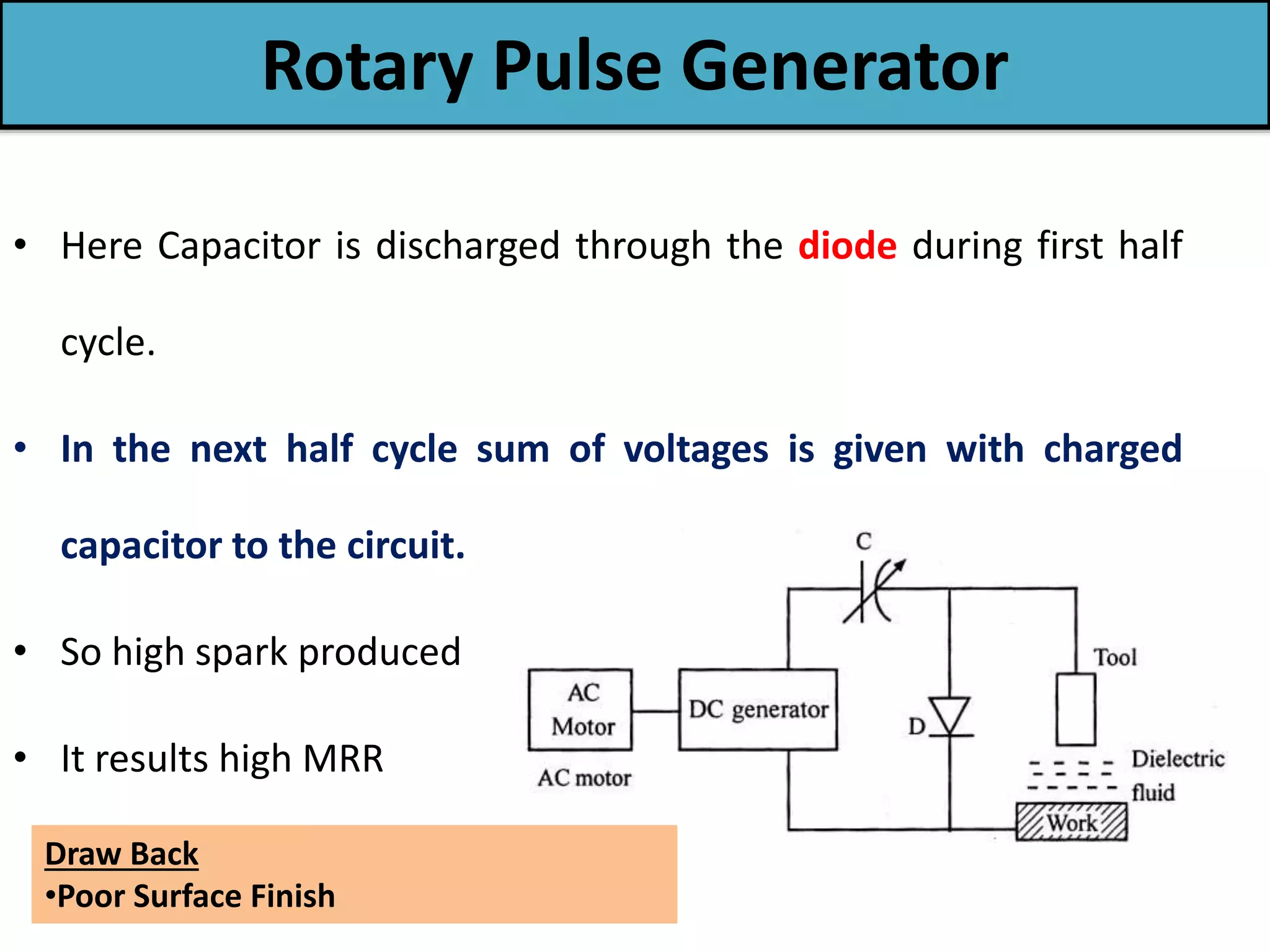
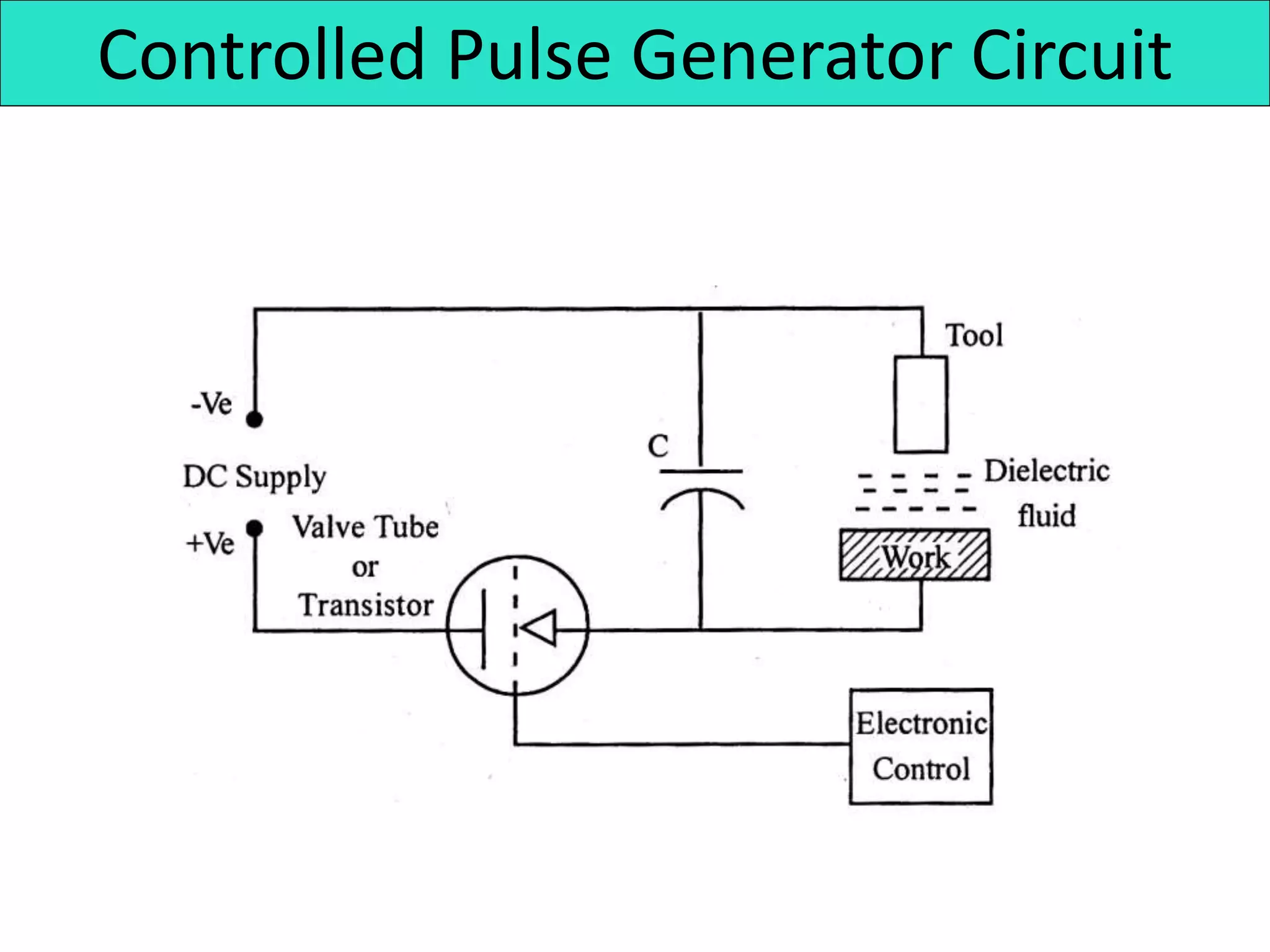
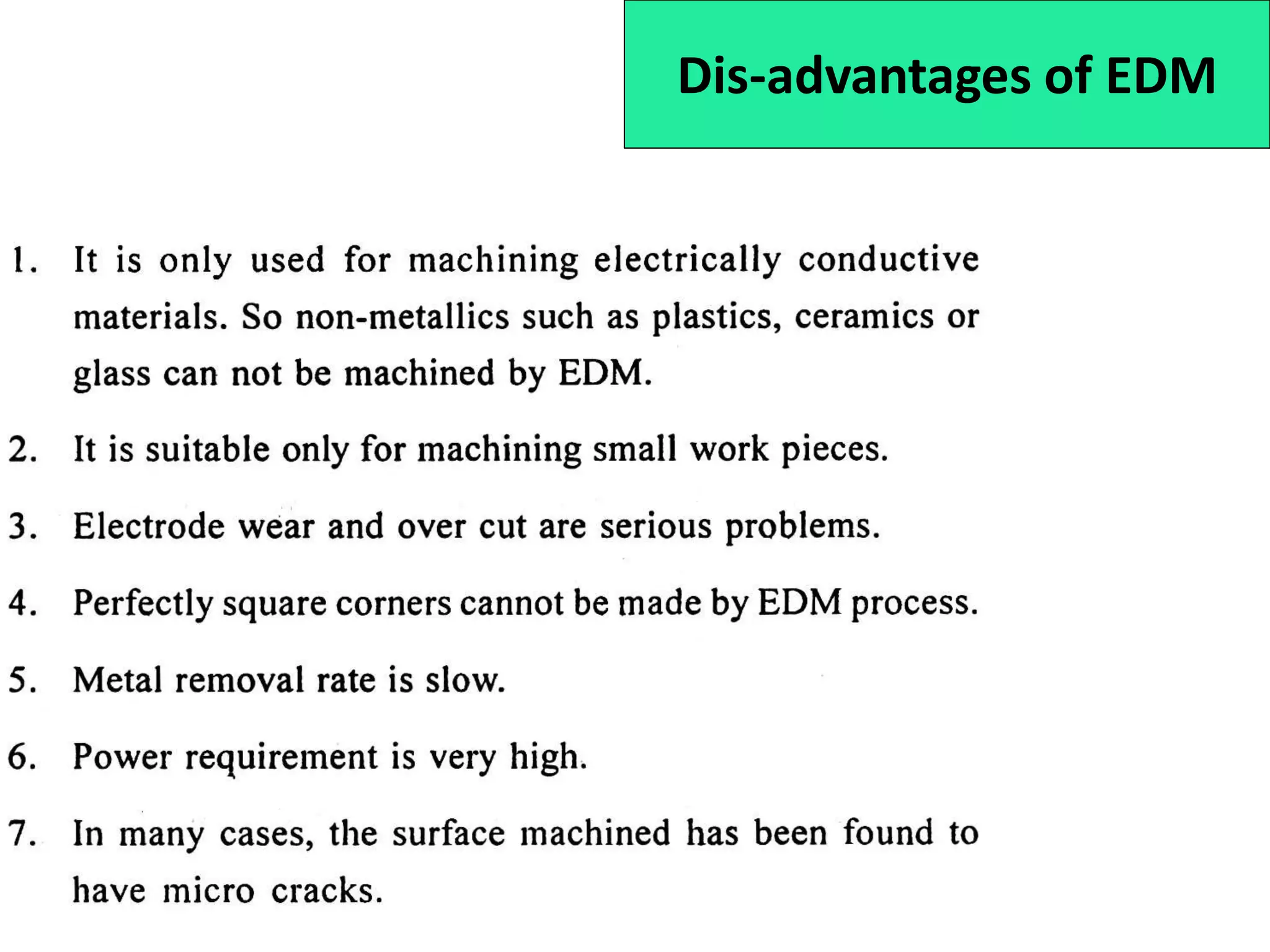
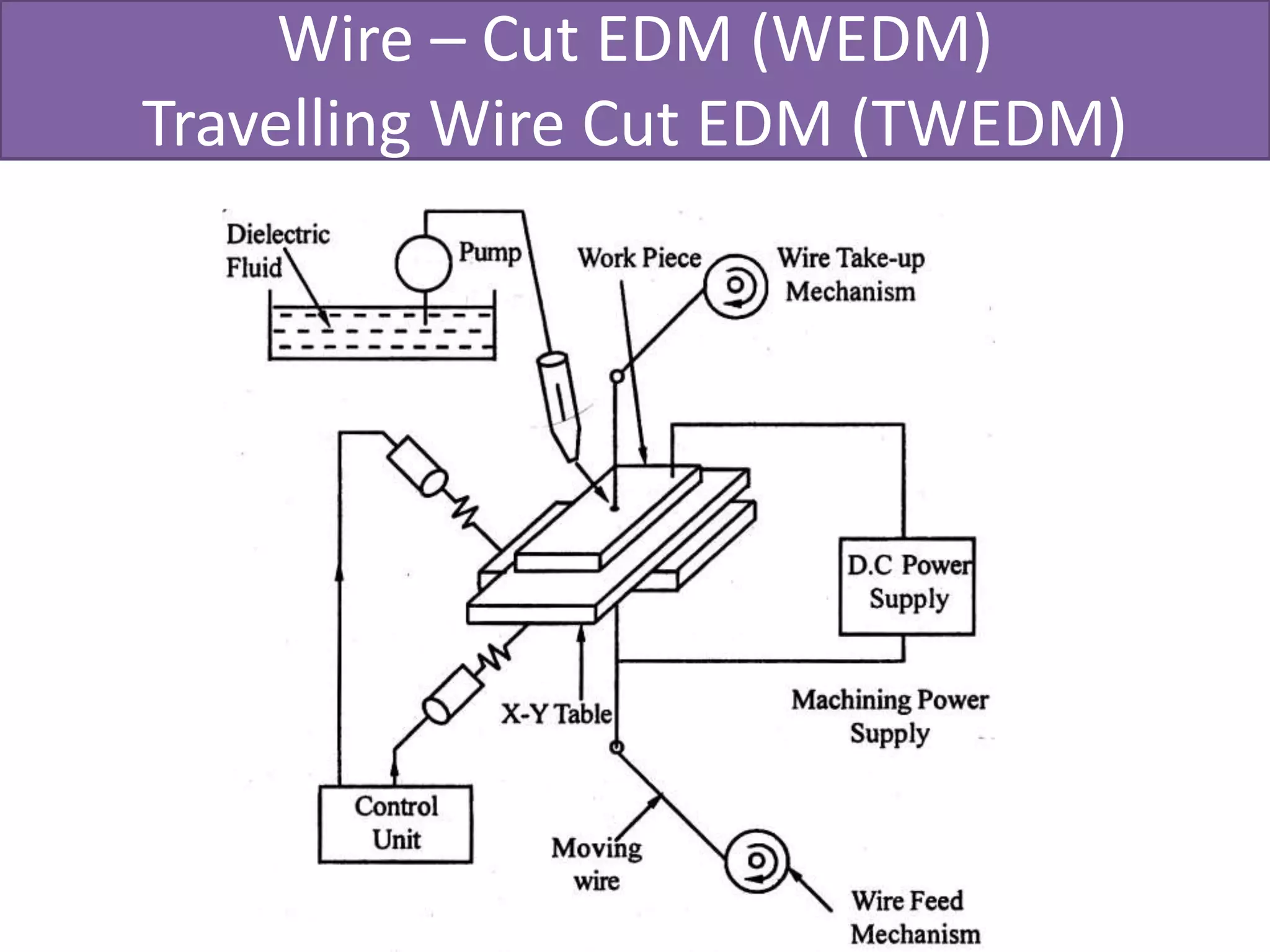
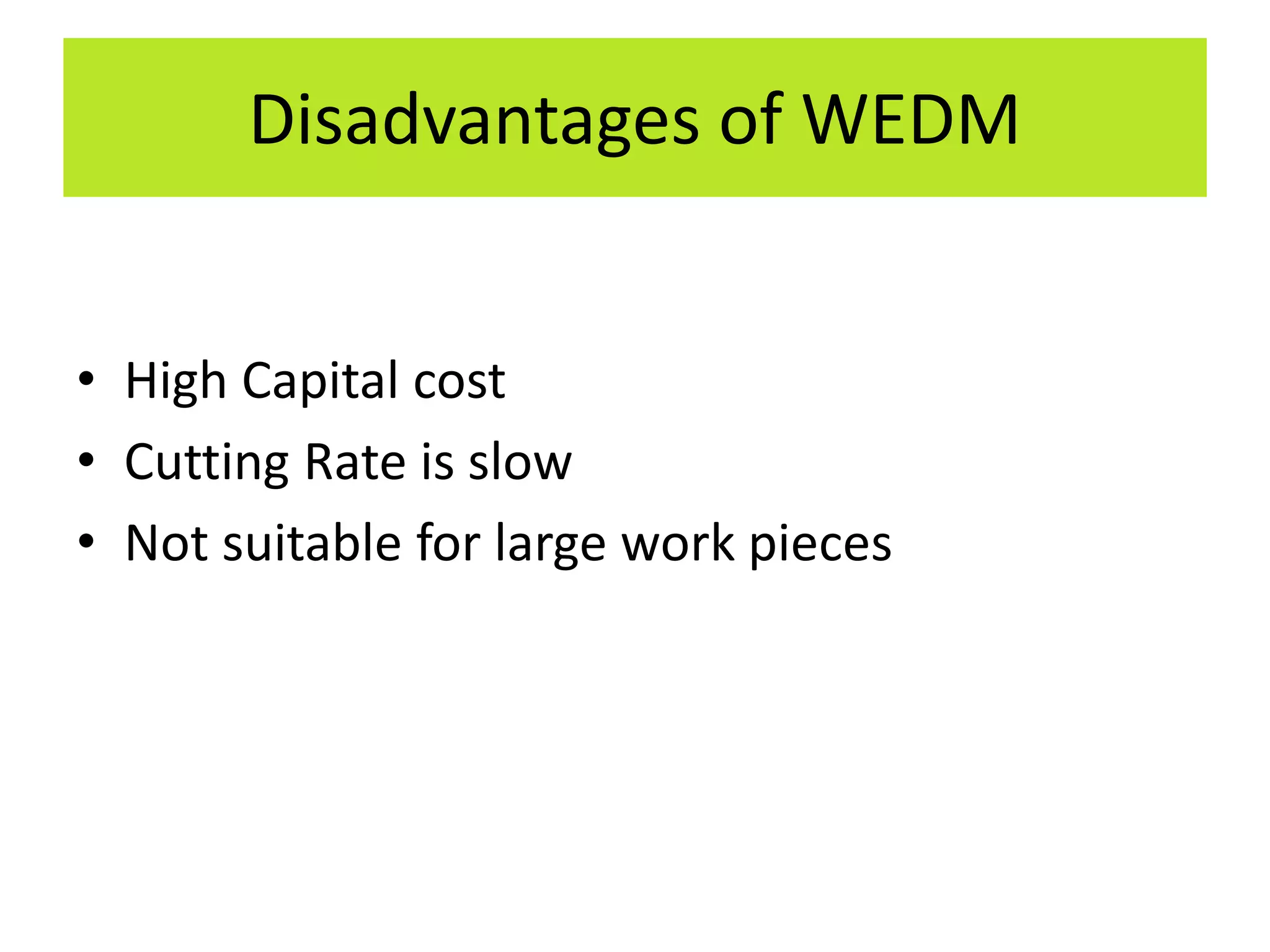
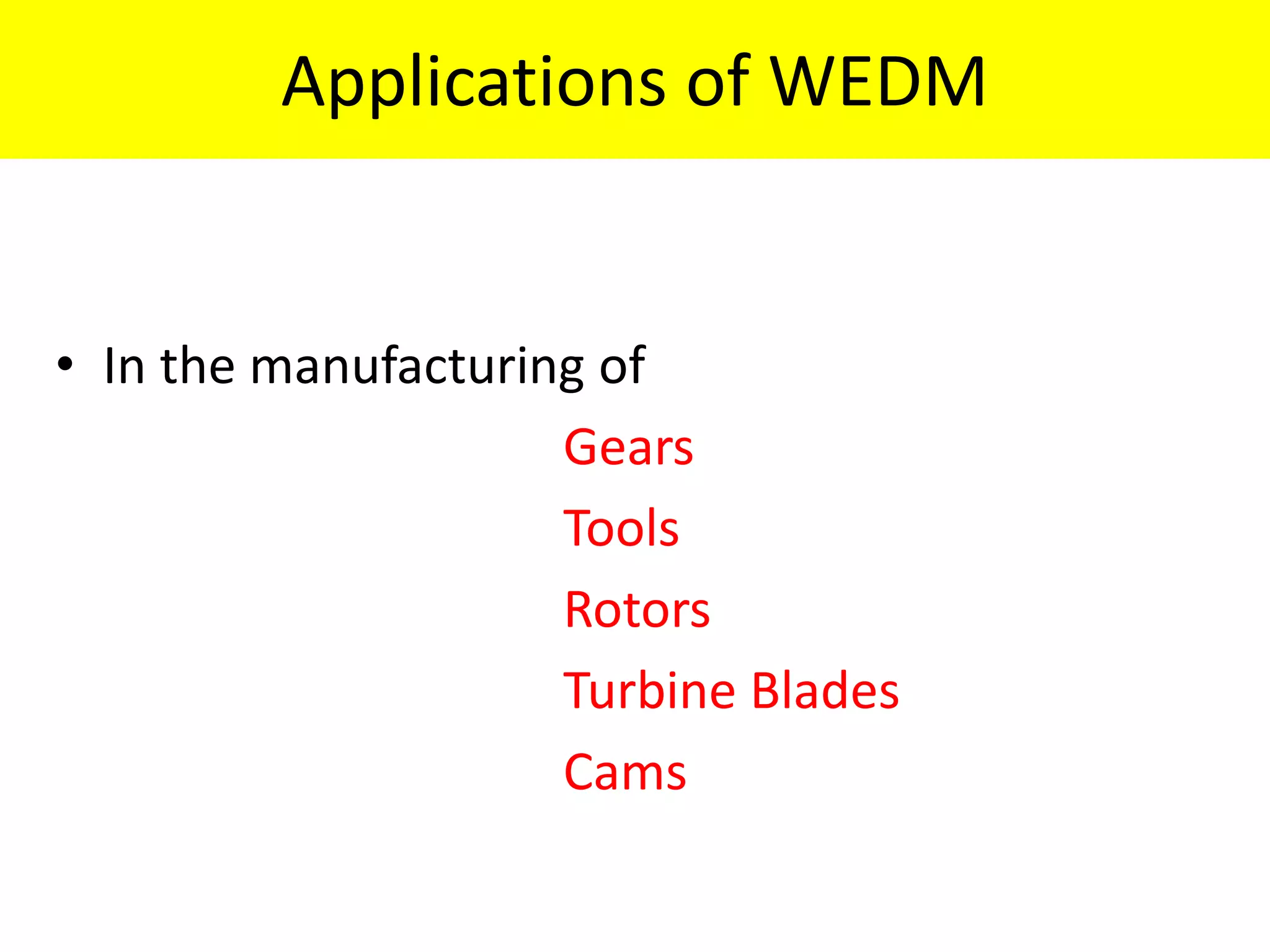
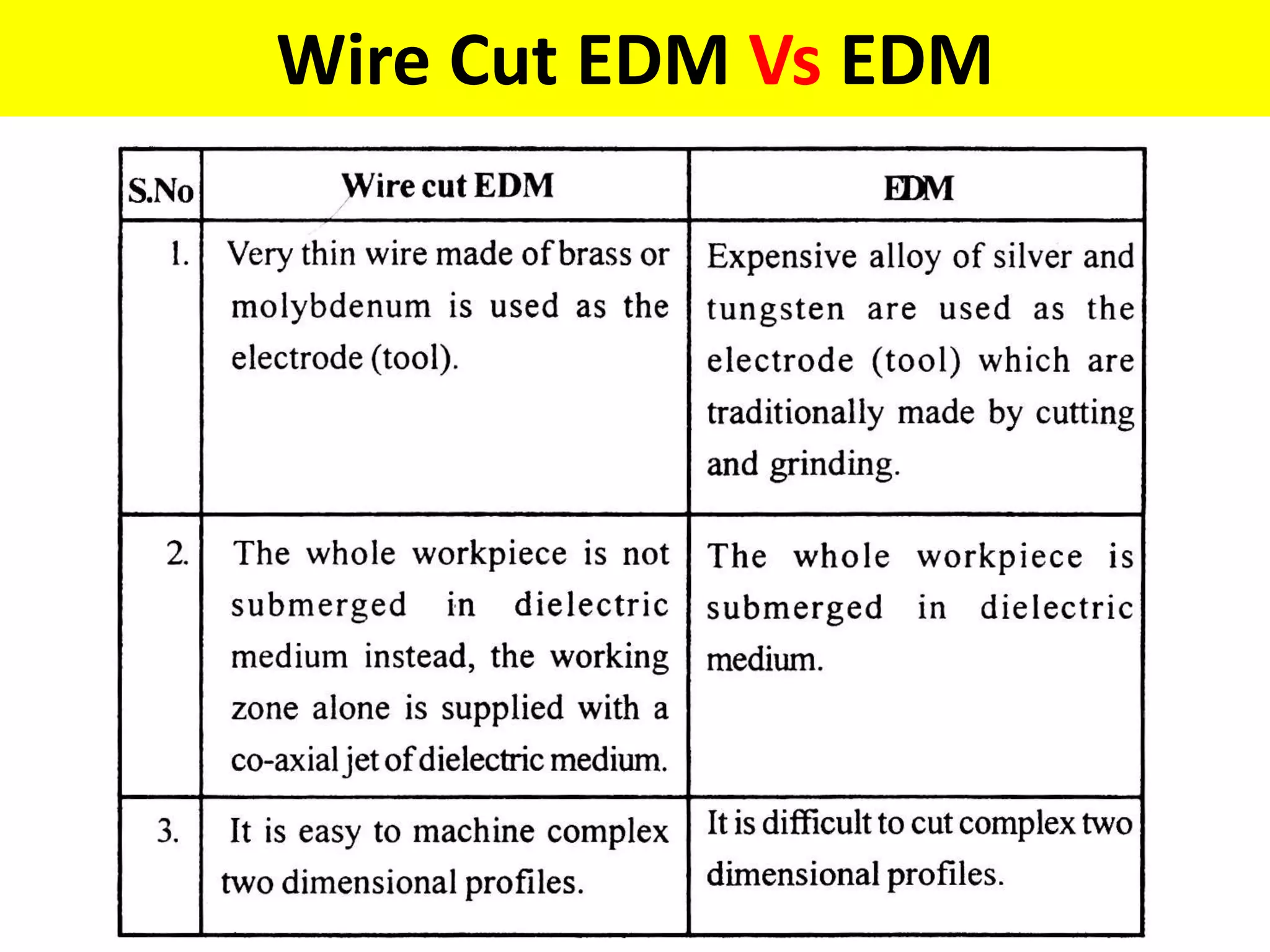
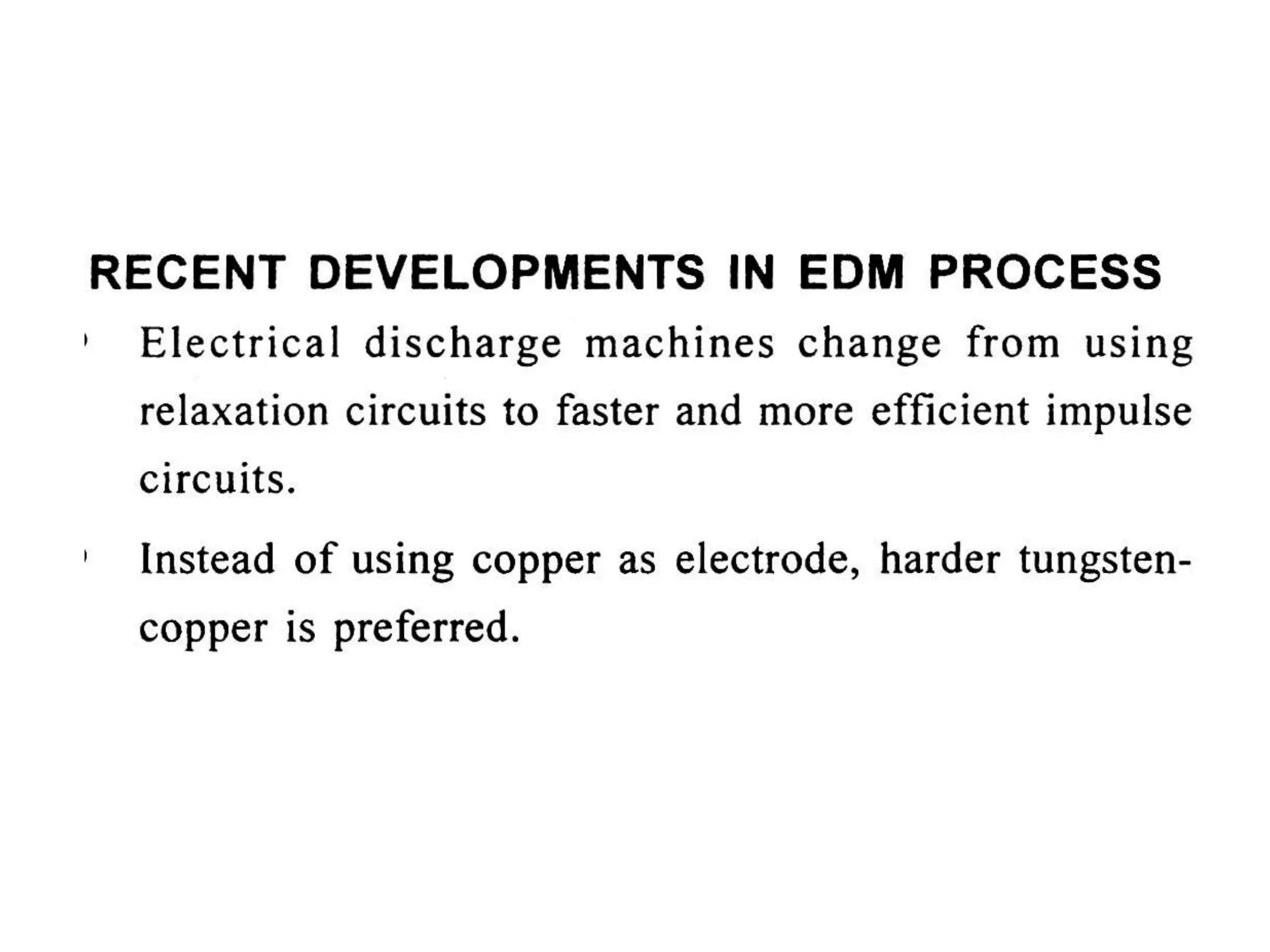
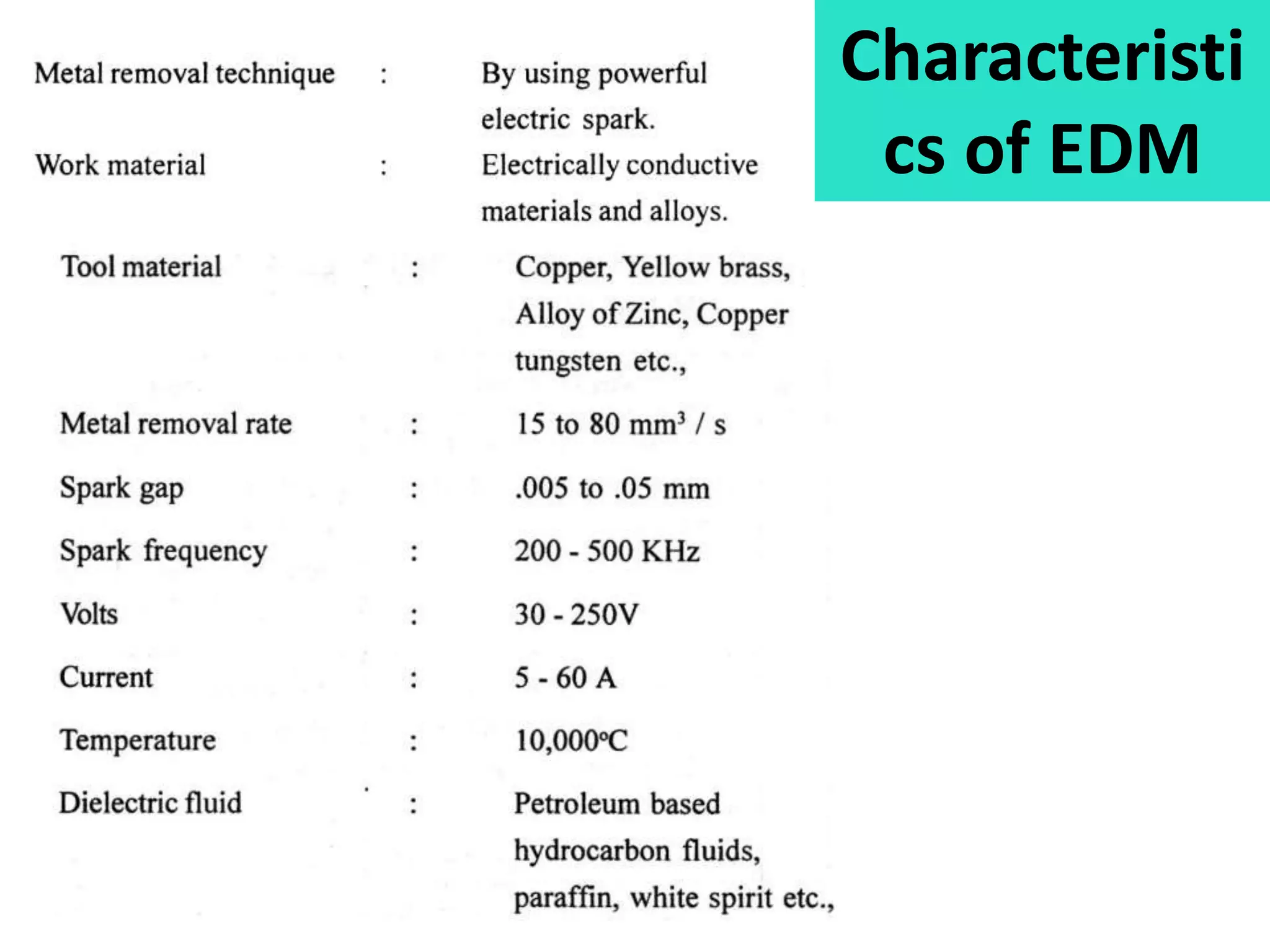
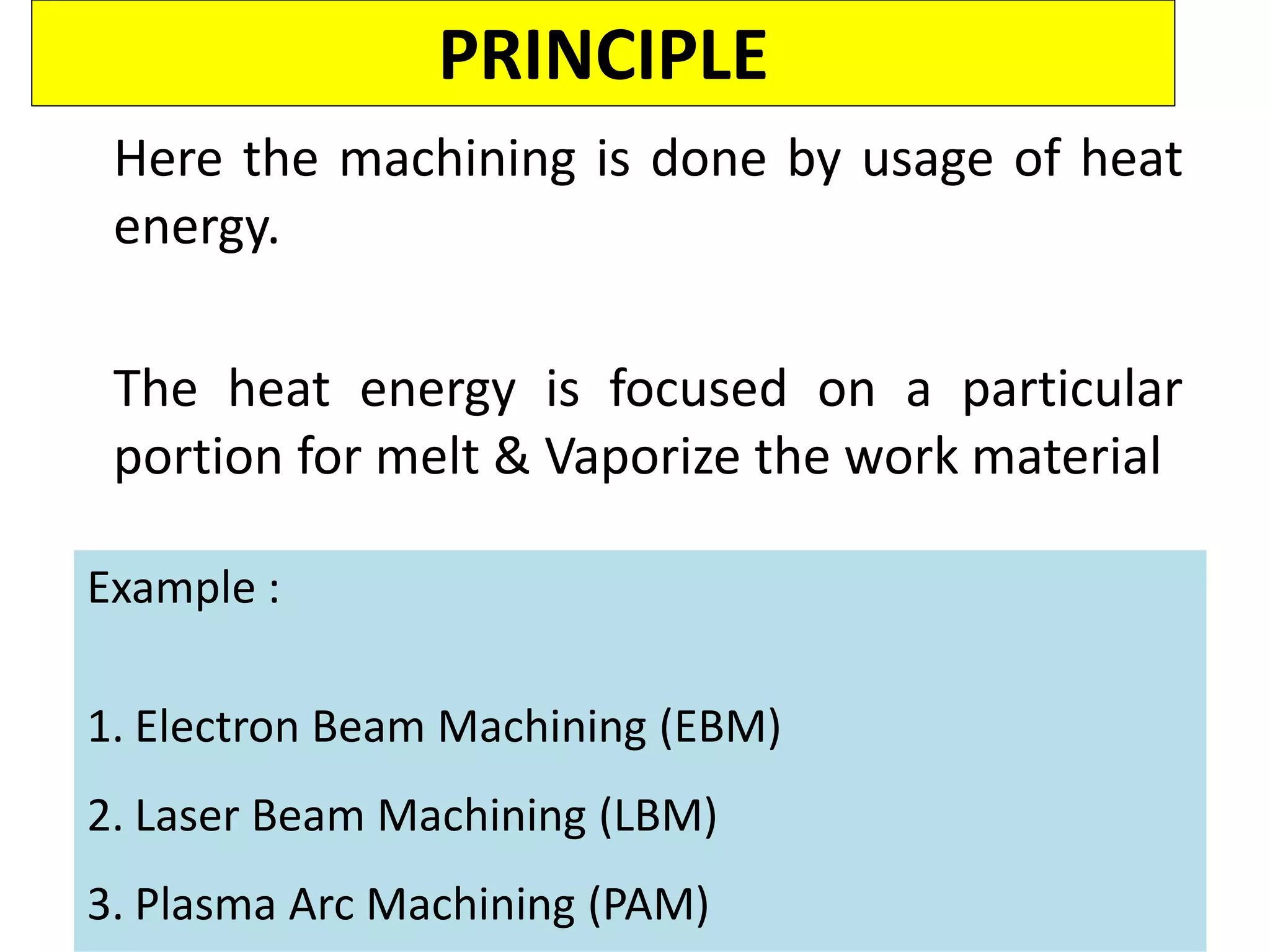
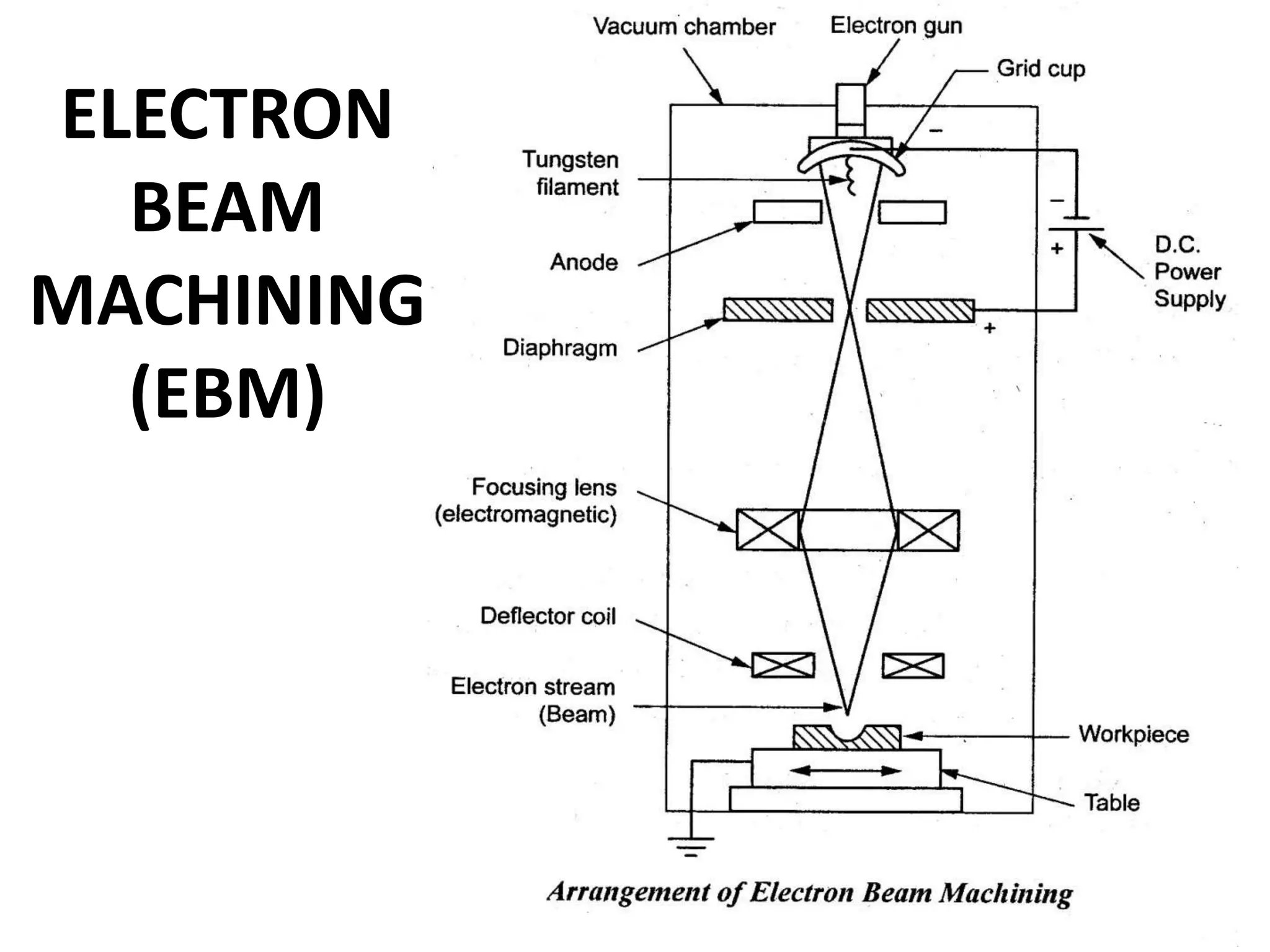
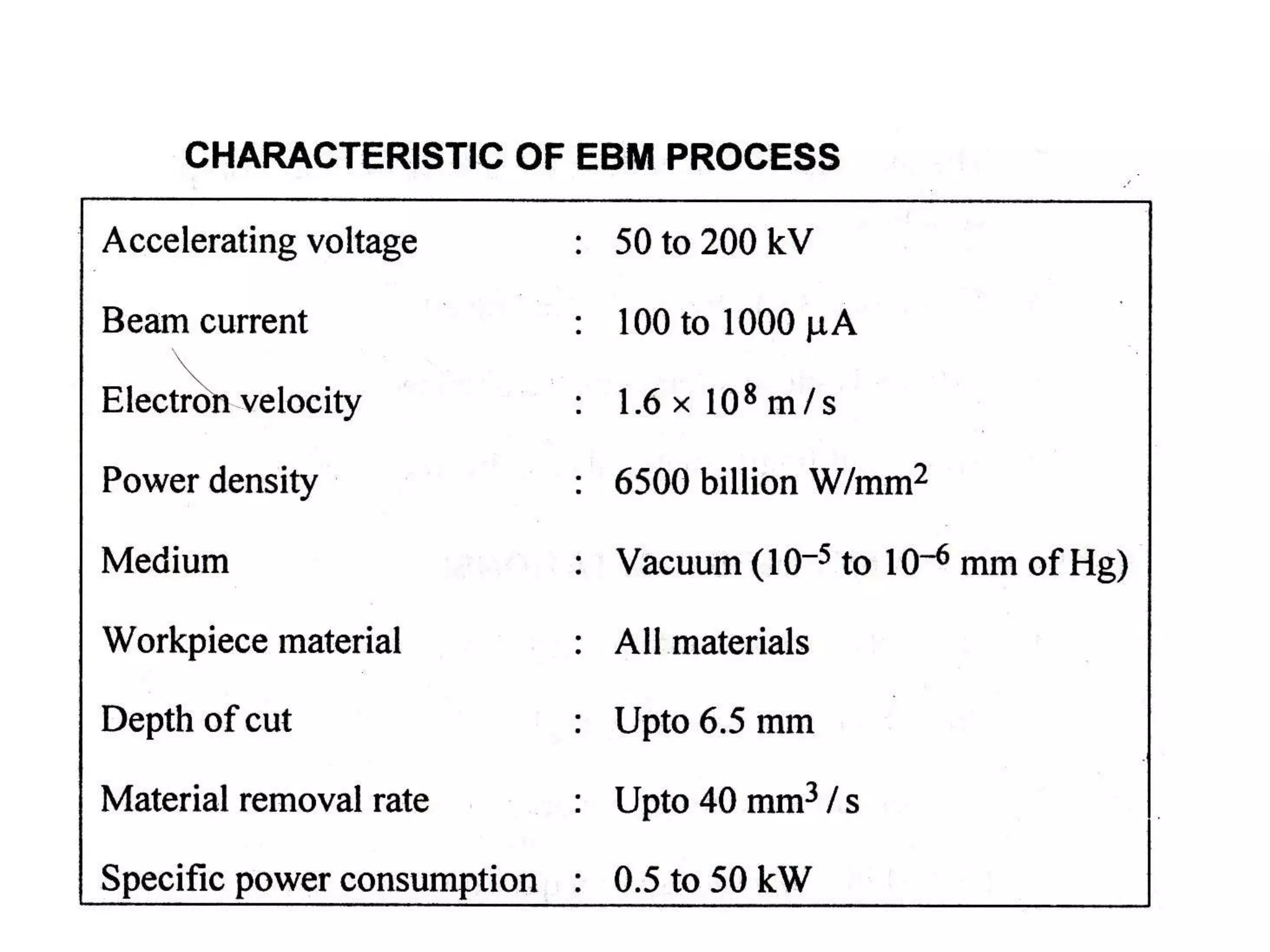
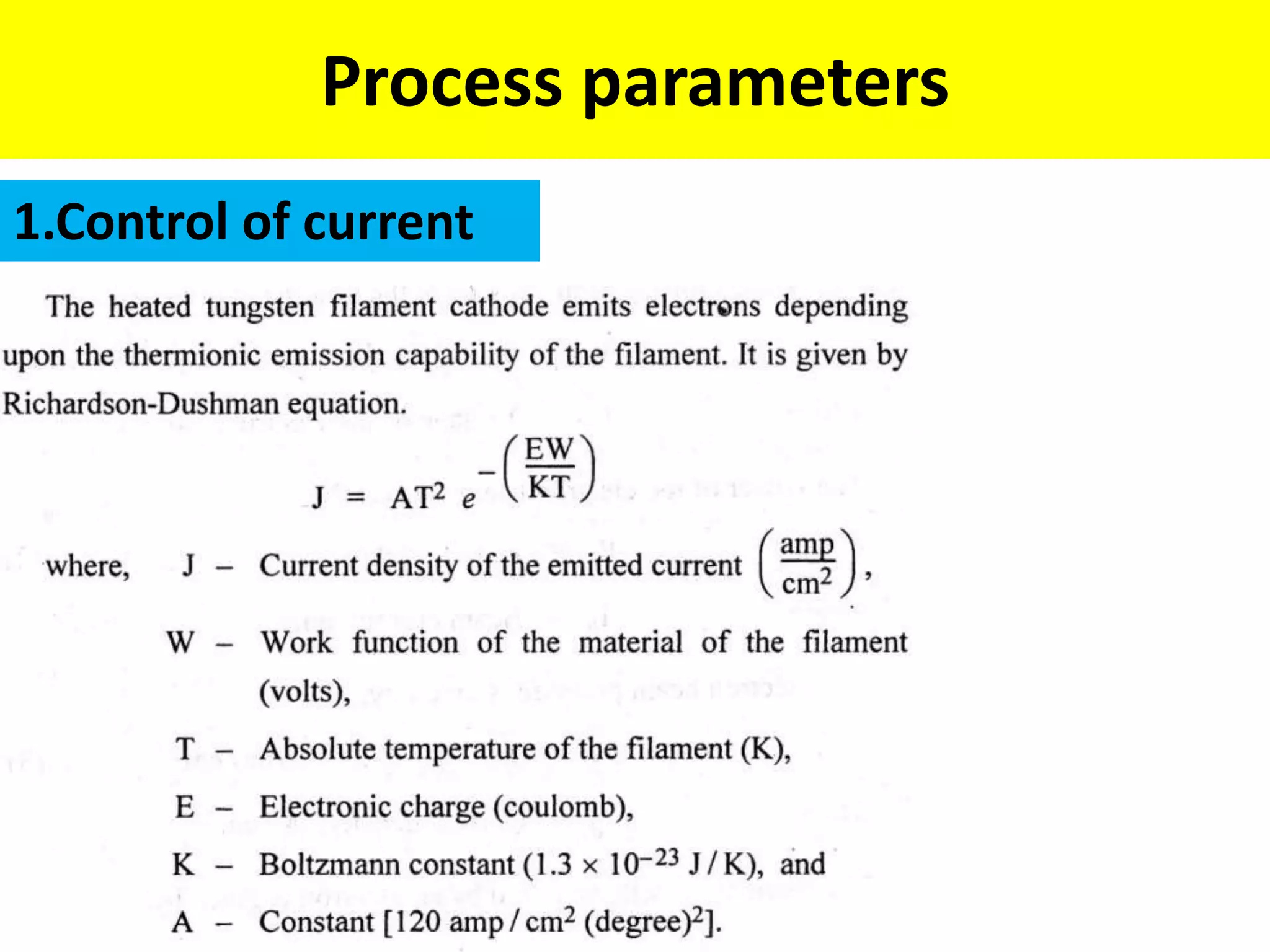
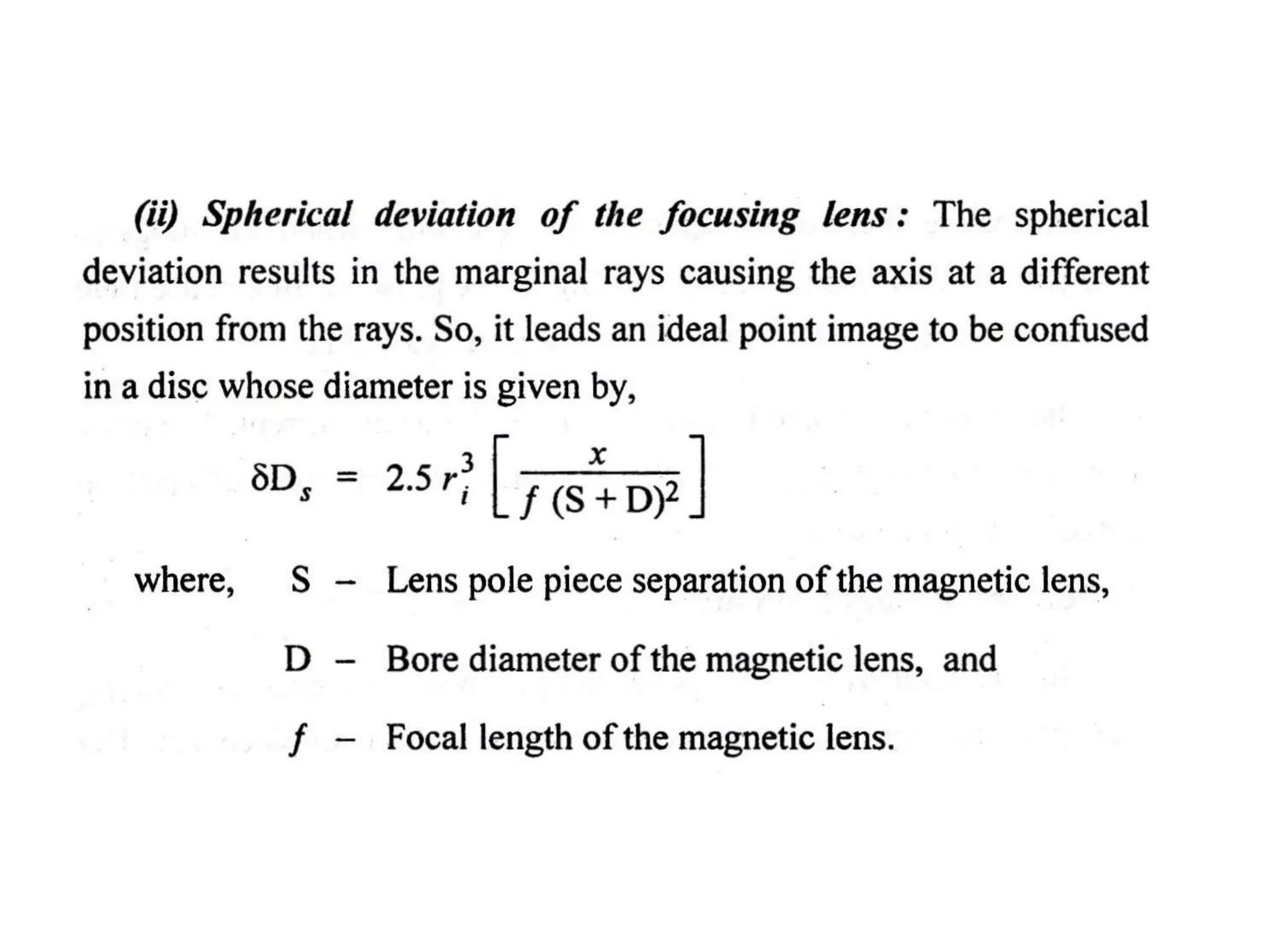
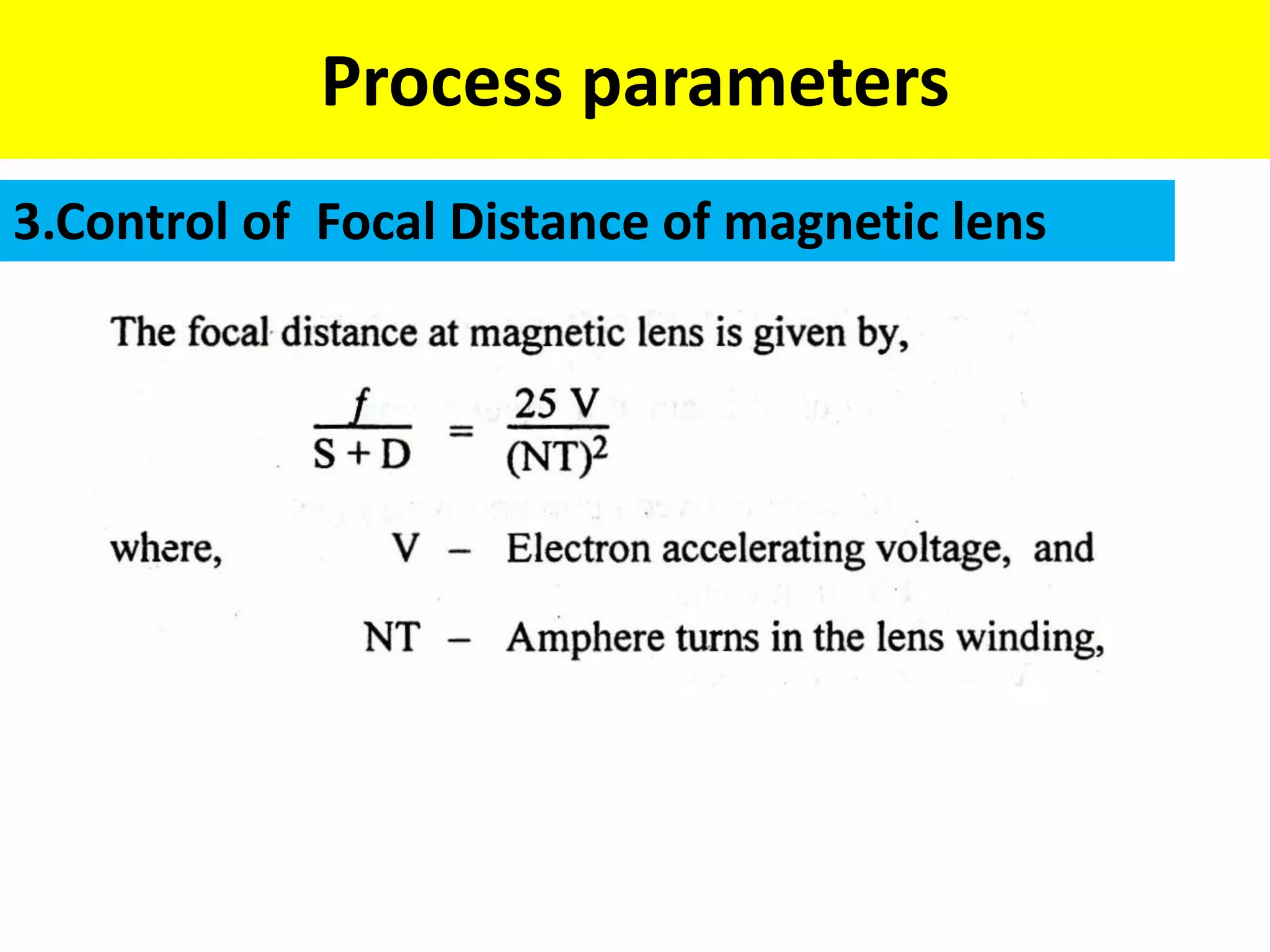
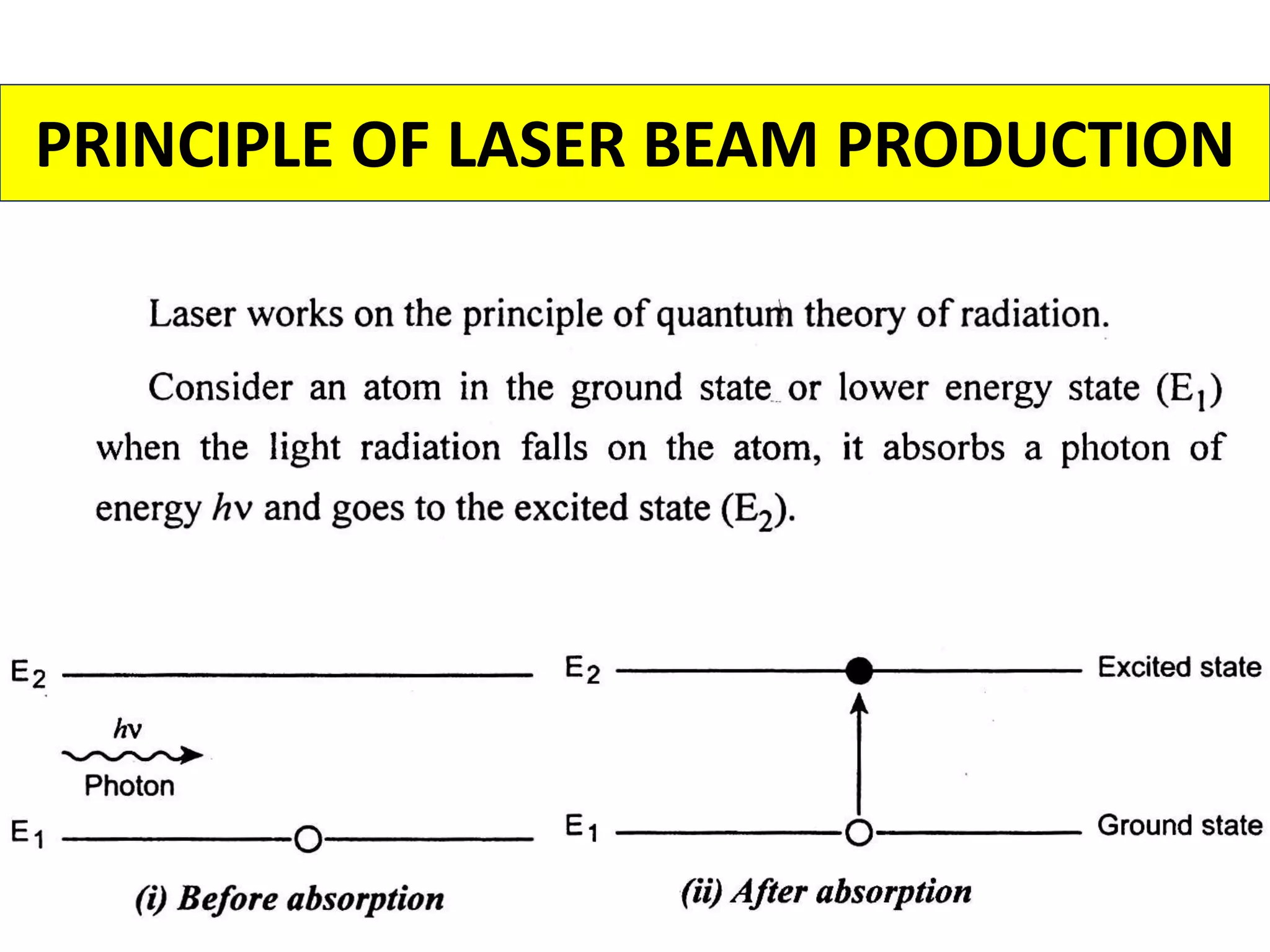
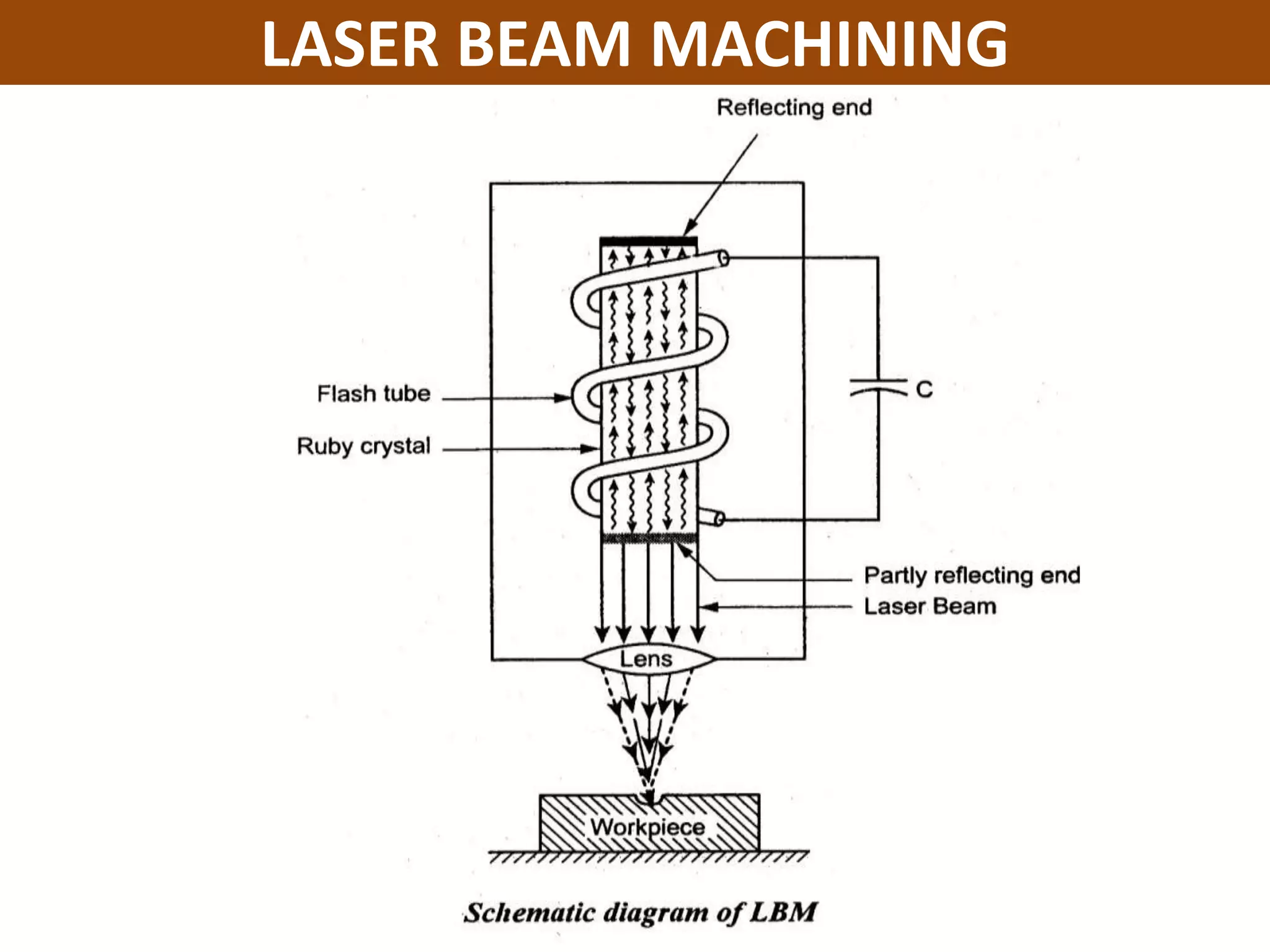
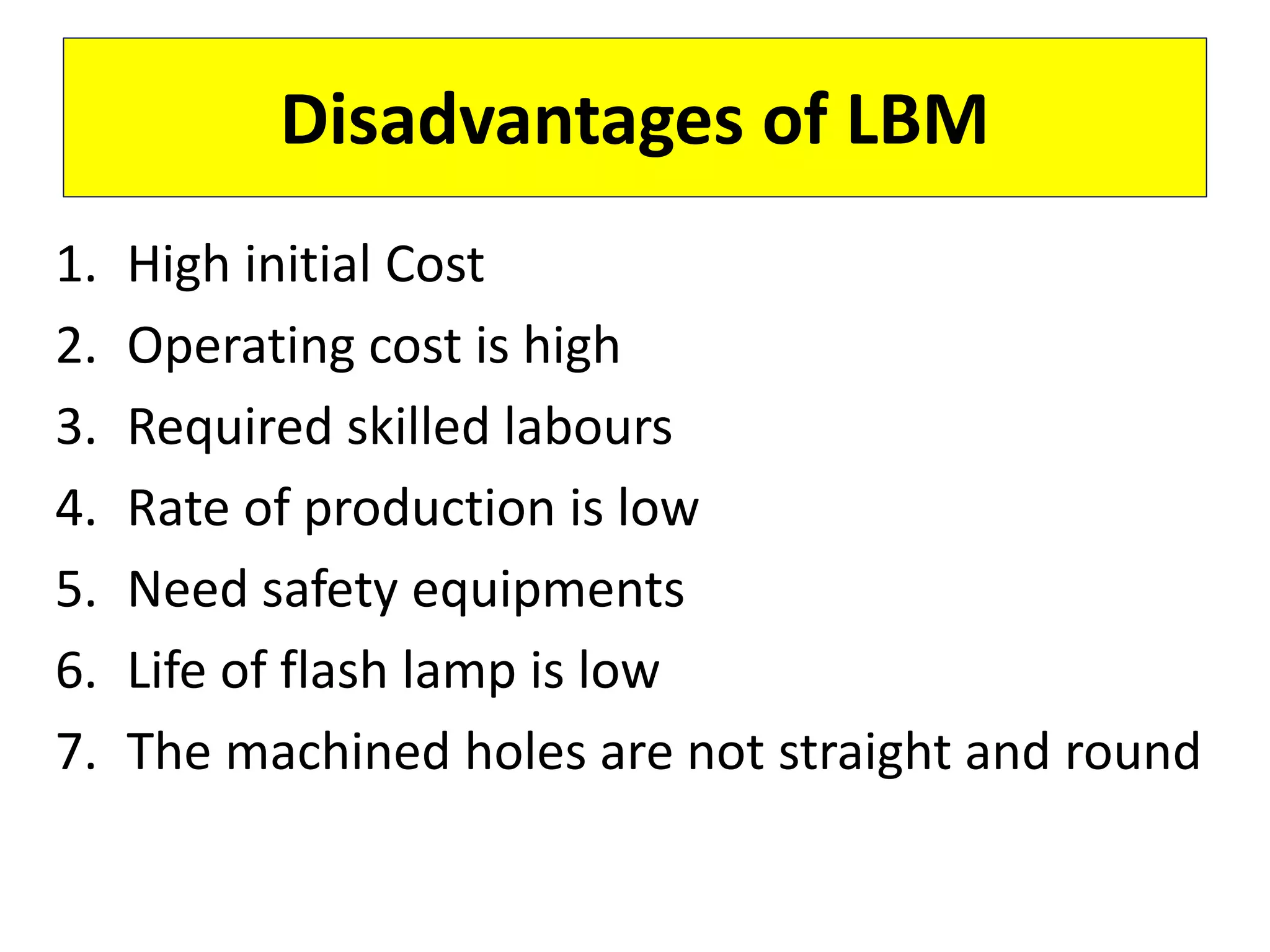
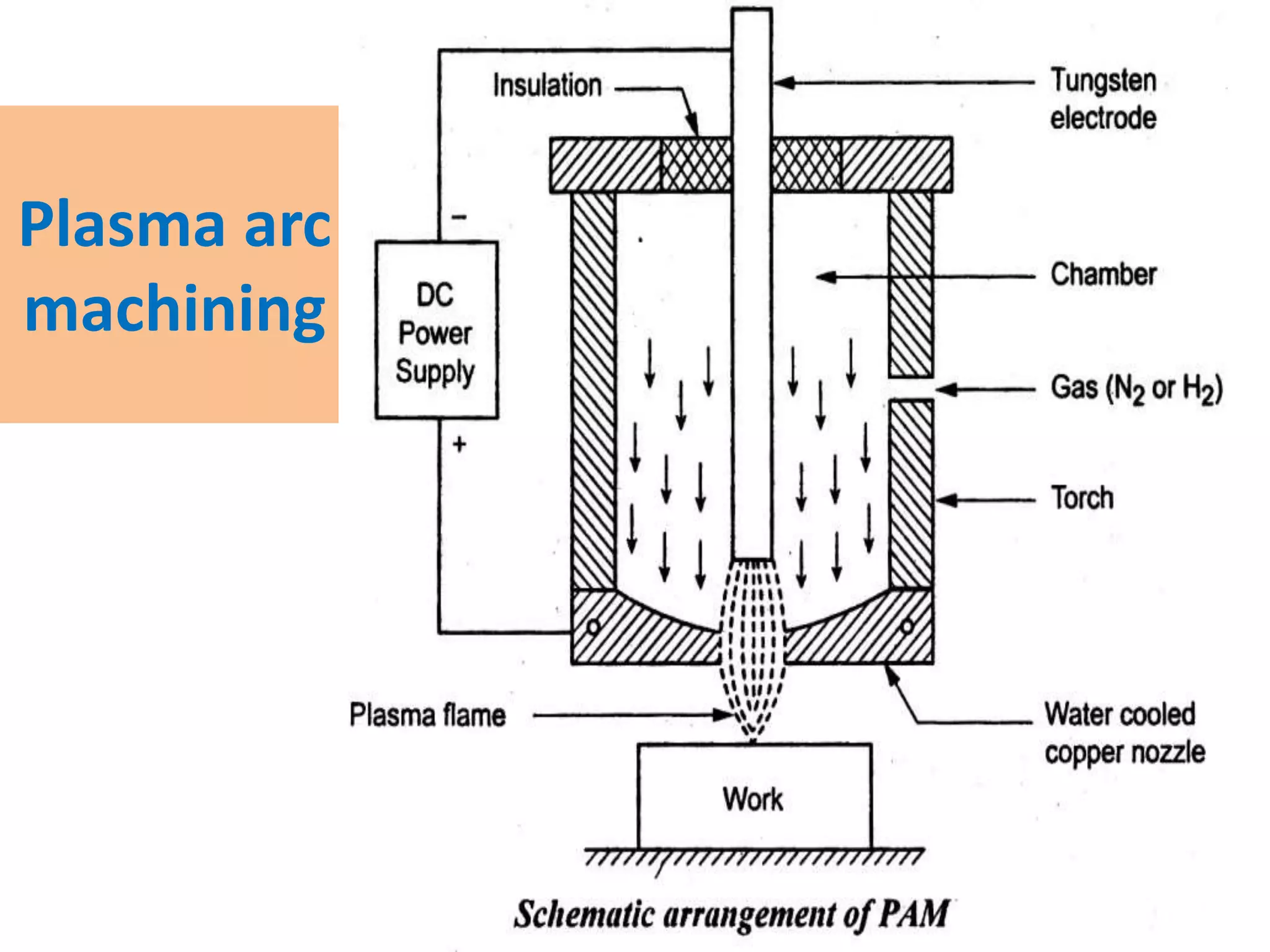
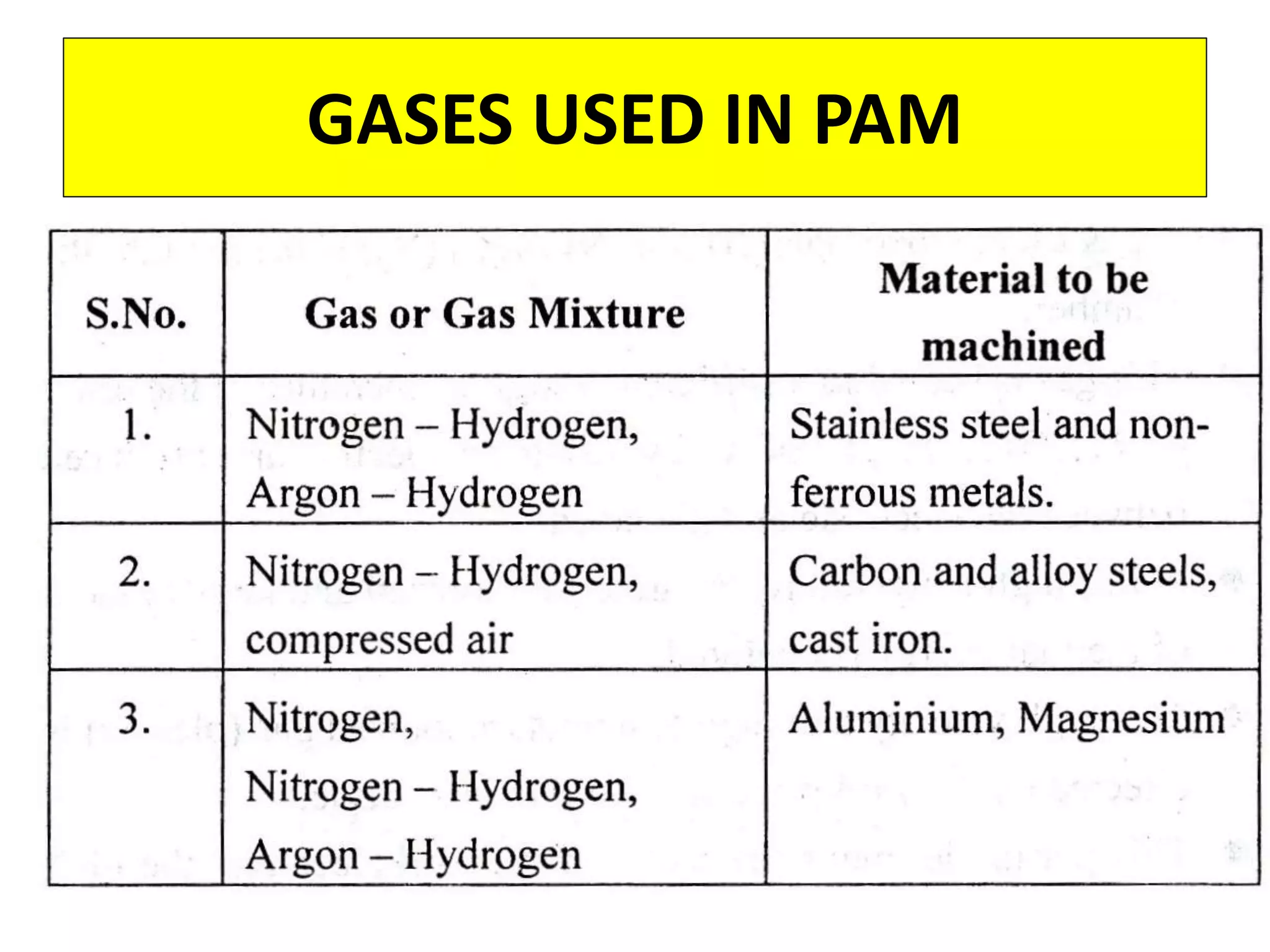
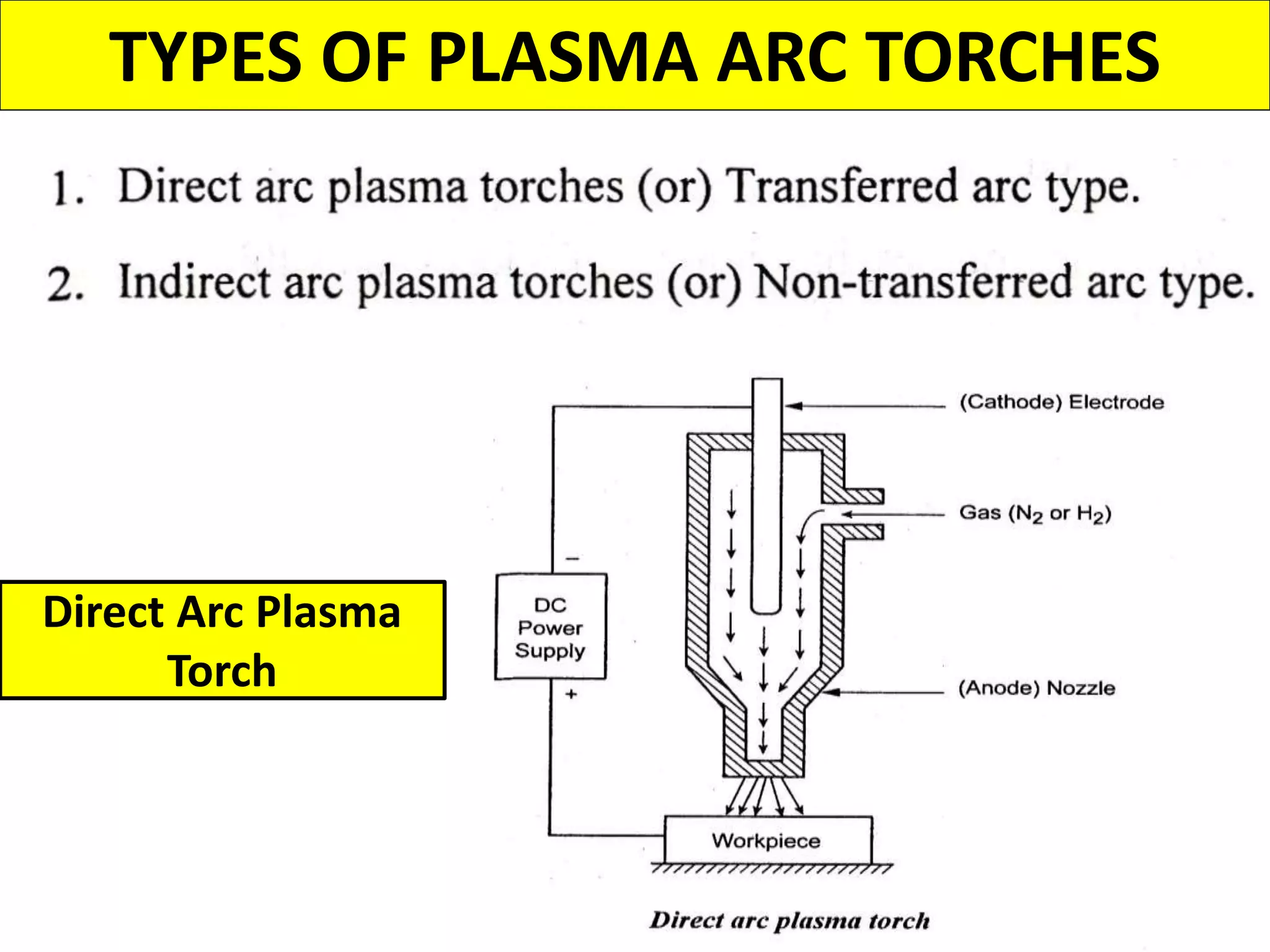
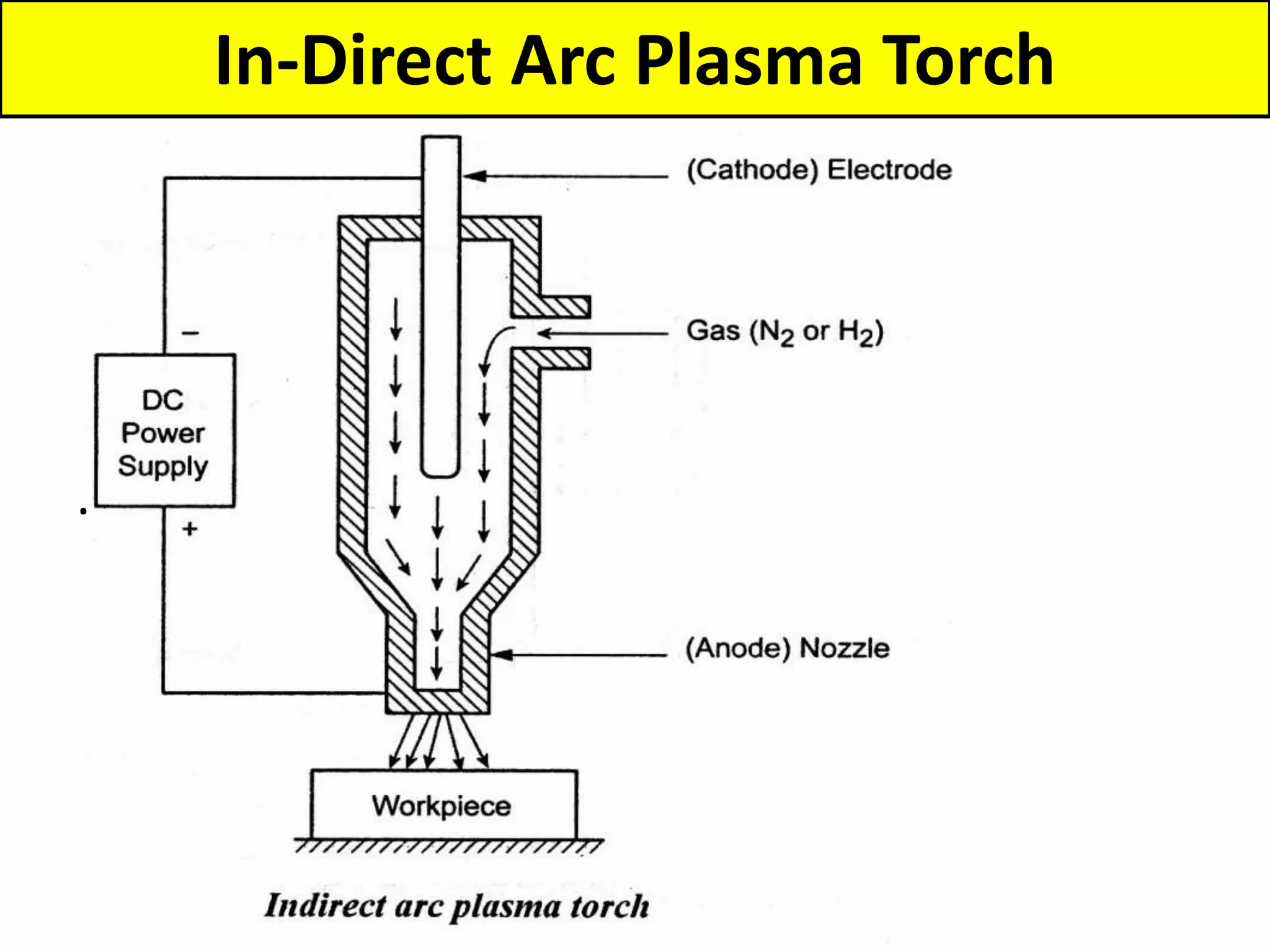
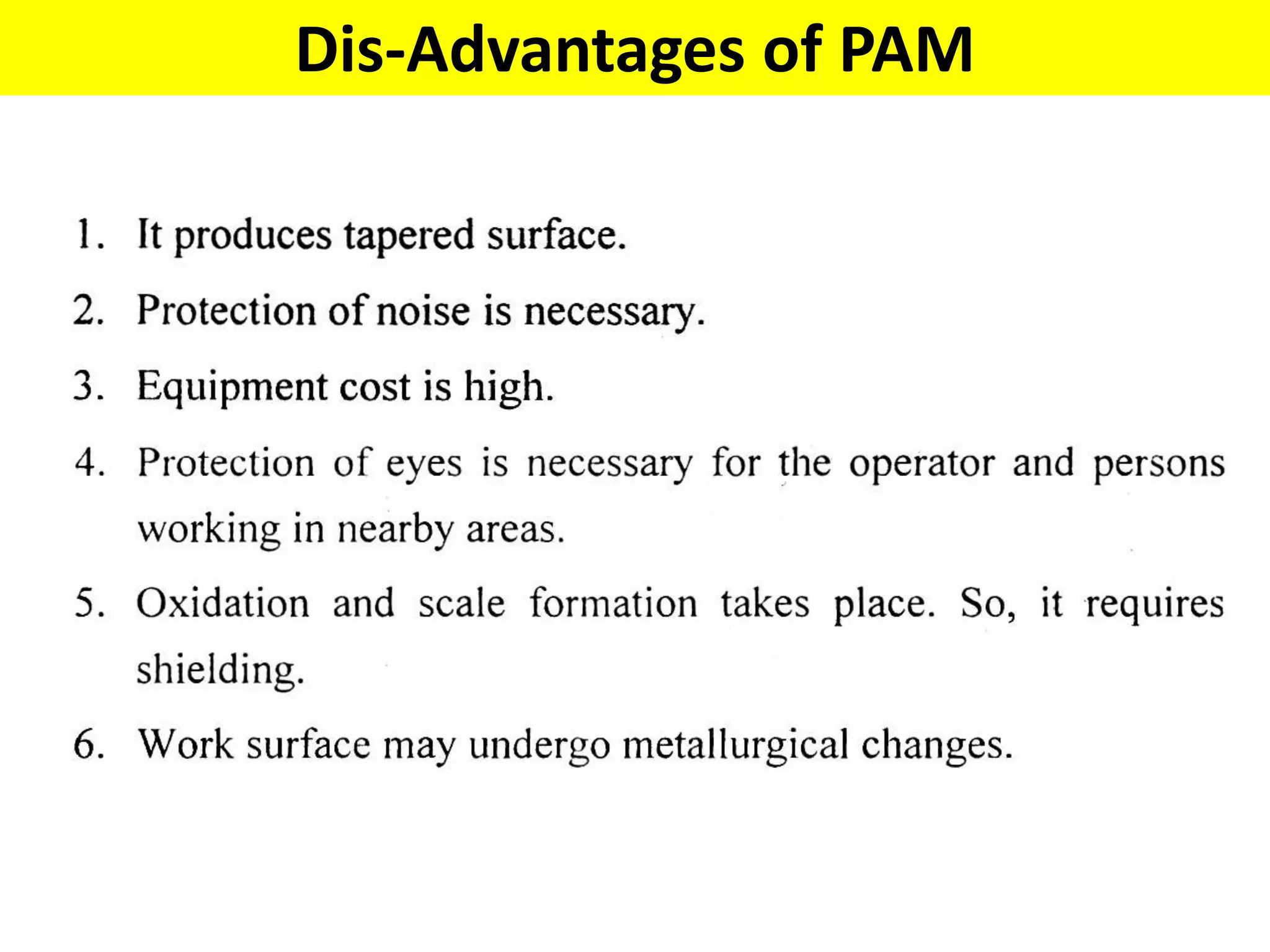
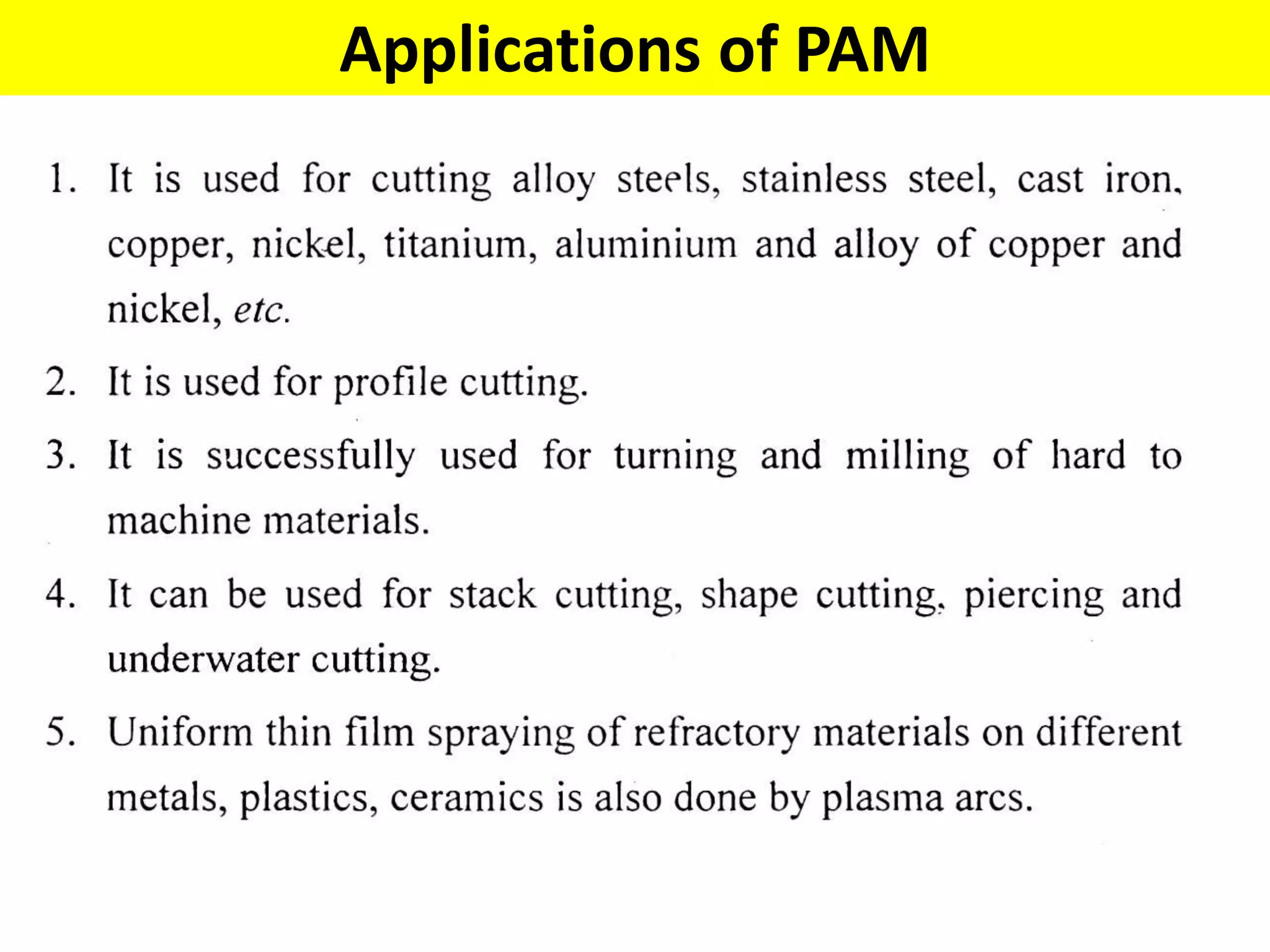
This document discusses various thermal and electrical energy based machining processes. It provides details on electrical discharge machining (EDM) including its principle of using a wire electrode to generate sparks and melt workpiece material. It describes EDM process parameters, circuits, flushing methods, and applications. The document also covers laser beam machining and plasma arc machining, explaining their working principles and key factors like accuracy and gases used. Application areas for different thermal processes are highlighted.