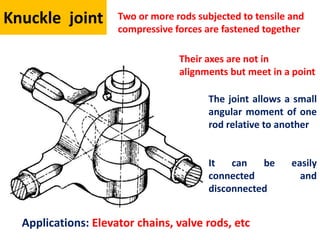
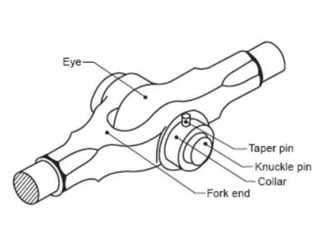
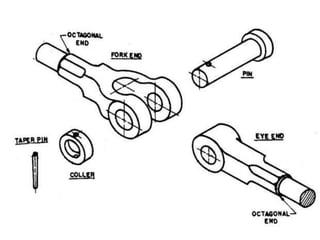
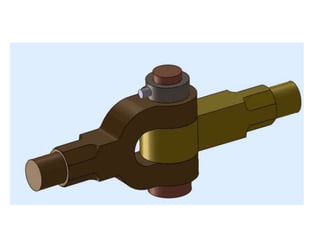
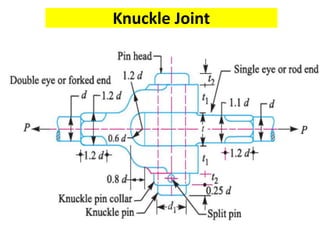
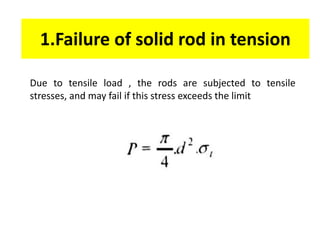
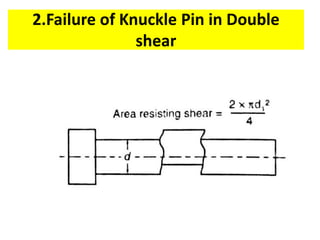
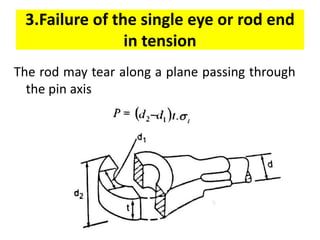
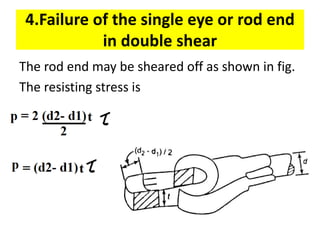
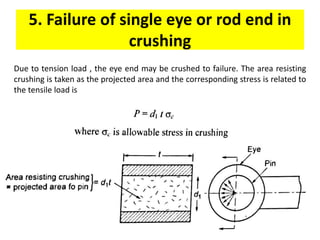
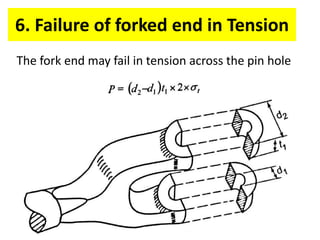
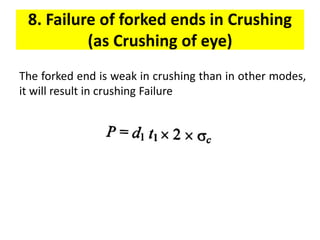
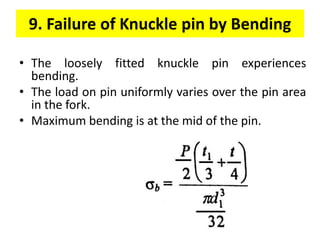
A knuckle joint connects two rods under tensile loads and consists of three main elements: a fork or double eye rod, a single eye rod, and a knuckle pin. It allows for angular movement and is used in applications such as elevator chains and valve rods, but may experience various types of failures such as tension failure in rods, shear failure in pins, and crushing in forked ends. Understanding these potential failures is essential for ensuring structural integrity in applications involving knuckle joints.