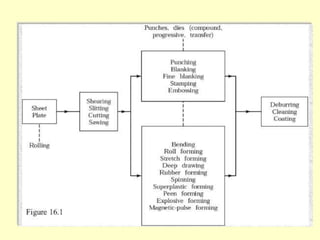
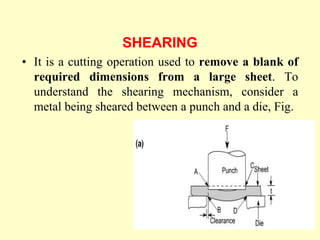
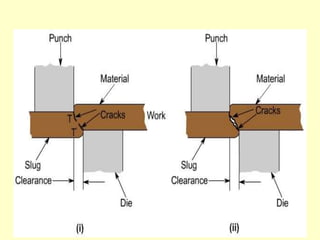
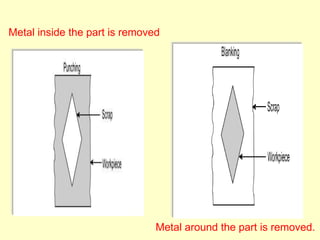
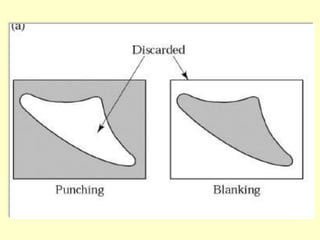
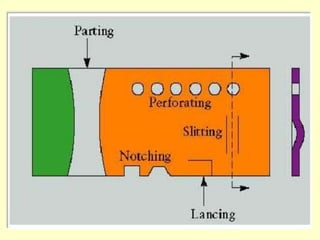
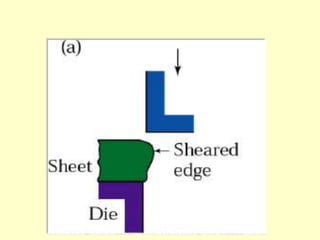
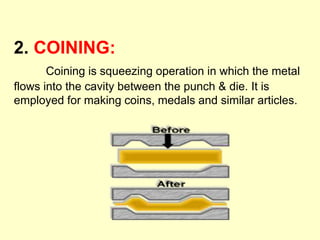
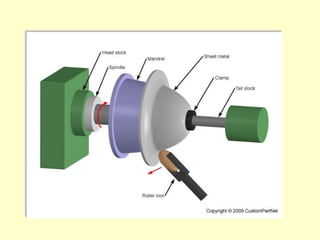
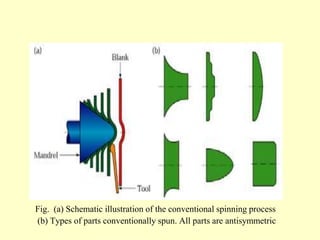
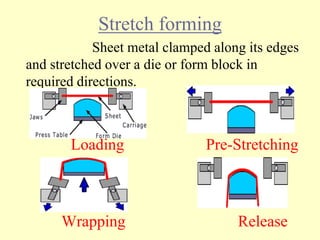
Sheet metal operations involve cutting, forming, and finishing processes to manufacture components from thin metal plates less than 5mm thick. Cutting processes like shearing, punching, and blanking apply forces to separate material, while forming processes like drawing, spinning, bending, and embossing shape the metal without cracking. Common sheet metals include steel, aluminum, and titanium used in automotive and aircraft bodies, appliances, and more. Key forming operations are stretching, spinning, bending, and embossing which deform the metal over dies into desired contours.