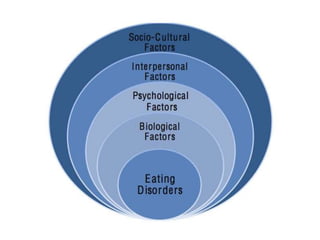
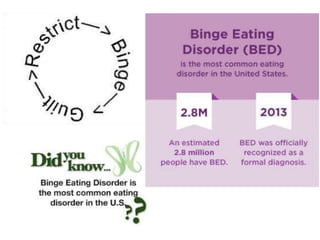
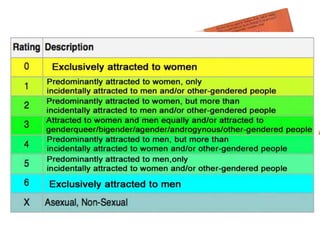
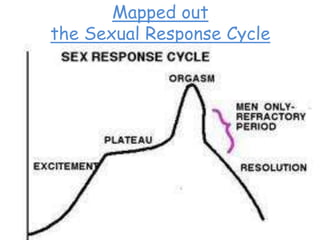
The document discusses various theories of motivation, including drives to satisfy biological needs like hunger and sex, as well as the need to belong. It covers motivations at both the biological and psychological levels, such as instincts, arousal theory, Maslow's hierarchy of needs, and theories of work motivation. Key motivators discussed include basic drives, achievement, and belongingness.

















































![Another Motivation: “To Belong”
What do people need
besides food and sex?
Aristotle: friends
Alfred Adler: community
In Middle English, to be
wretched [wrecche] means
to “be without kin nearby”
Roy Baumeister, Mark
Leary, and Abraham
Maslow:
“To Belong.” Belonging refers to being
connected to others; part of
a group or family or
community.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/motivation-200313164852/85/Motivation-58-320.jpg)


![The Psychology of the
Workplace:
Industrial-
Organizational
[I/O]Psychology
I/O psychology includes three
different areas of focus
Personnel psychology:
hiring and evaluating
Organizational
psychology:
management,
supervision, leadership,
and teamwork
Human factors
psychology:
how workers interface
with machines and the
environment](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/motivation-200313164852/85/Motivation-63-320.jpg)


