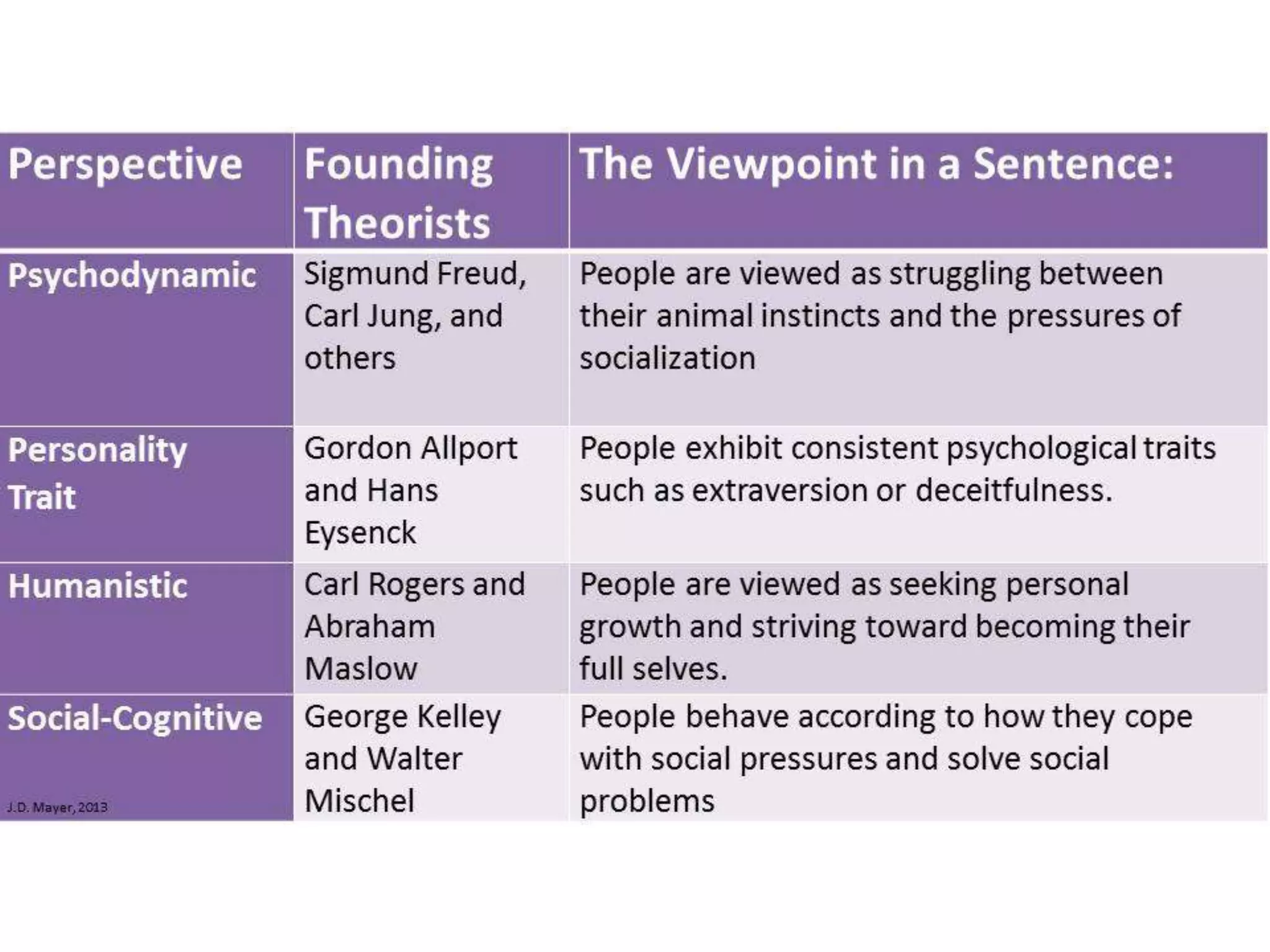
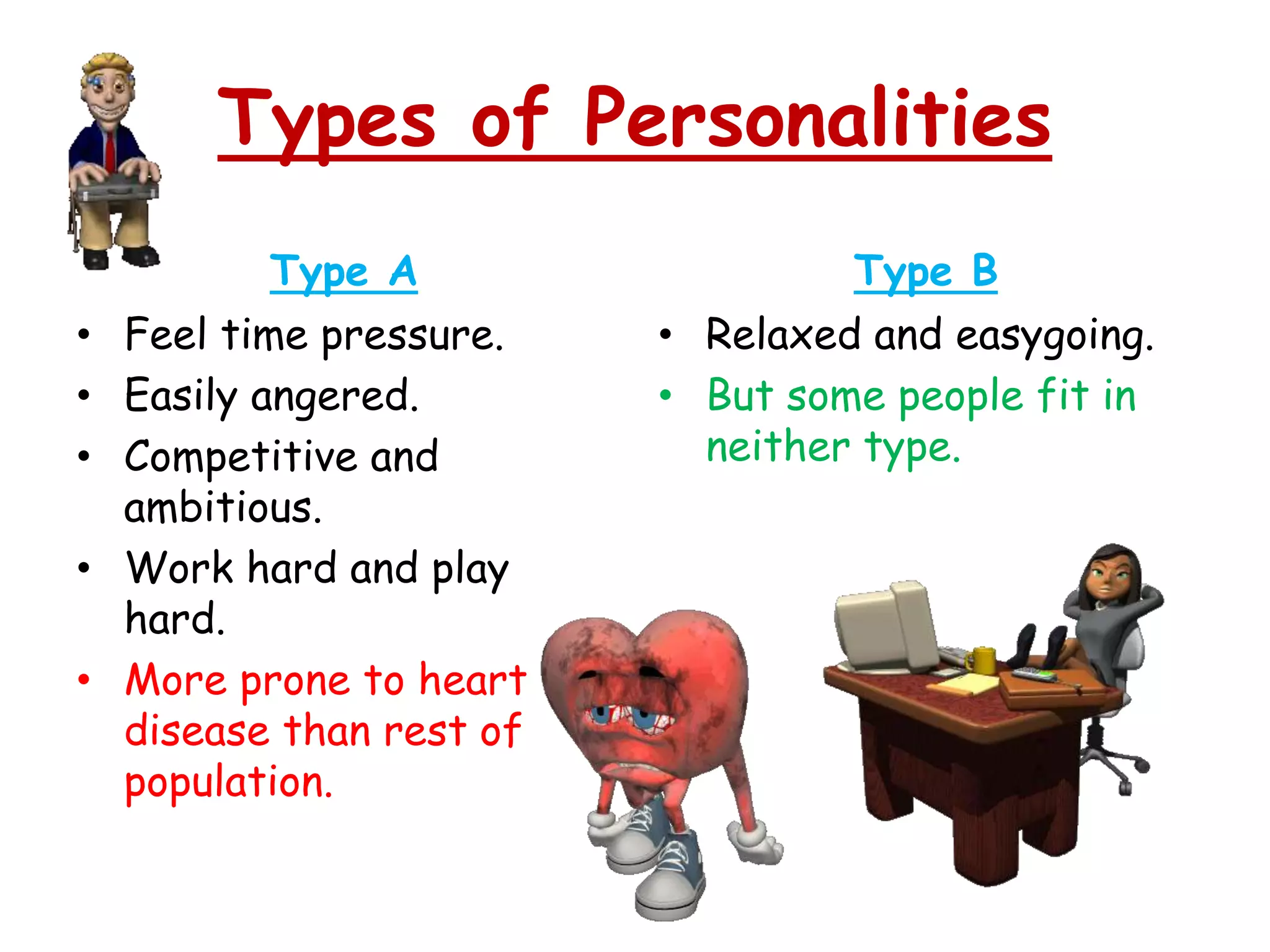
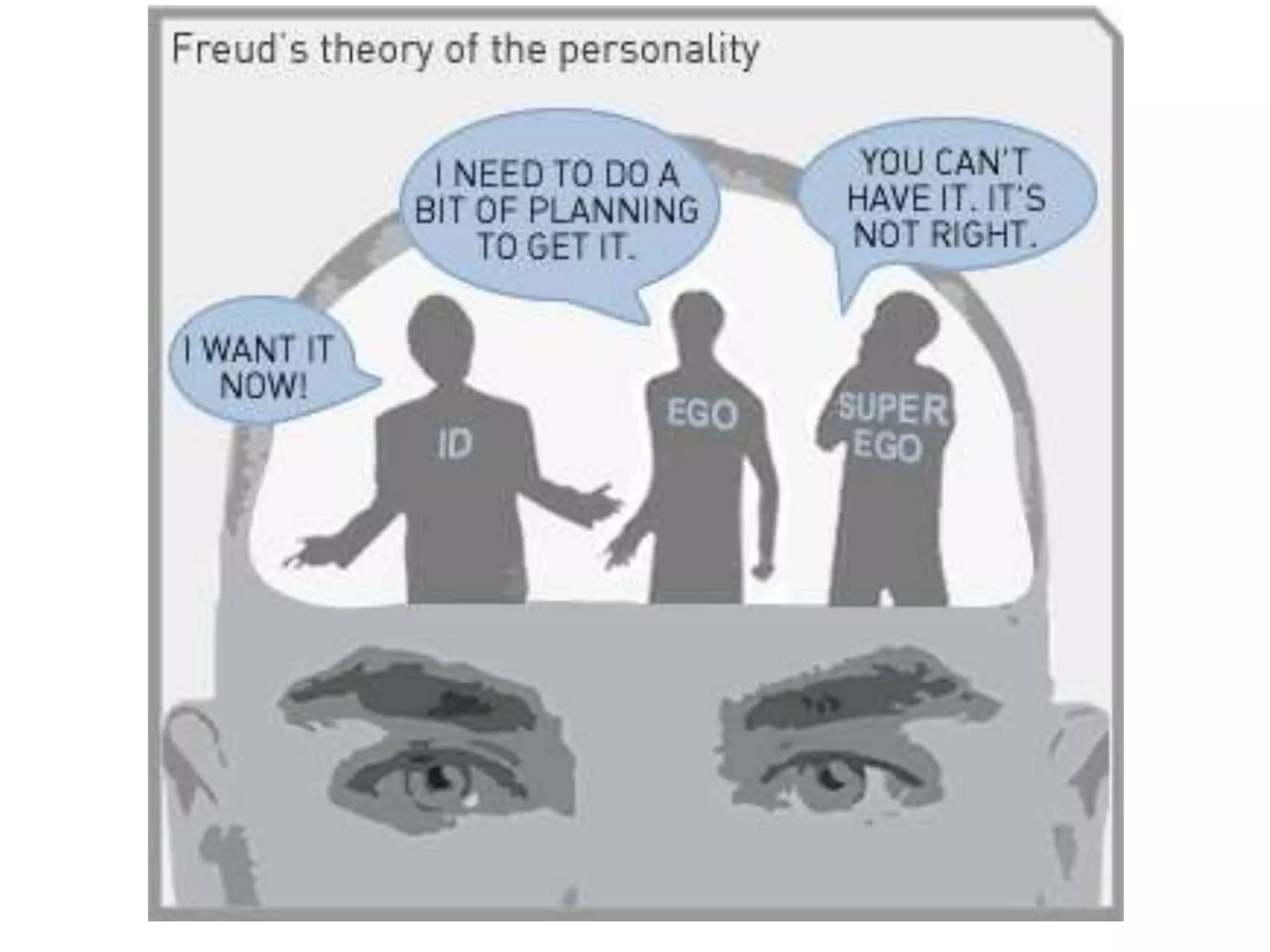
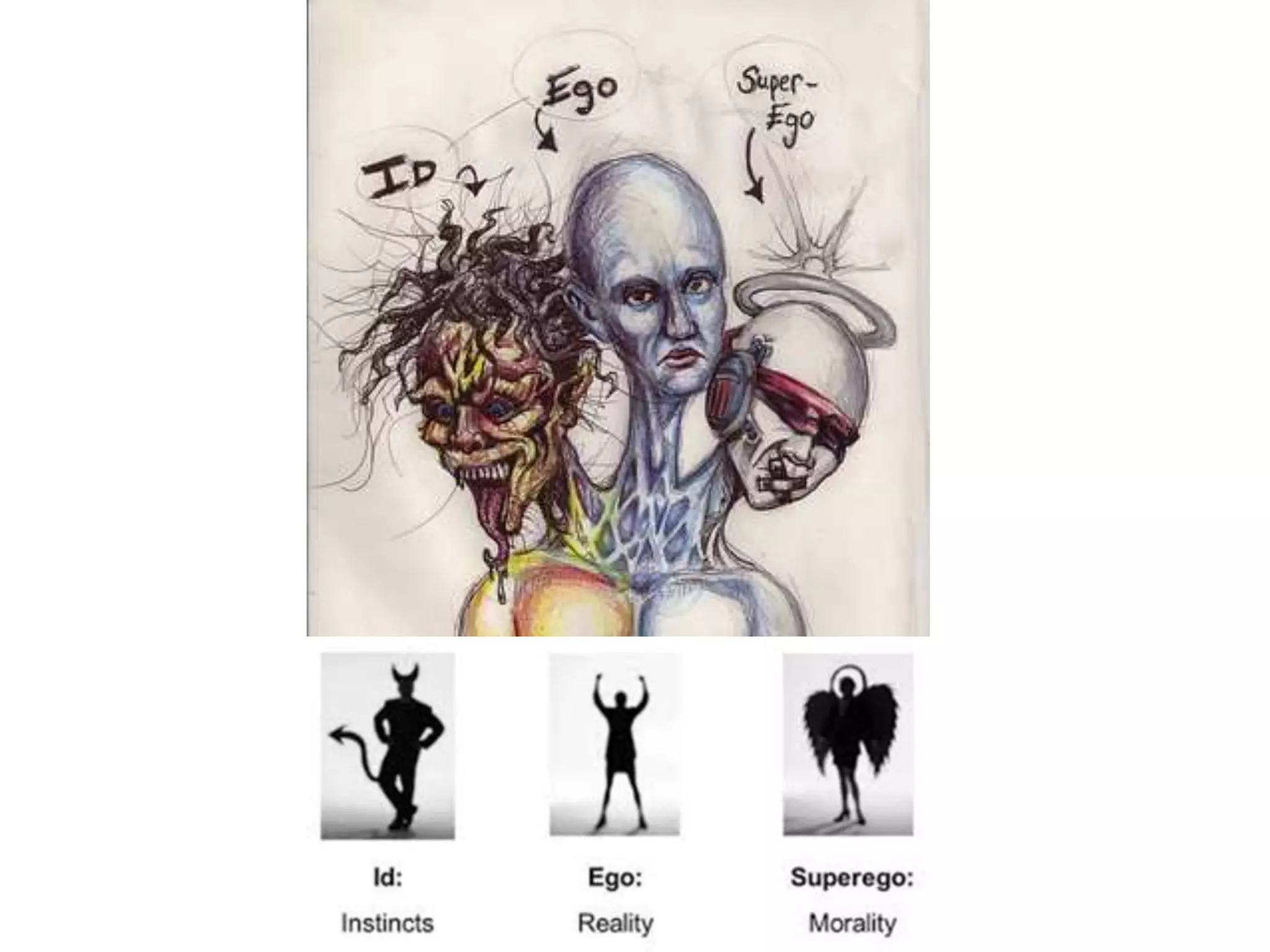
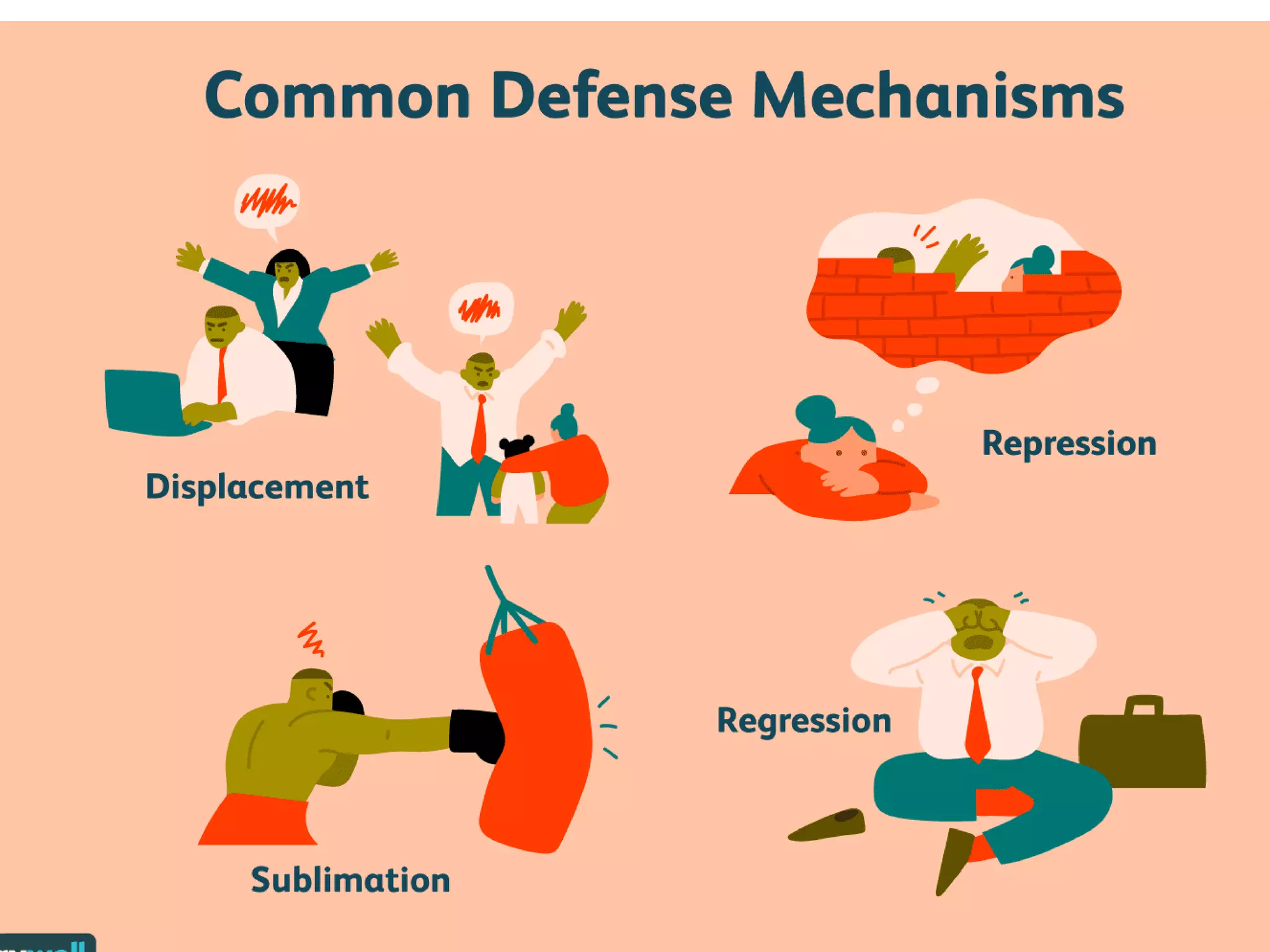
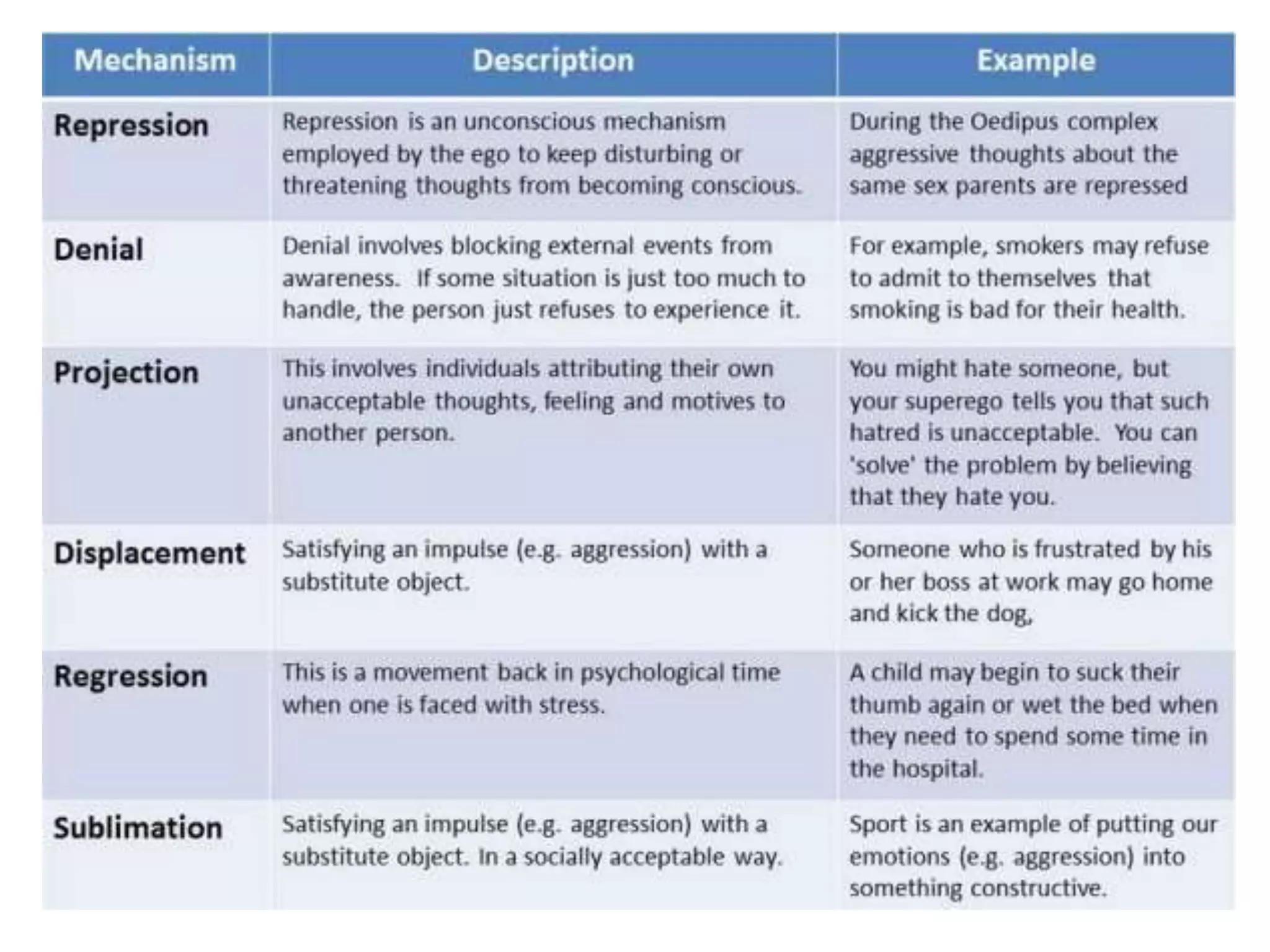
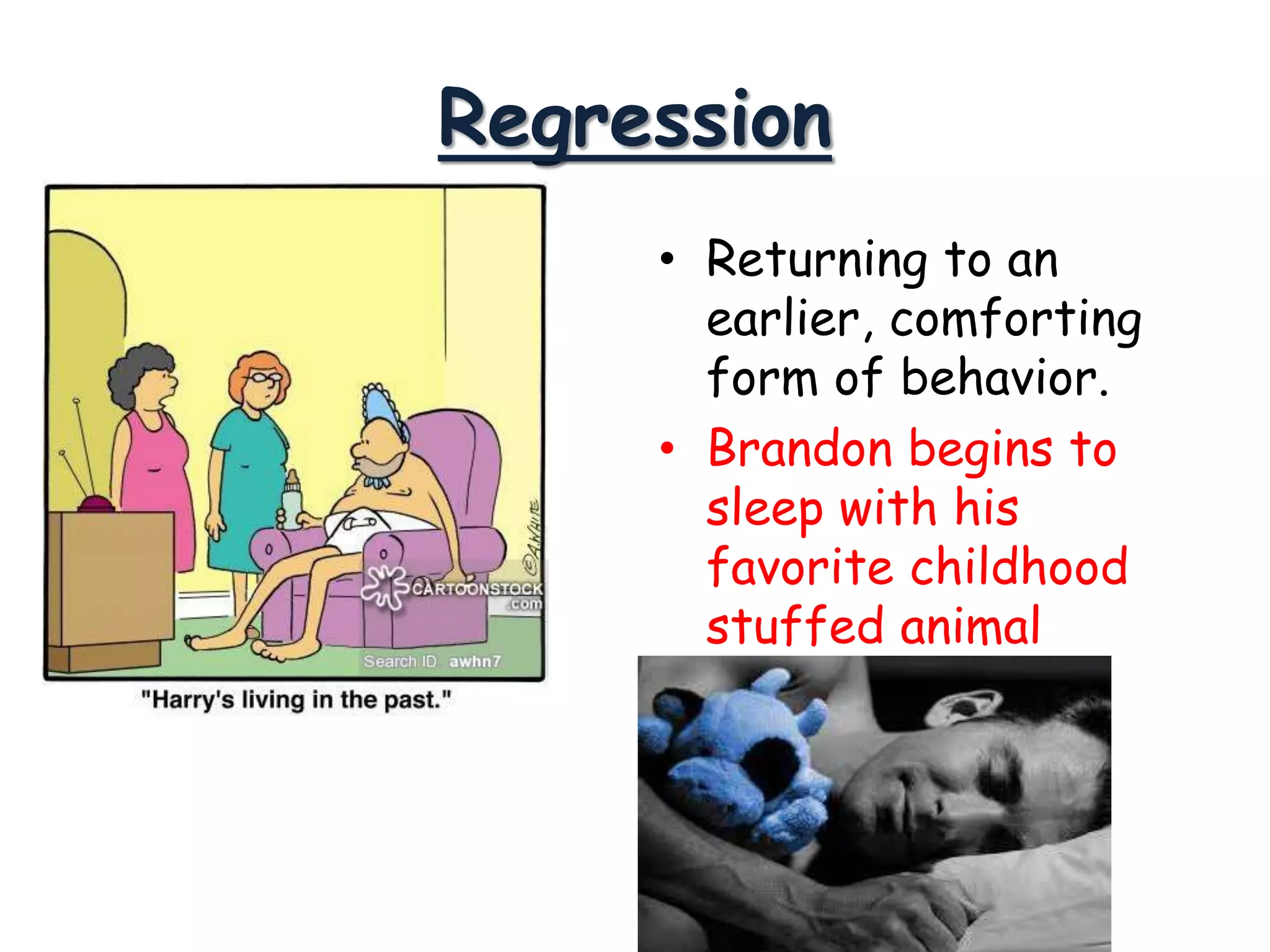
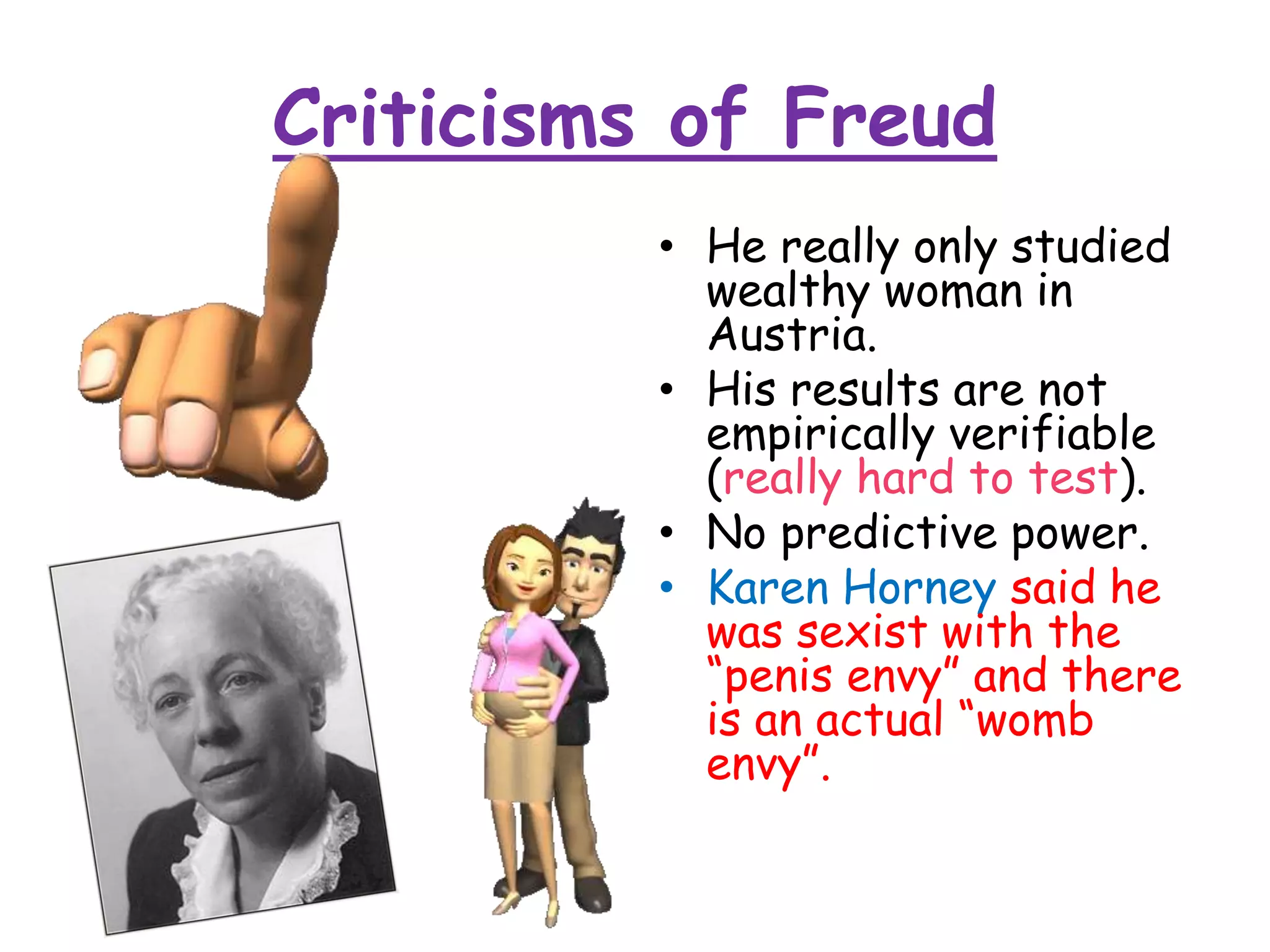
This document discusses theories of personality from several perspectives. It begins by defining personality as characteristic patterns of thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that persist over time and across situations. It then outlines Freud's psychoanalytic theory, including the id, ego, superego, defense mechanisms, and stages of psychosexual development. It also discusses trait theories, behaviorist perspectives, humanistic theories like Carl Rogers' concept of self-actualization, and social-cognitive approaches like Albert Bandura's reciprocal determinism. The document examines various methods of assessing personality, including projective tests, self-report inventories, and the widely used MMPI.


![Personality: An individual’s characteristic
patterns of thoughts, feelings, and behaviors
[persisting over time and across situations]
Sensitive,
Reactive
Naïve
Agreeable, Open
Introverted
Neurotically
irritable
Conscientious
Contentedly
lethargic](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch-200416044926/75/Ch-13-personality-lecture-notes-3-2048.jpg)