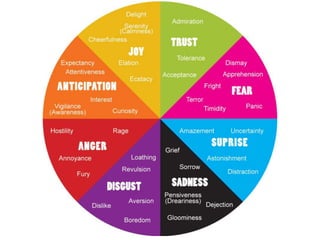
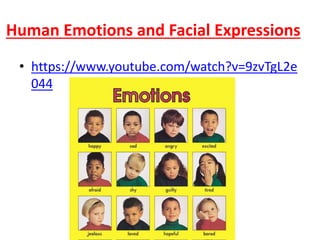
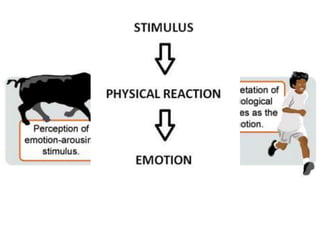
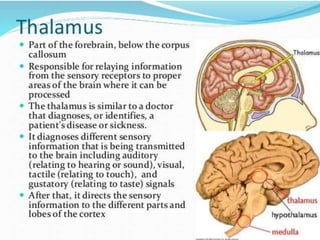
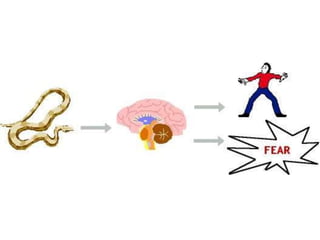
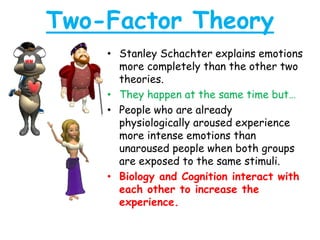
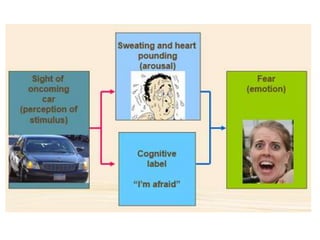
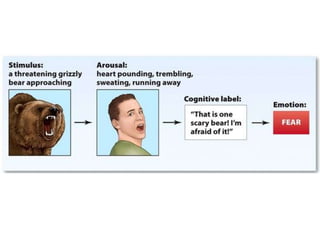
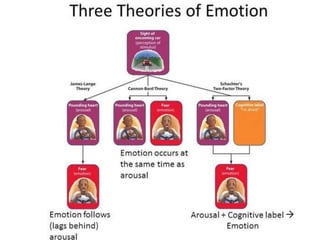
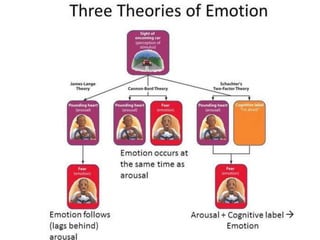
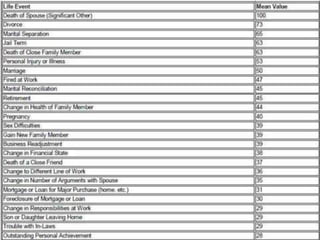
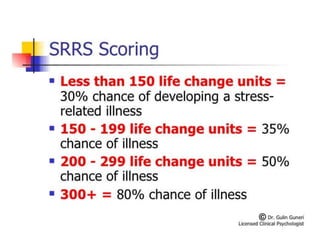
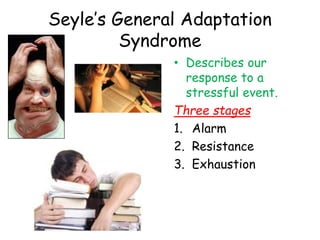
There are several theories on the nature of emotions. The James-Lange theory proposes that physiological arousal precedes emotional experience. The Cannon-Bard theory argues that emotional experience and physiological arousal occur simultaneously. The two-factor theory suggests that both biological and cognitive factors interact to influence the intensity of emotional experience. Basic emotions include happiness, sadness, fear, anger, surprise and disgust.