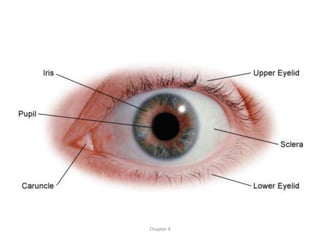
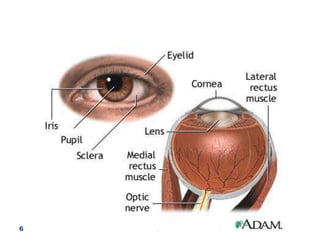
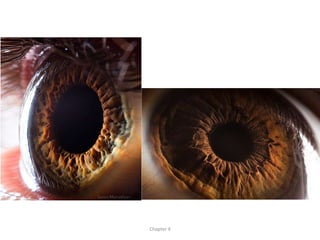
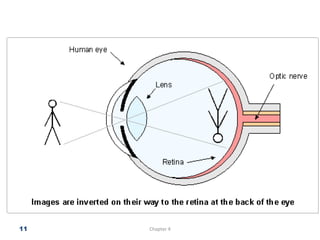
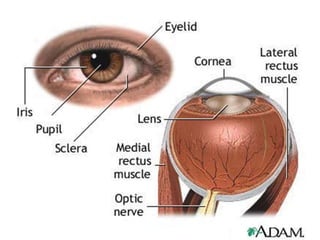
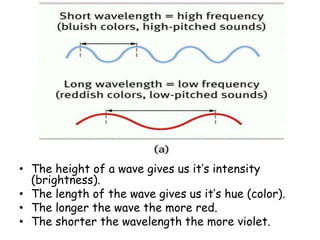
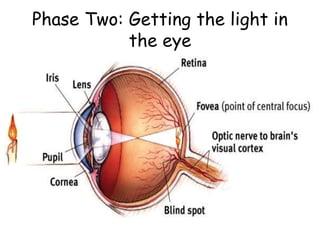
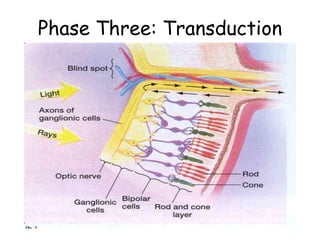
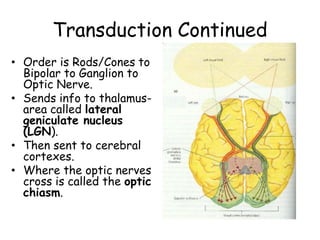
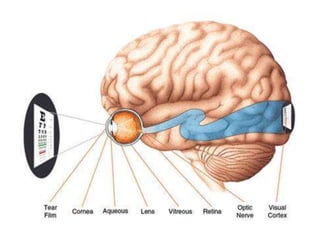
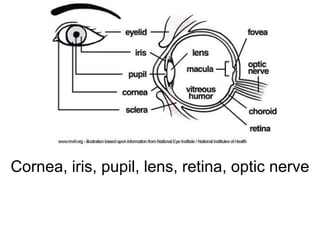
The document discusses the process of vision and how the eye works. It begins with light entering the eye and being projected onto the retina. Photoreceptors in the retina are sensitive to light and transmit visual information via the optic nerve to the brain. The brain processes this input in the visual cortex located in the occipital lobe, where features are detected through parallel processing. The key stages are gathering light entering the eye, transduction of light signals in the retina, and processing of this information in the visual areas of the brain.