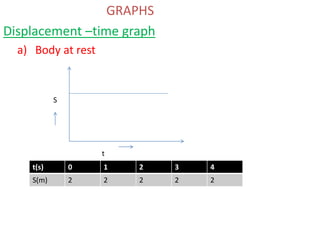
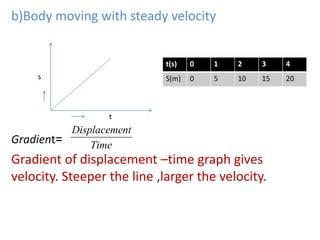
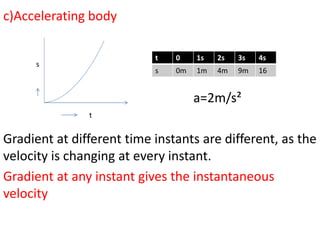
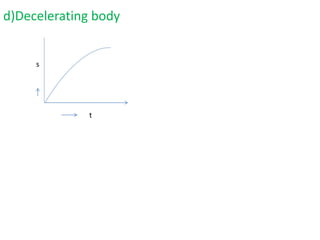
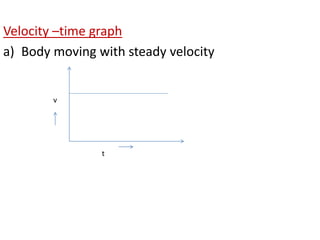
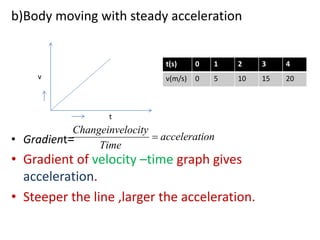
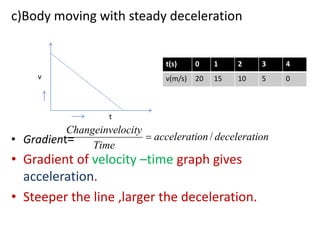
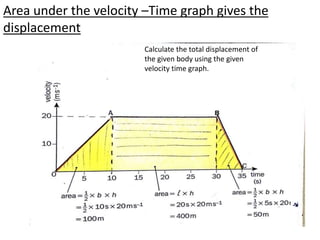
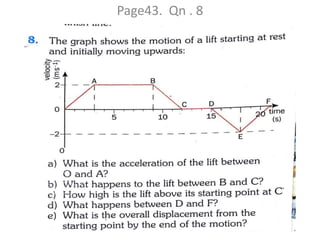
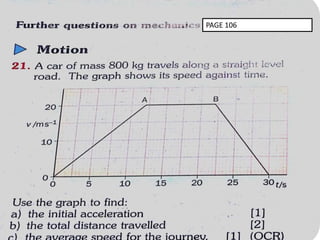
This document discusses speed and velocity. It defines speed as the distance moved per second, which is a scalar quantity measured in m/s. Velocity is defined as the rate of change of displacement, which is a vector quantity also measured in m/s. The document provides examples of calculating speed and velocity from distance and time measurements. It also includes graphs showing displacement and velocity over time to illustrate constant, accelerating, and decelerating motion.