This document provides an overview of projectile motion concepts including:
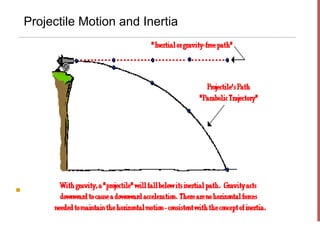
- A projectile is any object upon which the only force acting is gravity and it moves in a parabolic trajectory.
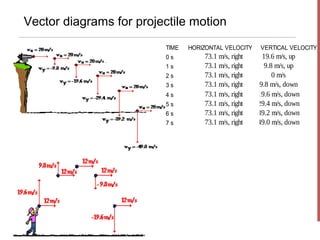
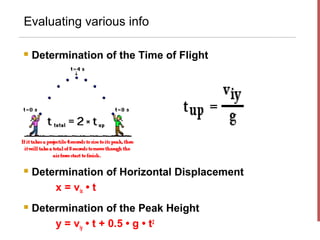
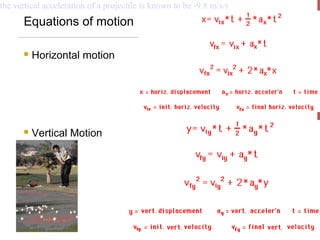
- The horizontal motion of a projectile is independent of its vertical motion, with the horizontal velocity remaining constant and no horizontal acceleration. Vertically, gravity causes acceleration of -9.8 m/s2.
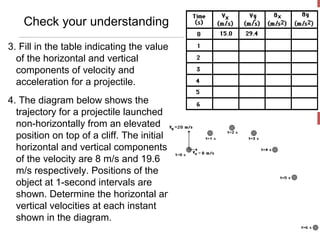
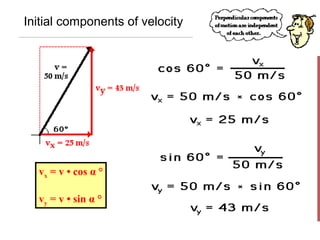
- Key equations presented include those relating the horizontal and vertical displacement and velocity as functions of time, as well as resolving initial velocity into horizontal and vertical components using trigonometry.
- Examples are provided of solving projectile motion problems by identifying knowns and unknowns, selecting appropriate equations, and applying a