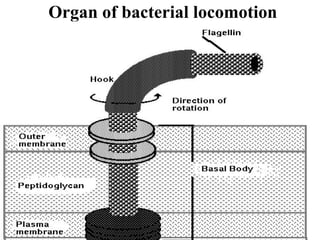
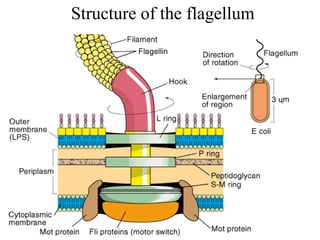
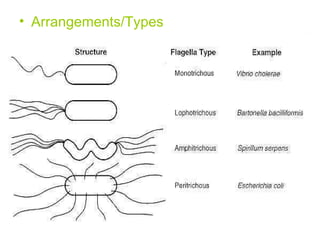
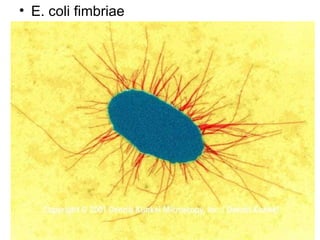
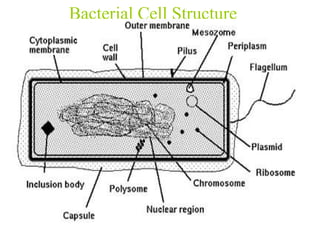
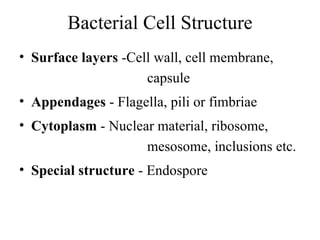
Bacterial cells have several structures that carry out important functions. These include a cell wall and cell membrane that provide shape and protection. Flagella and pili help with locomotion and adhesion. The cytoplasm contains ribosomes for protein synthesis and DNA in the nucleoid region. Some bacteria form spores as resistant structures during unfavorable conditions. Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria have differences in their cell wall and membrane compositions that affect staining and antibiotic susceptibility.


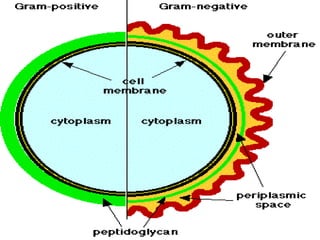
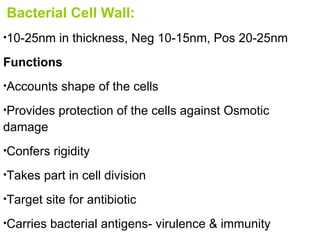
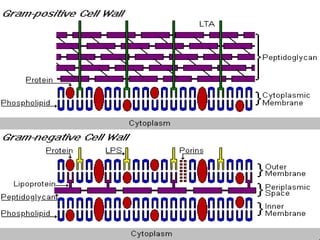
![General structure : Chemically made up of Peptidoglycan. It is made by two hexose sugars N- acetylglucosamine [NAG] and N- acetylmuramic acid [NAM] in alternating chains interconnected by tri, tetra or penta pedtide chains.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/morphologyy-100124000428-phpapp01/85/Morphologyy-7-320.jpg)





![CAPSULE AND SLIME LAYER Amorphous viscid bacterial secretion surrounding the bacteria Loose undemarcated secretion-slime layer Sharply defined structure – capsule Very thin- microcapsules Protects bacteria against phagocytes,adherence promote virulence, reservoir of food, Demonstrated by negative staining and capsule swelling reaction [ Quellung reaction].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/morphologyy-100124000428-phpapp01/85/Morphologyy-16-320.jpg)