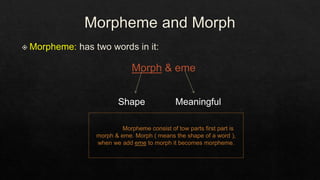
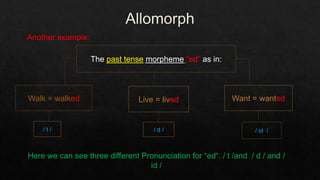
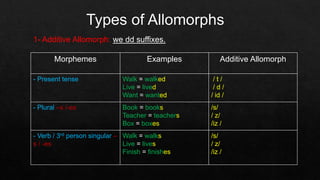
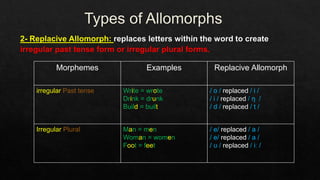
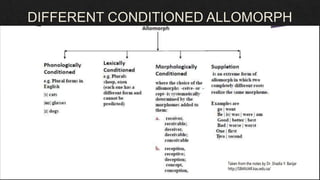
The document discusses morphemes, which are the smallest units of meaning in language. It defines morphemes as consisting of two parts: a morph, which is the shape of a word, and an eme. There are two types of morphemes: free morphemes, which can stand alone, and bound morphemes, which cannot. The document provides examples of different types of morphemes and discusses allomorphs, which are variations in pronunciation or spelling of a single morpheme.