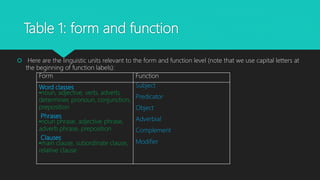
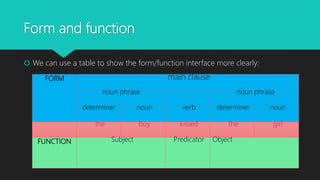
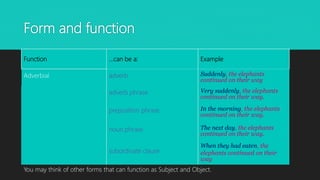
The document discusses the distinction between grammatical form and function, explaining how form relates to linguistic units while function refers to their roles in sentences. It provides examples illustrating how subjects and objects can have different forms yet serve the same grammatical function. The document also includes resources for further reading on the topic.