Morchella
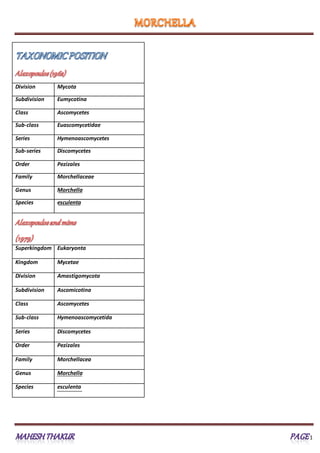
- 1. 1 Division Mycota Subdivision Eumycotina Class Ascomycetes Sub-class Euascomycetidae Series Hymenoascomycetes Sub-series Discomycetes Order Pezizales Family Morchellaceae Genus Morchella Species esculenta Superkingdom Eukaryonta Kingdom Mycetae Division Amastigomycota Subdivision Ascomicotina Class Ascomycetes Sub-class Hymenoascomycetida Series Discomycetes Order Pezizales Family Morchellacea Genus Morchella Species esculenta
- 2. 2 The genusincludesa numbersof species. The importantones are Morchellaconica,M. elata,M. esculenta,M. hybrid, and M. crassipes.All the species grow as saprophytes. There isa suggestionthat some speciesof Morchellaare mycorrhizasbut there is no proofto substantiatethis. In Indiait isknown as Guchhi. - It mostly growsin soil rich organicmatter usuallyinthe dense deciduousforestlitter and fruitsin spring. - It is one of the delicious,ediblefungi whichare tasteful articlesin humandiet. The edible partis the fructification.The fructificationsarecooked with rice and vegetables andeaten all over India. - It is inconspicuousbutextensiveandsubterranean. It grows a few inchesdeep inthe soil andthus hidden from view. The myceliumconsistsof a massof looselyinterwovenbranched hyphae.The hyphaeramifythroughthe interstices ofthe soil nourishing themon the organicmaterial.Each segments or cell containsseveral nuclei.Under adverse circumstancesthe mycelia producesclerotia. - It beginsas a dense knot ofhyphae. Underfavourableconditionsoffoodand moisturethe myceliumhyphaegrow rapidlyand branchrepeatedly. They get interwovento formdense compact masses. These massesof hyphae are calledthe hyphal knots.They are formedjust beneath the surface of the soil.Each hyphal knotin the presence ofabundantfoodand moisturedevelopsinto an aerial stalked fructification calledanAscocarp. - The fructificationor the Ascocarpis a spore producingstructure. The mature ascocarp consistsofa stalk like portionthe stipe surmountedby a hollowconical cap likeobject the pileus. It is thick,Fleshy andhollowwitha waxy surface. The colourvaries from a dirty greyishwhite to a dark brown dependingonthe species andthe age. The terminal conical cap or the pileusconstitutesthe fertile portionofthe ascocarp. The ridgesunite the fertile areas whichform an irregularlydistributedhymeniumor thecium. A thinsection (figureMorchellaSp. Section throughdepressionof the pileusshowingparaphysesandasci) throughthe depressionreveals that it islined by a fertilelayer called the hymenium or thecium. Intermingledwiththe asci are elongated sterile slenderhyphae calledthe paraphyses? Beneath the hymeniumis the sub-hymeniumorhypothecium. A cross-sectionthroughthe stipe reveals that it is made upof pseudoparenchymatoustissue.Thistissuein the regionof the depressionof the pileusforms the hypothecium. - The tipsof mature asci abovethe level of the hymeniumand turn towardslightbeing positively phototrophic.The residual cytoplasmwithineach ascuschangesinto sugarsof highosmoticvalue. The latter absorb water. As a result considerableamountof pressure is set up in the asci.The pressure set up withinthe asci aidedby the turgor pressure set up in the paraphysescauses the release of ascosporesthrougha preformed apical pore whichopens by a lidhingedat the top ofthe ascus.The internal force projects the ascosporeshighup into the air where they are caughtup by the aircurrents. The explosionsofthe asci are successiveand not simultaneous.The pileusgraduallyshrinks as it dries up.Eventuallyit withers. The ascosporesare large colourlessoval andmultinucleate when mature. - It is reported that the catabolicactivitiesin the ripe fruitingbodyare highduringthe periodof dehiscence. Thisis indicatedby the marked rise in the temperature ofthe tissue.Conventional currentsare set upin the surroundingair.These are inducedby the warm tissue of the ripe fructification.Theseconventional currents ofair are suggestedto playan importantrole inthe dispersal ofthe liberate ascospores.They are carried by windto distant places.
- 3. 3 - Onfallingona suitablesoil each ascosporegerminates to produce a new myceliumsoonafter release. The ascosporesthat happento fall on unsuitablesoil perish.Ascosporesdo notremain viableafter one year near the soil surface. Accordingto the latter the ascosporesgerminate anddevelop extensivemyceliumat 15◦c under highly nutritiousnon-competitiveconditions. - The sex organs whichconstitutethe accessoryparts of sexual process are completely suppressedin Morchella.Consequentlythe sexual process isextremely simplified.Itinvolvestwodistinctprocesses: - Itconsistsinthe unionofcytoplasmic contentsof two cells withoutnuclear fusionwhichisdelayed. This resultsin a sequence of binucleatecell generationsconstitutingthedikaryophase. - The two nuclei in the ascus mother cell fuse.The fusioncell with a diploidnucleusiscalledthe young ascus.It represents the transitory diplophasesinthelife cycle. the youngascuscell elongates.The synkaryon in the ascusundergoes two successivedivisions.These constitutemeiosis. (Graphicrepresentationof the lifecycleof morchella) SalientFeature- 1Morchellaisa saprobicdiscomycete. 2 The so calledmorels(guchhi)are the aerial fructificationsorascocarpsof the fungus. 3 The pileushasa pittedsurface. 4 Asexual reproductionsbysporesare lacking. 5 Nohookformationtakesplace.