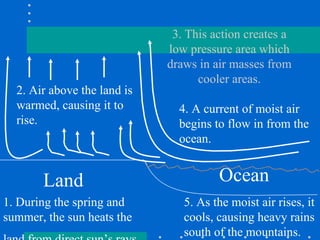
The document discusses the monsoon seasons of South and Southeast Asia. It describes how seasonal winds and temperature differences between land and ocean create distinct wet and dry seasons. During the summer, warm, moist winds blow inland from the ocean, bringing heavy rains. In the winter, cool, dry winds blow from the interior out toward the ocean, creating drought-like conditions. The monsoon patterns greatly impact the regions' climates, agriculture, and populations.