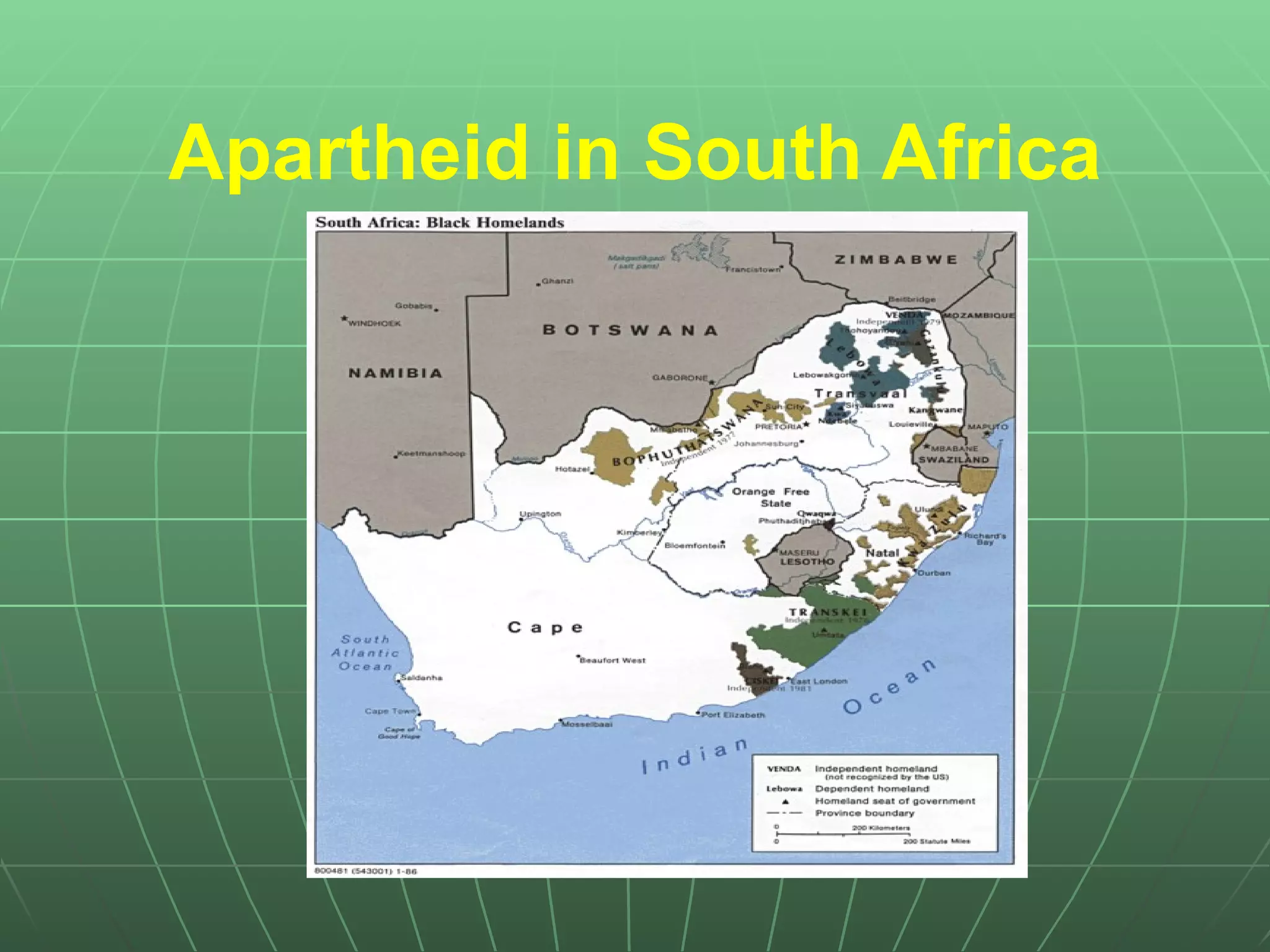
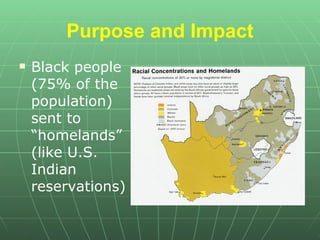
Apartheid was a system of racial segregation and discrimination in South Africa between 1948 and 1994. It kept political and economic power in the hands of the white minority population, who made up around 15-20% of the total population. The black African majority, who made up around 75% of the population, were forcibly removed from their homes and sent to live in segregated townships with inferior services and no political rights. Apartheid faced increasing resistance through the 1980s from violence, protests, and international pressure, and it was formally ended in 1990 when President F.W. de Klerk dismantled the system. Nelson Mandela had protested apartheid and spent 27 years in prison before becoming South Africa's first black president from