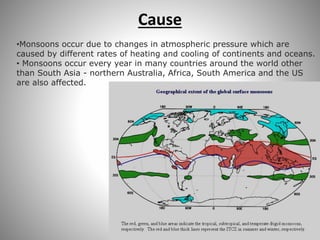
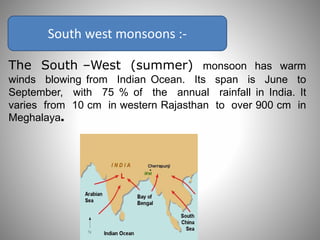
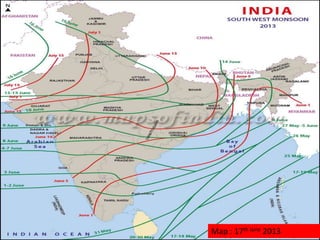
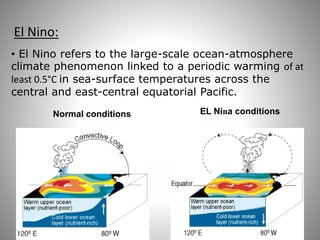
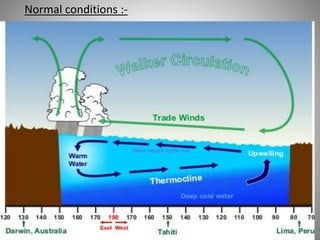
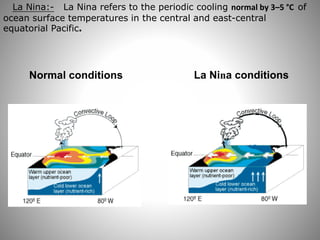
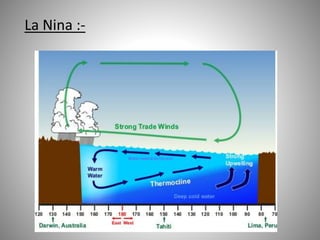
This document discusses monsoons and their causes. It defines monsoons as seasonal reversals of wind direction caused by temperature differences between land and sea. Monsoons occur due to changes in atmospheric pressure from different heating and cooling rates of continents and oceans. India's climate is dominated by monsoons, which bring most of the country's annual rainfall from June to September. There are two main types of monsoons in India: southwest monsoons which blow from the Indian Ocean, and northeast monsoons which blow from Siberia. The document also explains El Nino and La Nina phenomena and their effects on global weather patterns.