This document discusses monetary theory and the relationship between money supply and economic activity. It covers key topics such as:
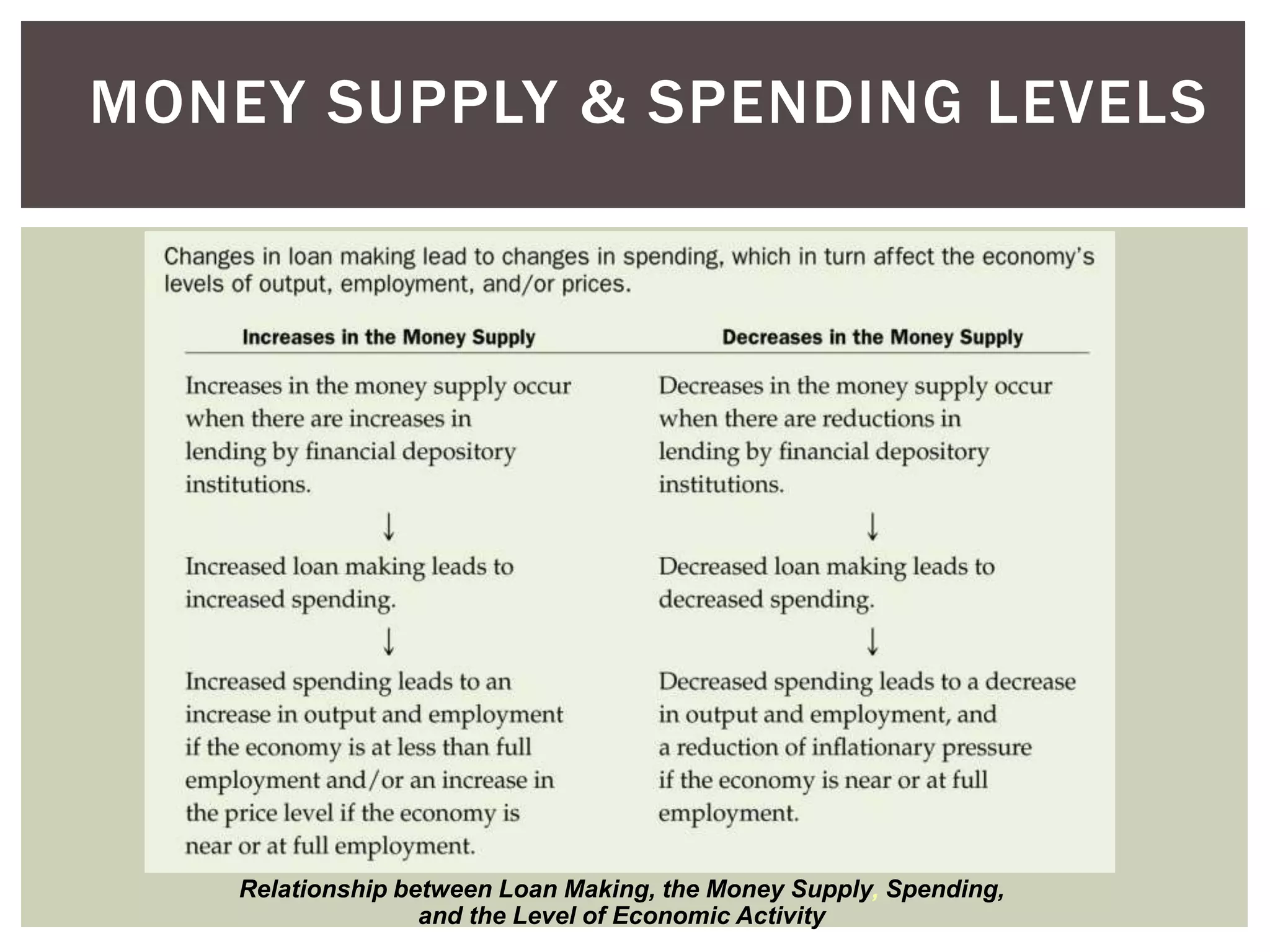
1) How changes in money supply can affect total output and price levels in the economy. An increase in money supply when the economy is not at full employment will lead to increases in output more than prices, while at full employment it will lead to price increases more than output.
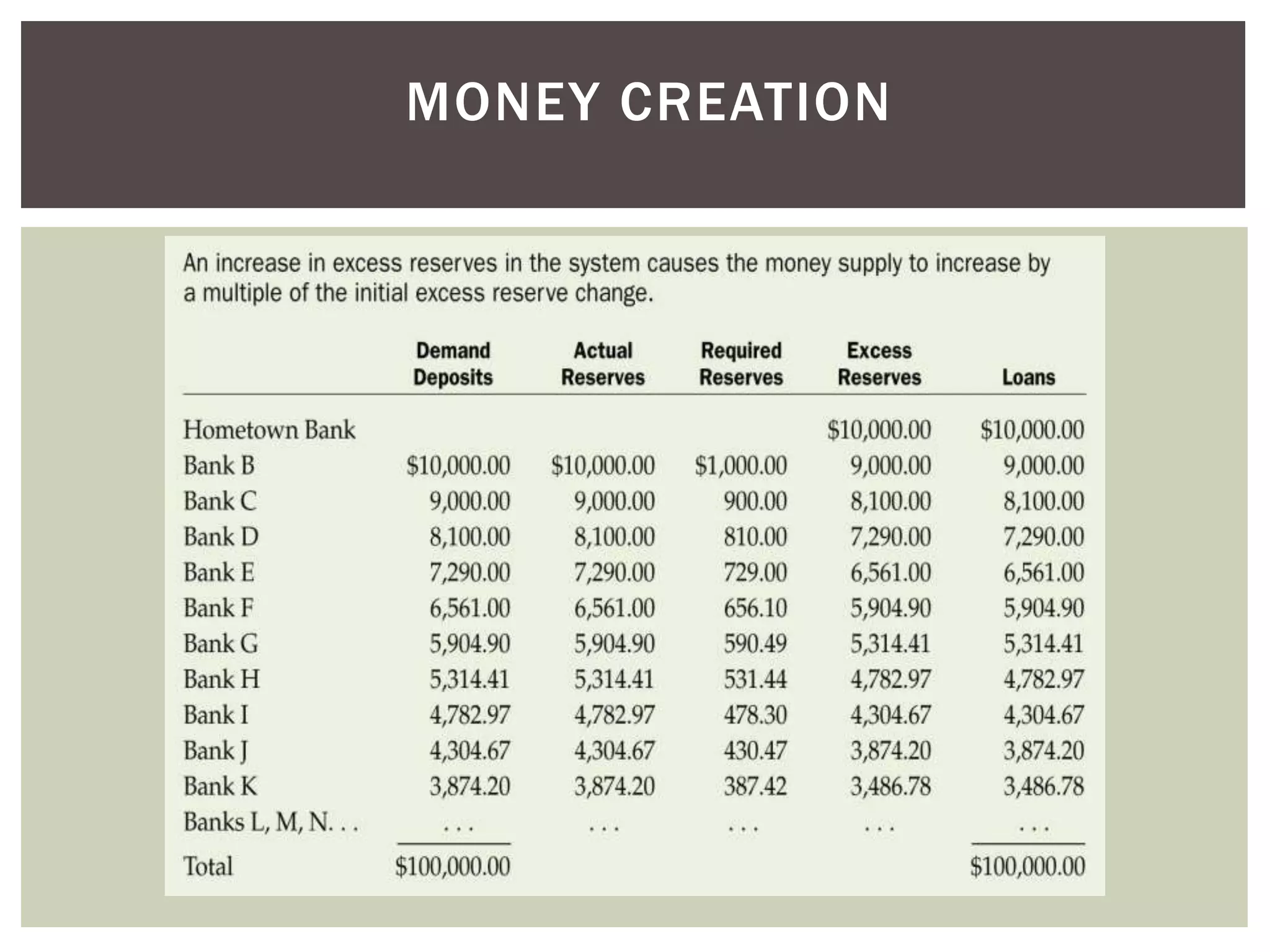
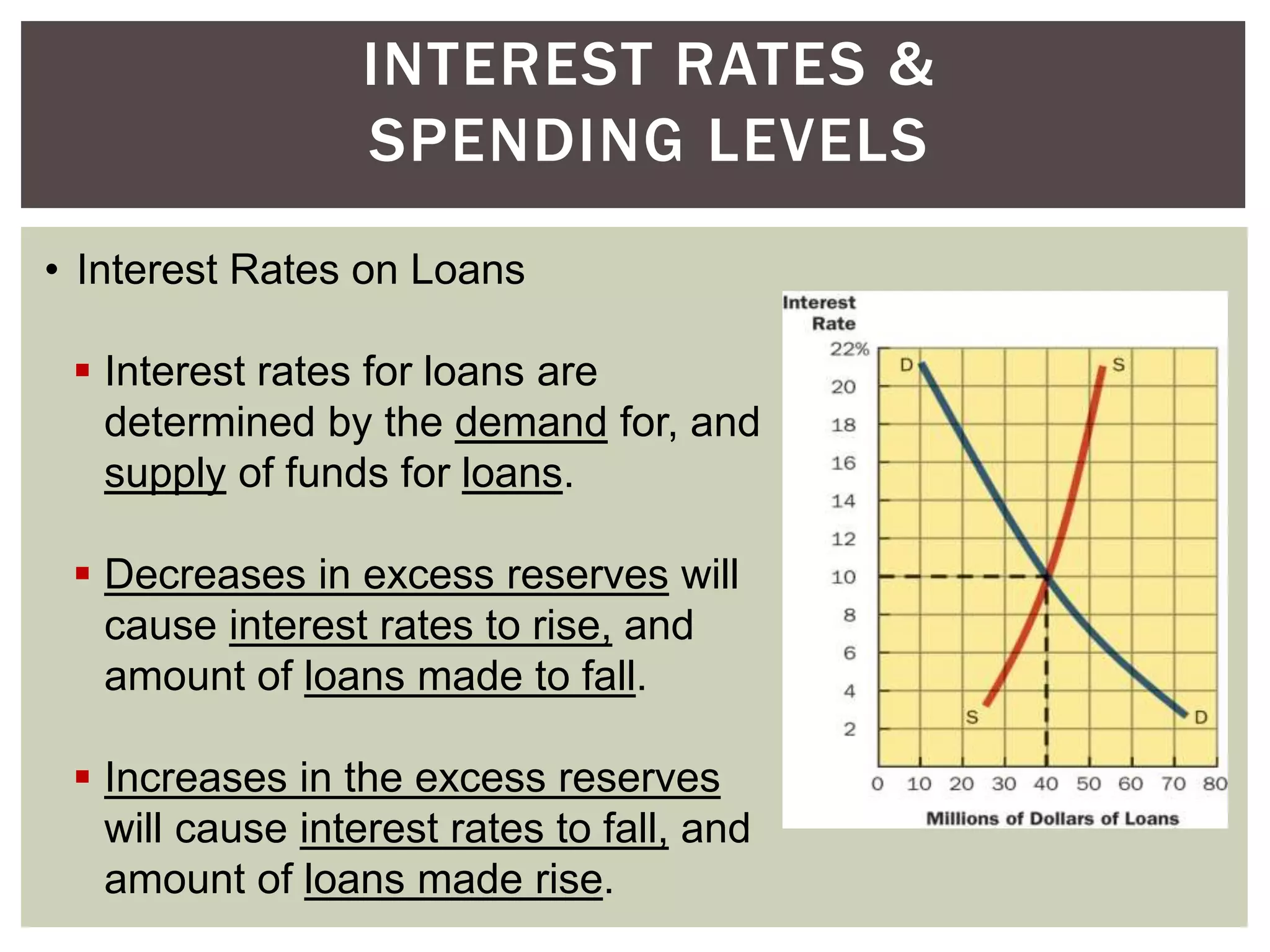
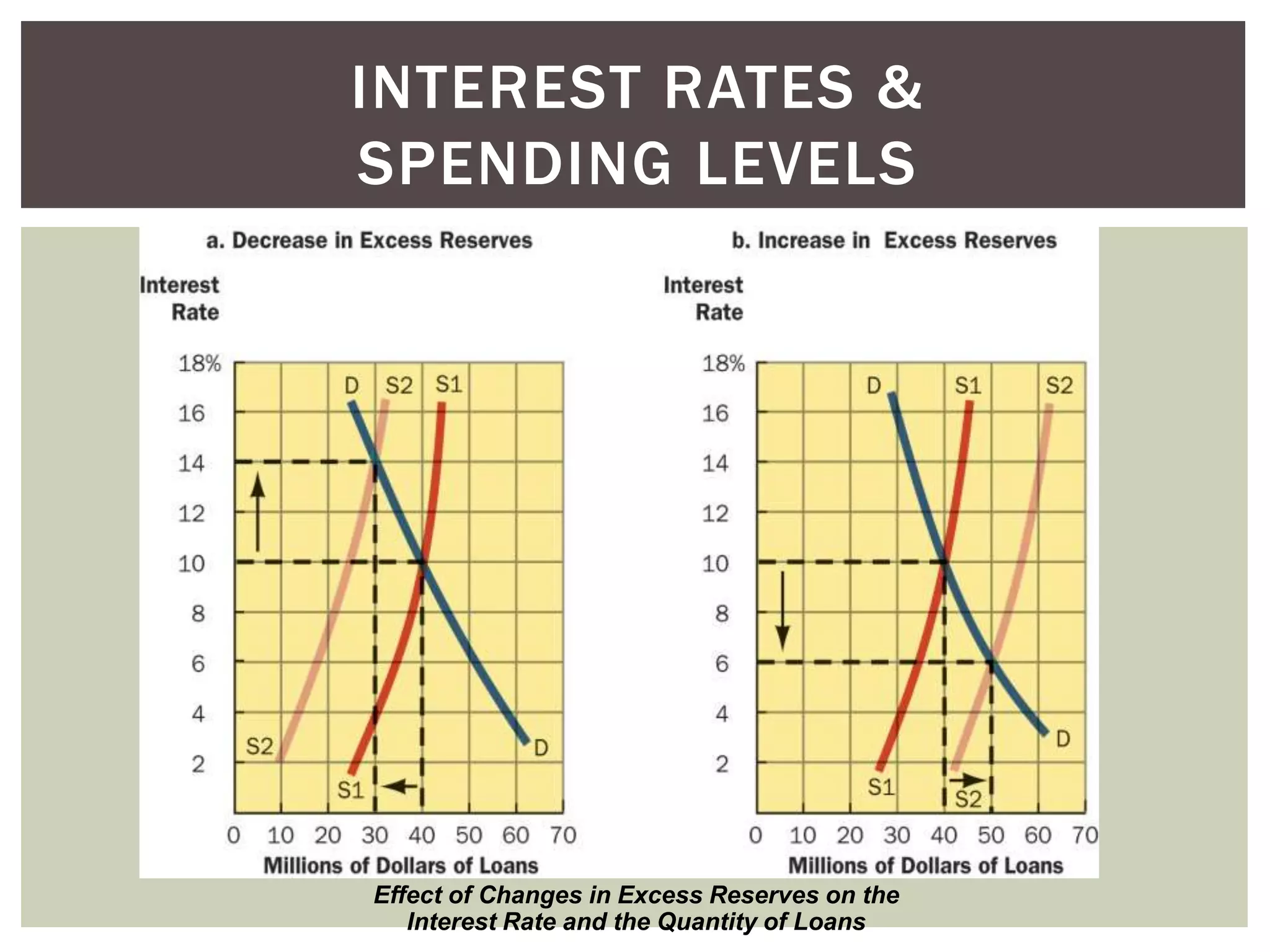
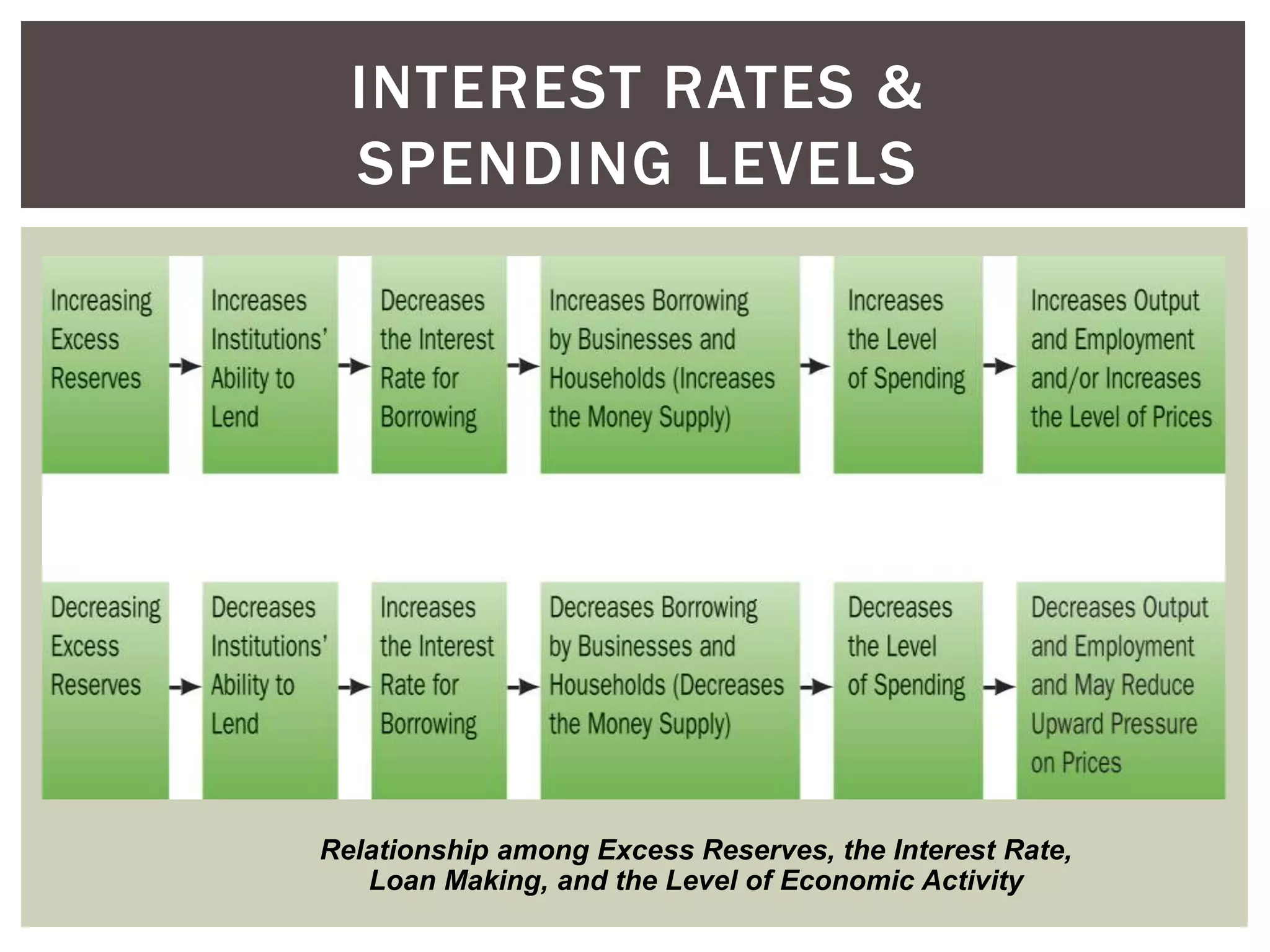
2) The components of bank reserves including actual reserves, required reserves, and excess reserves which forms the basis for commercial banks' lending and money creation.
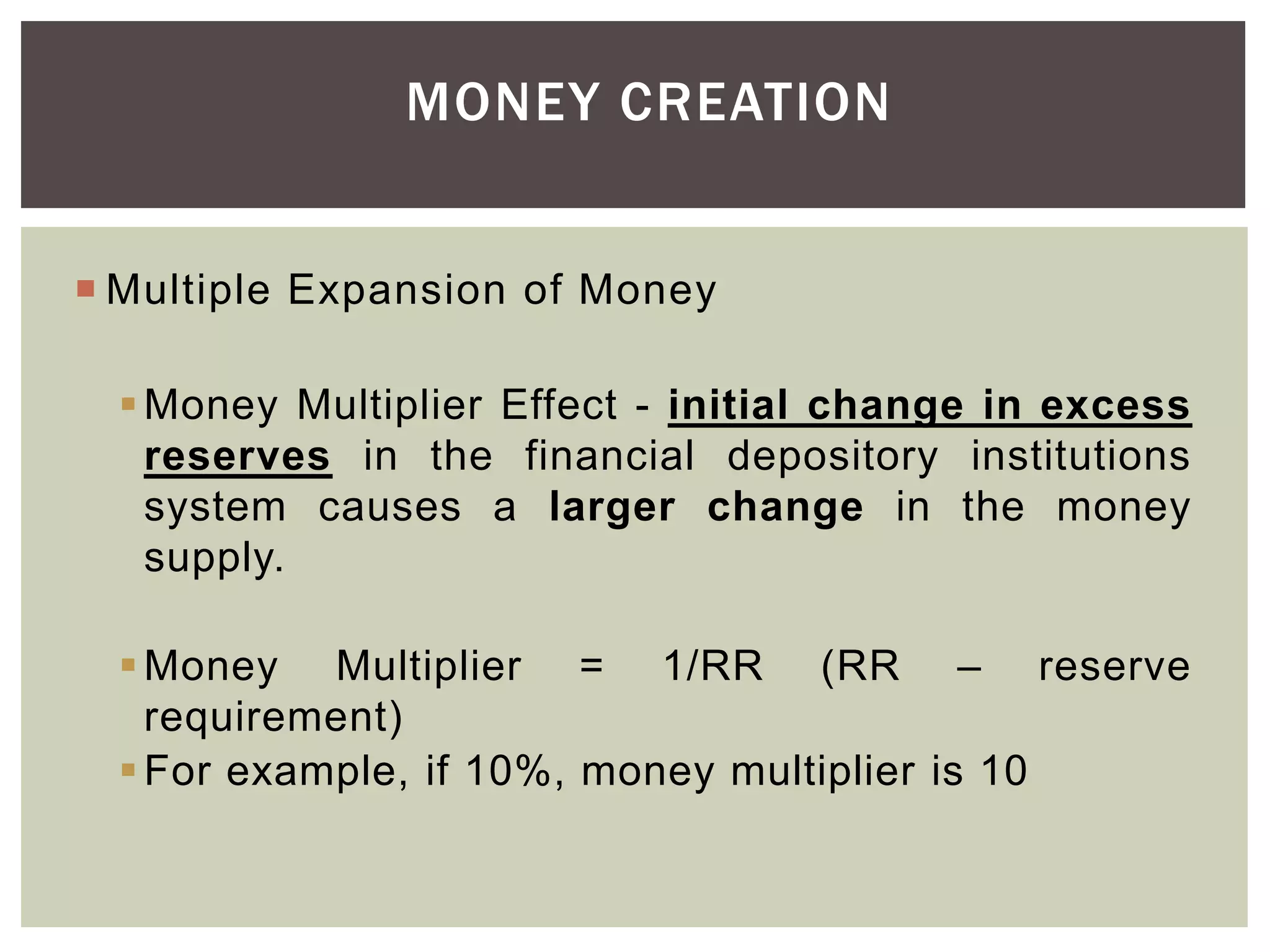
3) How the money multiplier effect works to amplify the impact of changes in excess reserves on the overall money supply through the banking system.