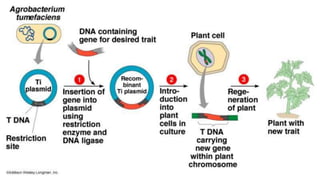
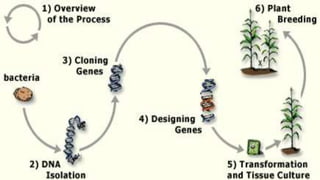
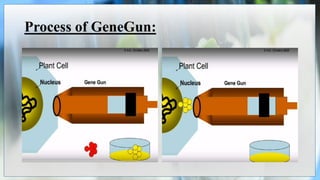
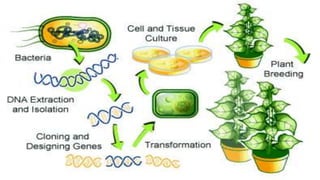
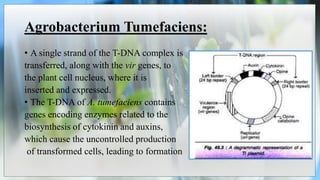
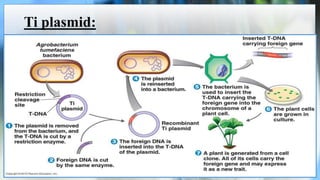
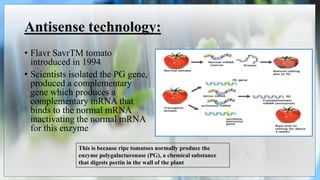
The document discusses the concepts of transgenic plants and biotechnology, highlighting the creation and benefits of genetically modified organisms (GMOs) through various gene transfer methods. It provides a historical timeline of significant advancements in plant genetic engineering and outlines the advantages and disadvantages of transgenic crops and GM foods. Additionally, it explores biopharming, the use of plants for pharmaceutical production, and addresses the risks and regulatory concerns associated with genetic modification.