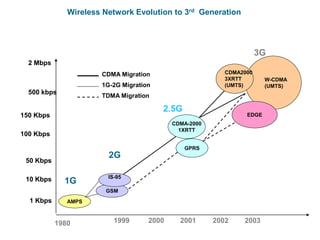
Cellular networks have evolved from 1G to 3G over several decades:
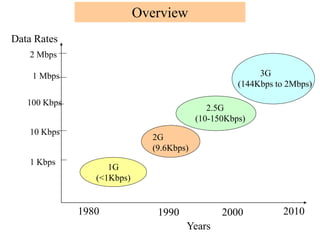
1) 1G networks in the 1980s used analog transmission for voice only. 2G networks in the late 1980s introduced digital transmission and low-speed data.
2) 2G networks in the late 1980s-2000s provided digital transmission for voice and low-speed data up to 144kbps. This included CDMA (IS-95) and GSM networks.
3) 3G networks from 2000s onward enabled broadband multimedia up to 2Mbps for mobile internet. This included evolutions of CDMA (CDMA2000) and GSM (UMTS). Future networks beyond 3G aimed for even