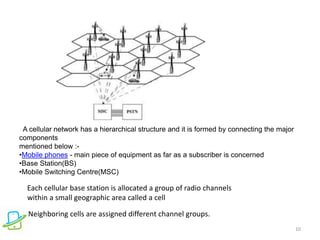
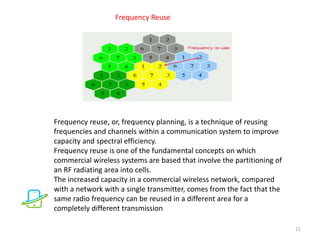
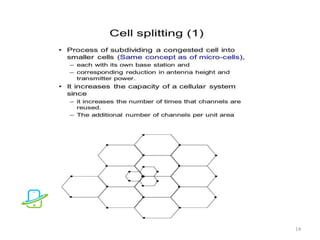
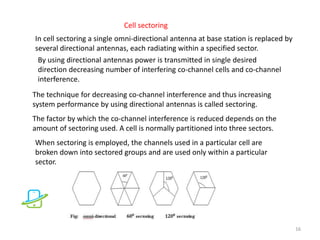
This document discusses the evolution of mobile communication technologies from 1G to 5G. It provides details on each generation including key features and technologies. 1G introduced analog cellular networks while 2G brought digital networks and basic data. 3G enabled increased data speeds and multimedia. 4G further increased speeds and capabilities. 5G is focused on high speeds, capacity, and supporting wireless web applications. The document also covers cellular concepts like frequency reuse, cell splitting, and cell sectoring which help improve network capacity and efficiency.