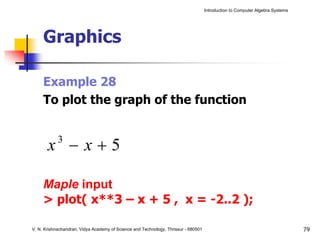
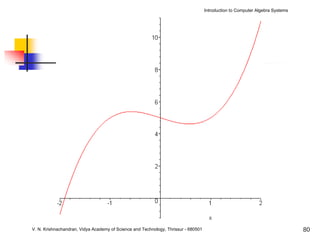
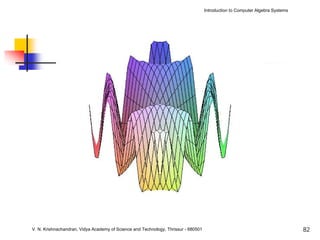
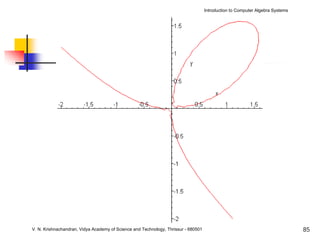
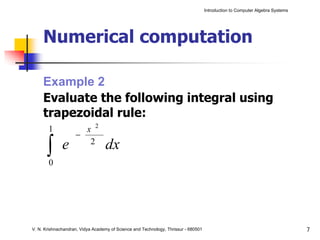
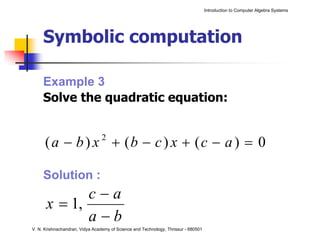
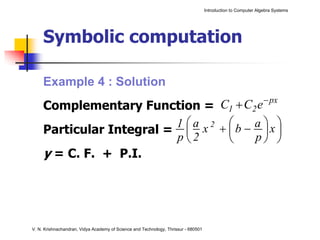
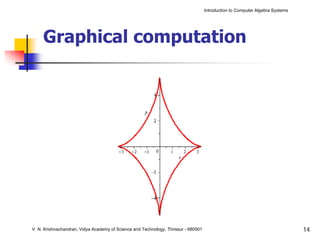
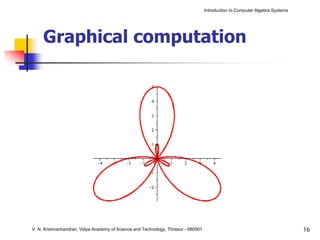
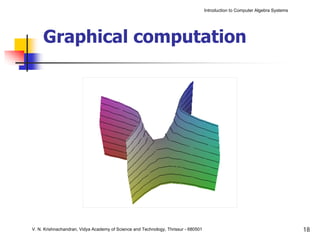
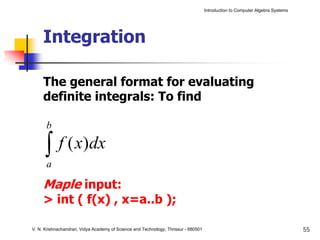
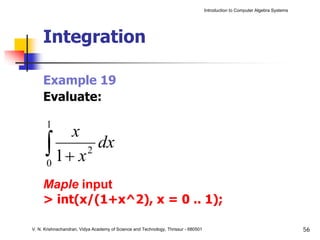
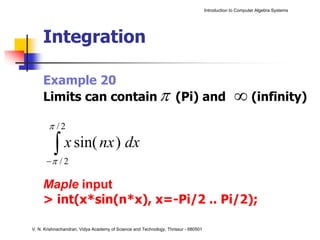
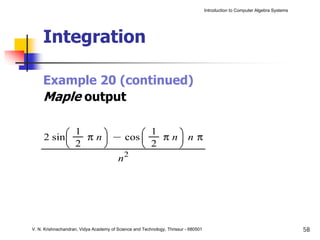
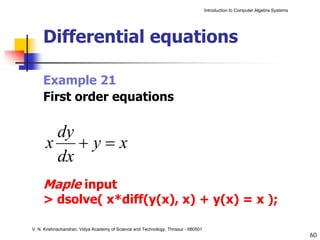
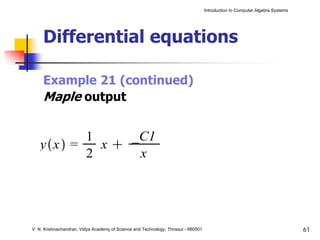
The document is an introduction to computer algebra systems (CAS), detailing their capabilities in numerical, symbolic, and graphical computations, with practical examples using the software Maple. It covers various operations and syntax for algebra, calculus, and solving differential equations within Maple, as well as the application of packages for different mathematical areas. Additionally, it includes multiple examples to demonstrate the functionalities of CAS in solving complex mathematical problems.


































![Introduction to Computer Algebra Systems
LinearAlgebra package
To define the matrix
⎡ 1 −3 4⎤
⎢
⎢ 2 ⎥
⎢ 3 4⎥
⎥
⎢
⎢−4 ⎥
⎣ 0 5⎥
⎦
Maple input
>A:=Matrix([[1, -3, 4],[2, 3, 4],[-4, 0, 5]]);
V. N. Krishnachandran, Vidya Academy of Science and Technology, Thrissur - 680501 69](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontocomputeralgebrasystems-091108111151-phpapp02/85/Introduction-to-Computer-Algebra-Systems-69-320.jpg)