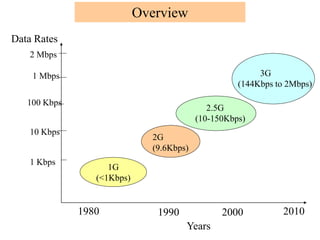
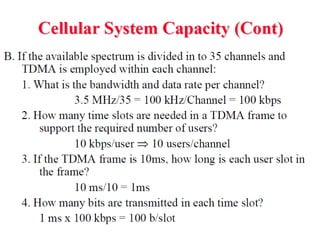
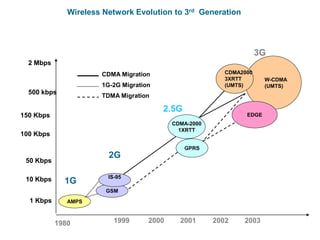
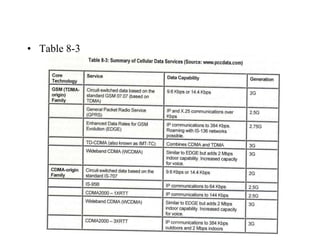
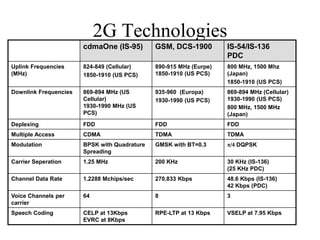
1) Cellular networks have evolved from 1G to 3G over several decades, with each generation providing higher data rates and capabilities. 1G networks in the 1980s provided analog transmission for voice, while 2G in the 1990s added digital transmission and low-speed data. 3G networks beginning in the 2000s enabled broadband multimedia with data rates from 144 kbps to 2 Mbps.
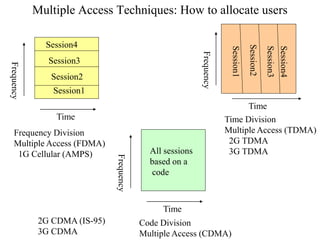
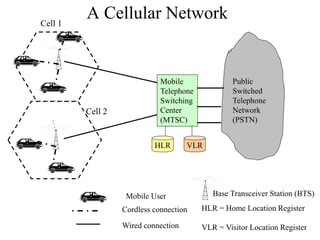
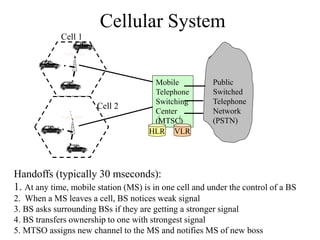
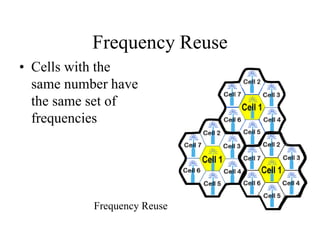
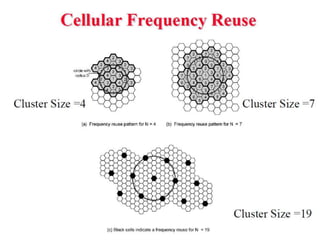
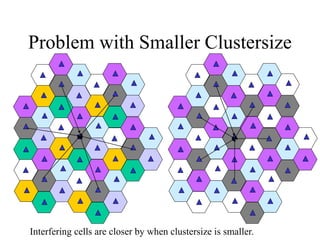
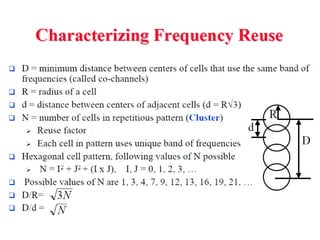
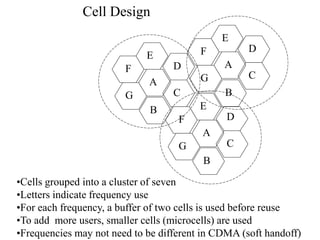
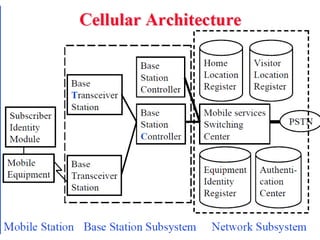
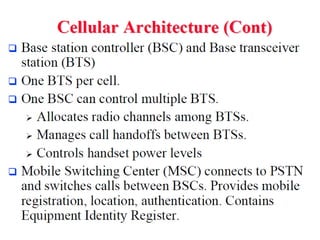
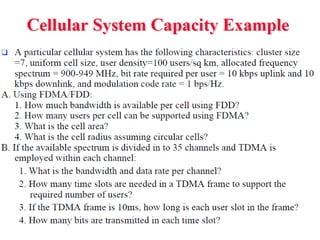
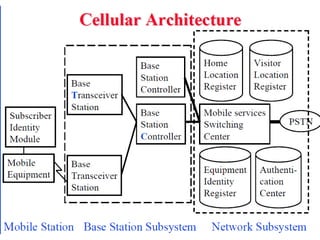
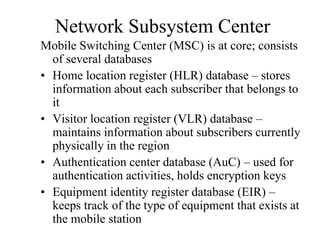
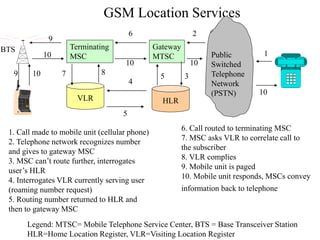
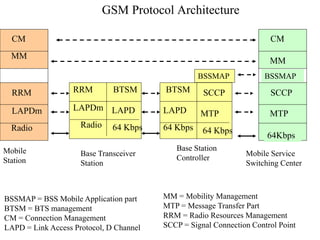
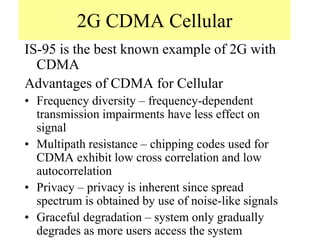
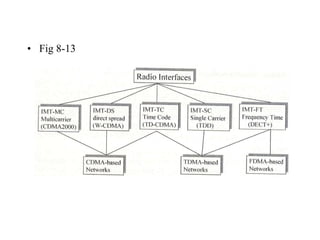
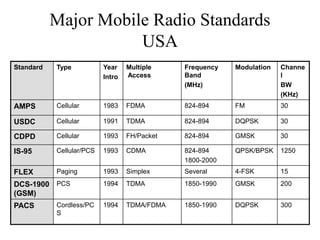
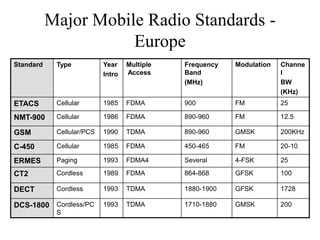
2) Key technologies enabling multiple access of many users over cellular networks include FDMA for 1G, TDMA for 2G and 3G, and CDMA for 2G and 3G. Cell sites are organized into a cellular structure with frequency reuse to improve capacity. Handoffs allow user mobility between cell sites.