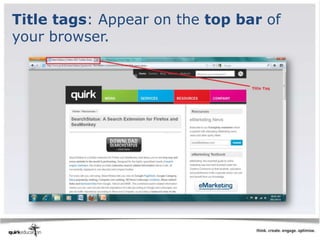
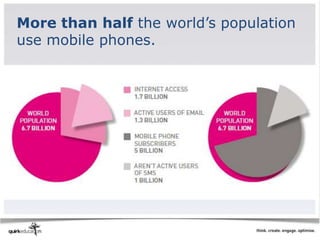
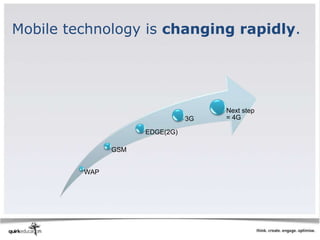
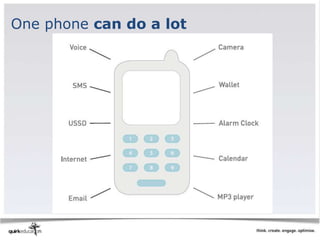
This document discusses best practices for web development and design. It emphasizes laying strong foundations by considering accessibility, usability, searchability and discoverability. Key recommendations include using standard conventions like bold text and bullet points, ensuring content is visible to search engines through metadata and alt tags, and testing sites thoroughly before launching. The document also covers opportunities and challenges of mobile development, such as small screens and navigation limitations on phones.