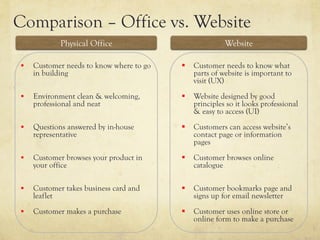
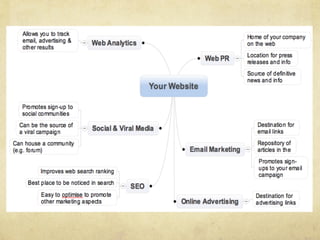
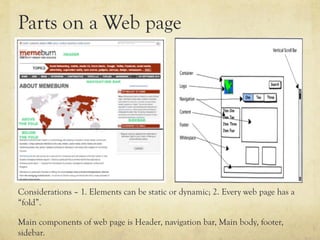
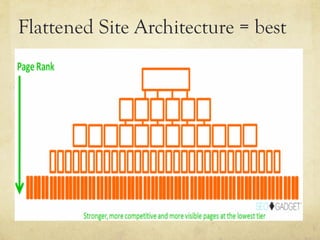
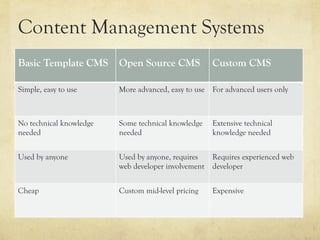
This document provides an overview of website design and development. It discusses key topics such as website specifications, visual design principles, content planning, user experience, and legal considerations. It also compares physical offices to websites. Website design involves specifying goals, required pages, visual elements, and user experience. Development turns design concepts into a functioning website through programming languages, hosting, and content management systems. Effective planning is important for meeting objectives and managing expectations.