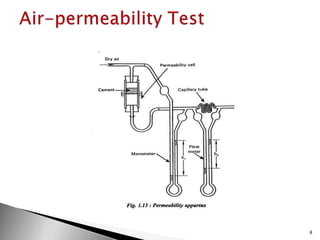
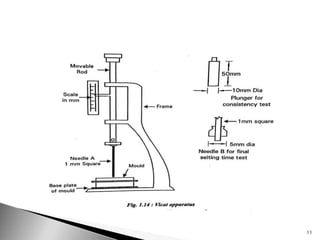
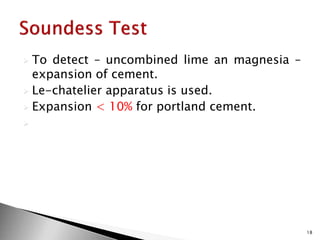
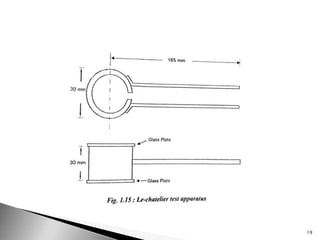
Cement tests can be divided into field tests and laboratory tests. Laboratory tests include fineness test, standard consistency test, setting time test, compressive strength test, soundness test, and tensile strength test. The fineness test measures the mean size of cement grains and finer cement results in earlier strength development but more shrinkage and cracking. The standard consistency test determines the percentage of water required to form a cement paste using a Vicat apparatus. The setting time test uses the Vicat apparatus to detect when cement paste reaches its initial and final set. The compressive strength test forms cement mortar cubes which are tested at 3 and 7 days to determine strength. The soundness test uses a Le-Chatelier apparatus to