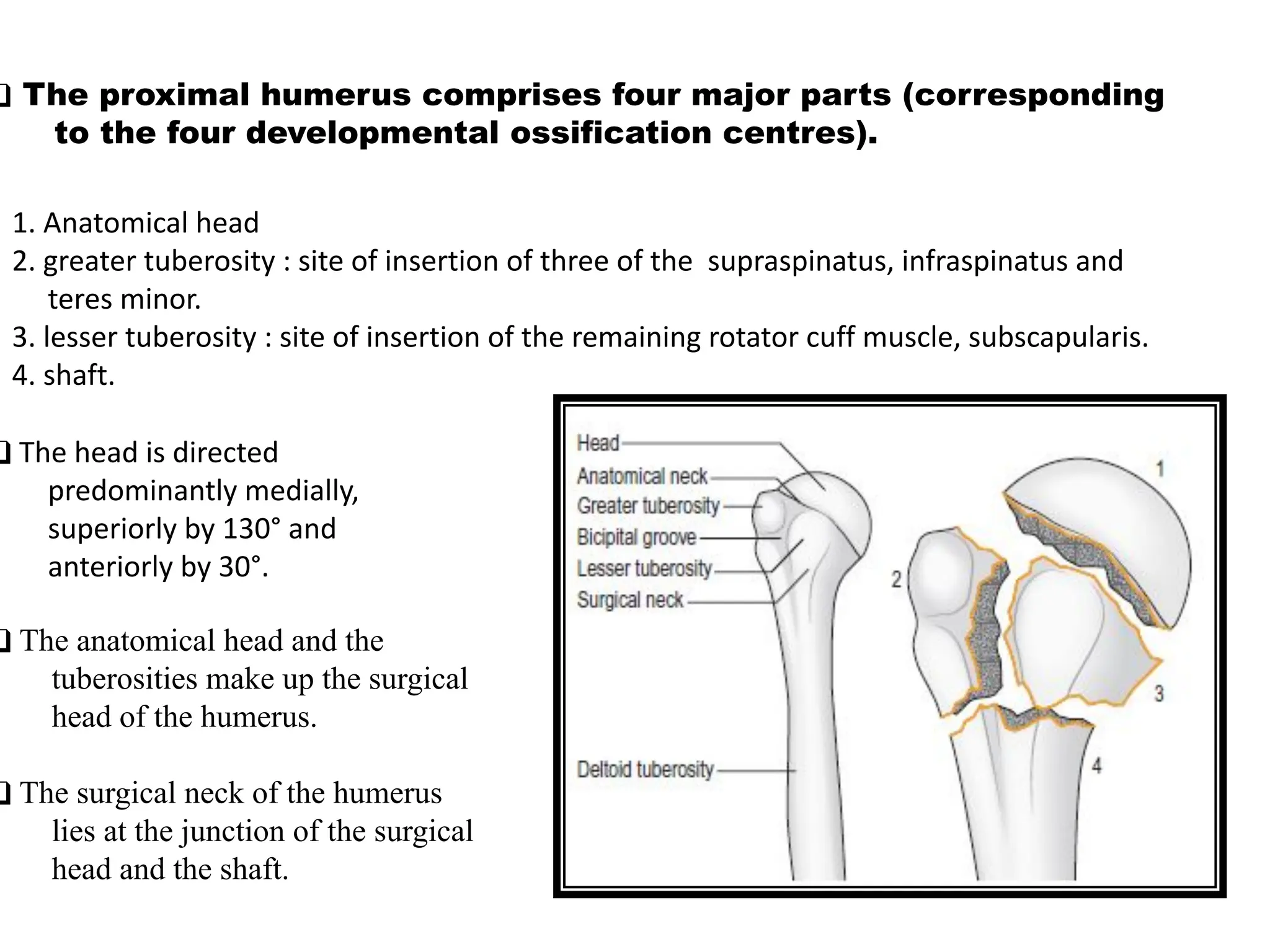
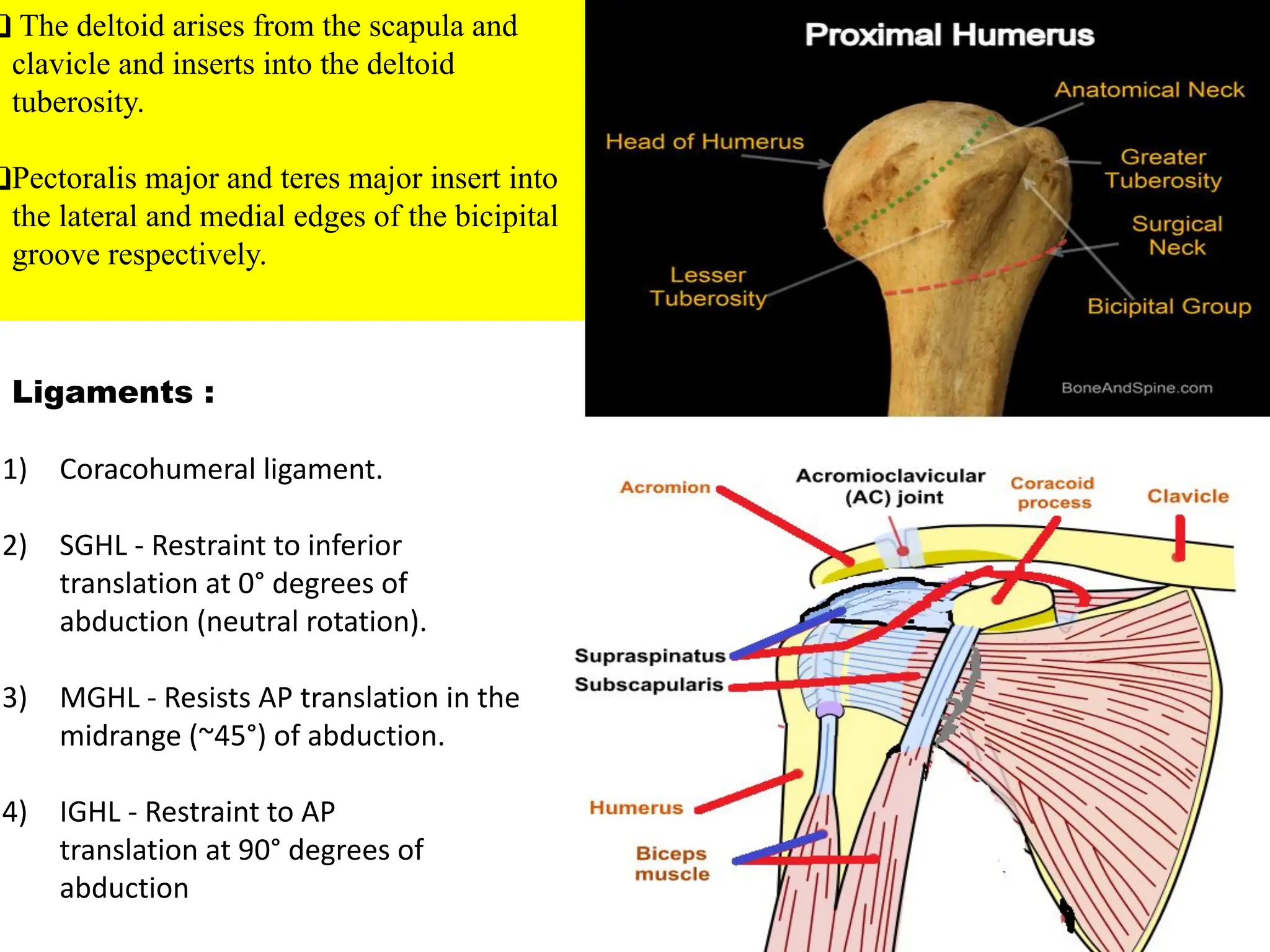
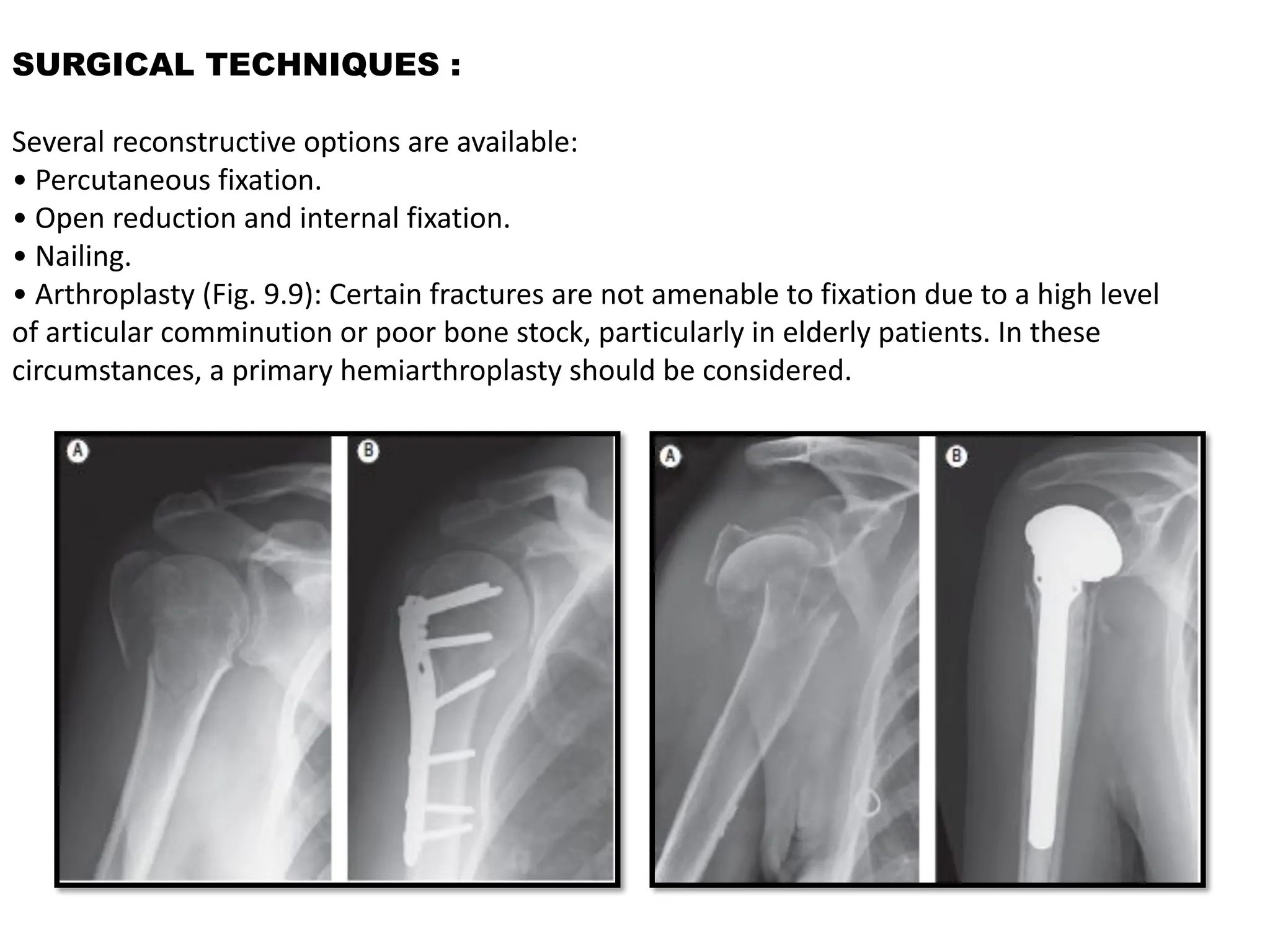
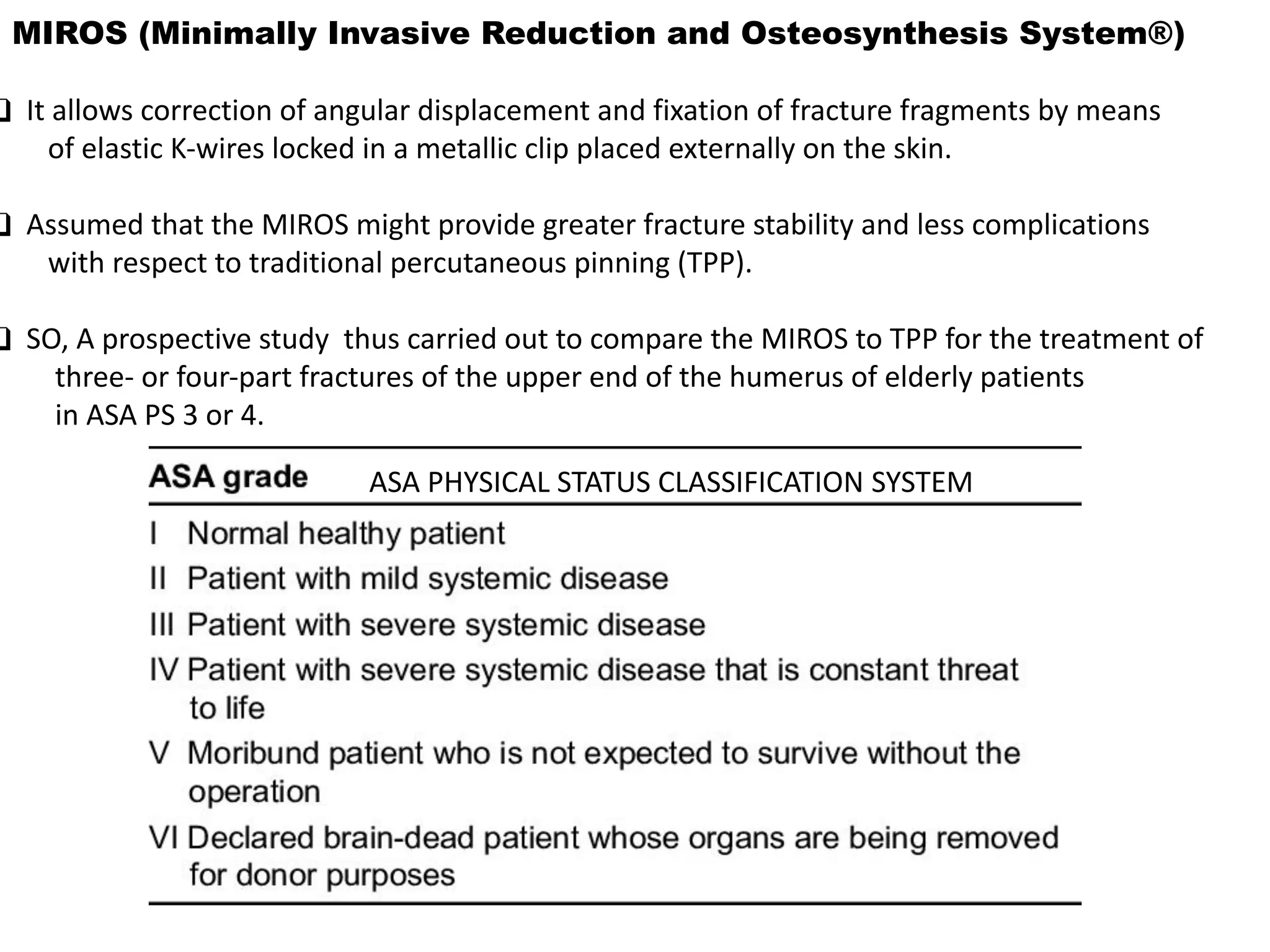
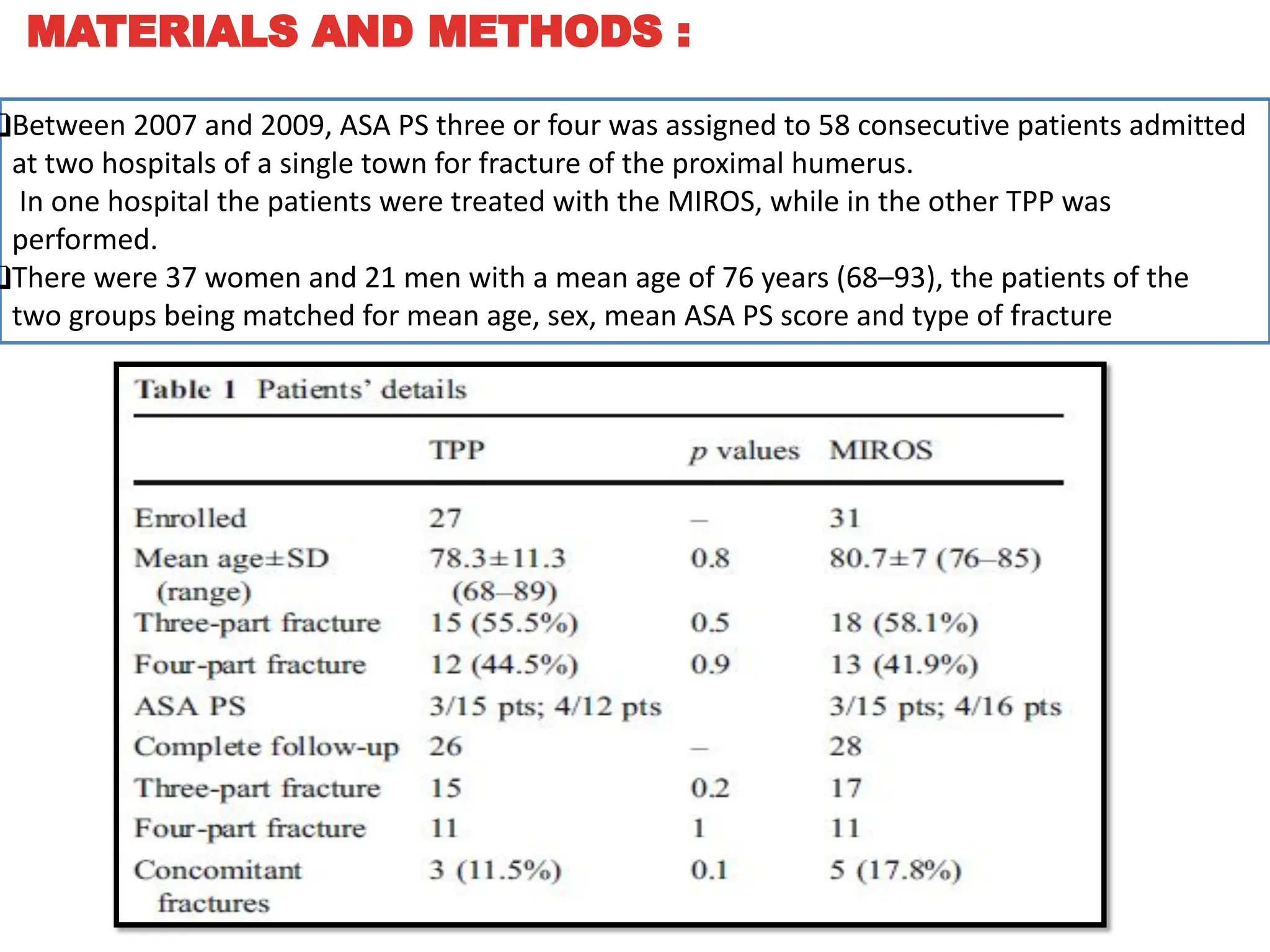
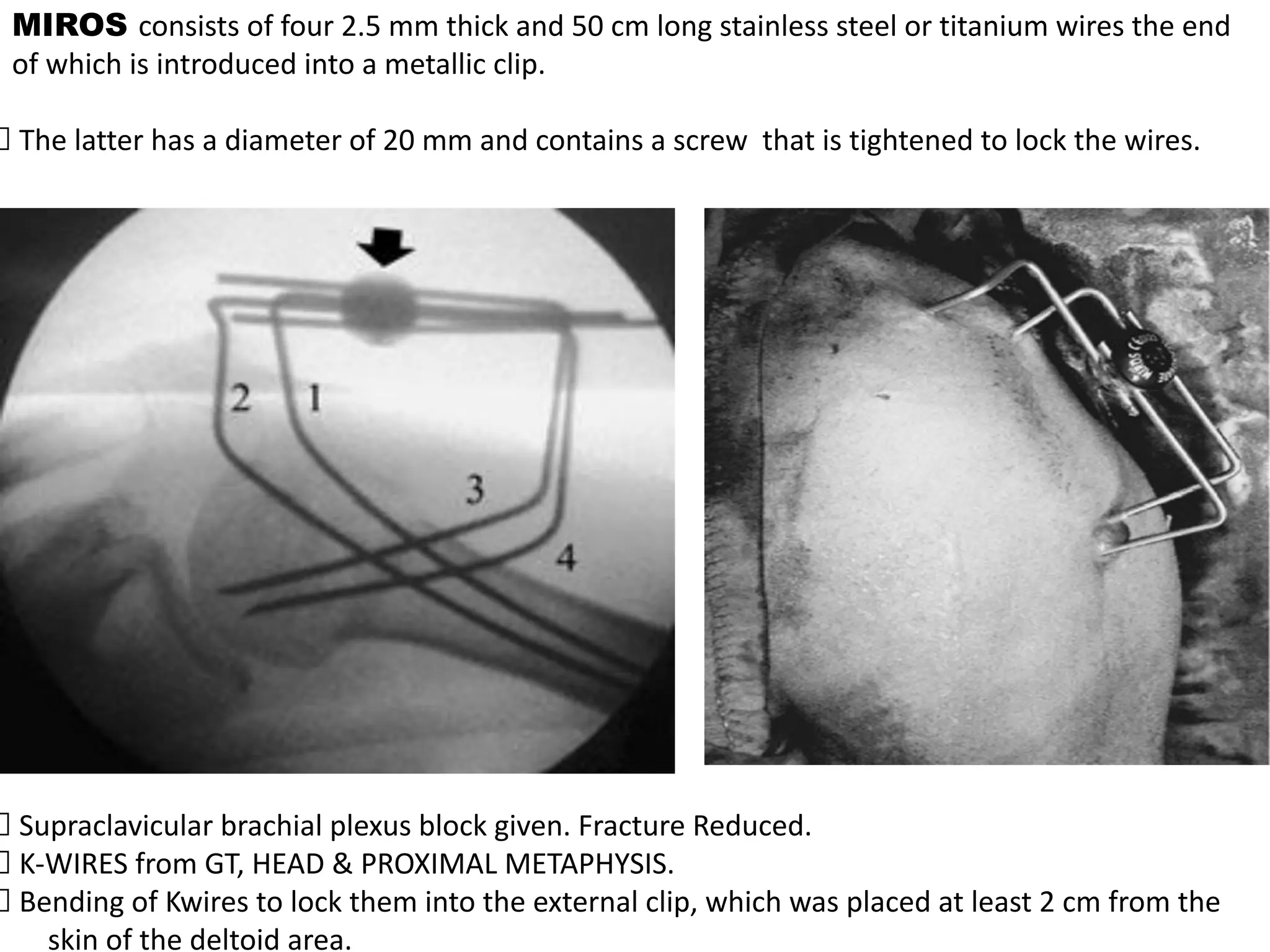
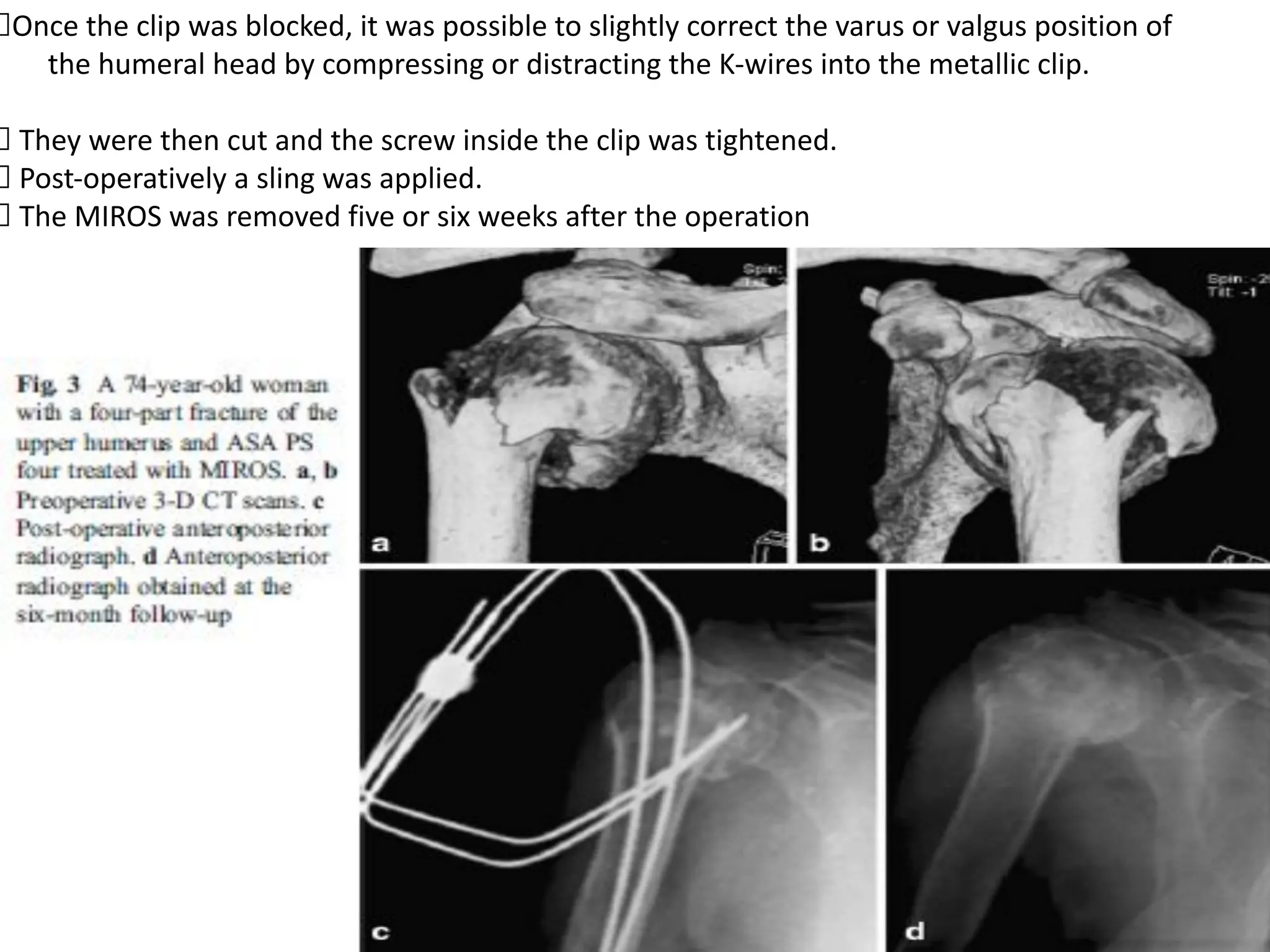
The document compares percutaneous pinning techniques, specifically miros® versus traditional pinning, for treating three or four-part fractures of the proximal humerus in elderly patients. The study suggests that miros may provide better outcomes, including fewer complications and improved shoulder function, compared to traditional methods, although both approaches rely on closed reduction of the fracture. It concludes that while traditional pinning is valid, miros offers advantages that may be more beneficial for elderly patients, especially those with complex fracture patterns.









![1). OPERATIVE TIME 37.3 MIN 40.1 MIN
2). FLUROSCOPY TIME 76 SECS 50 SECS
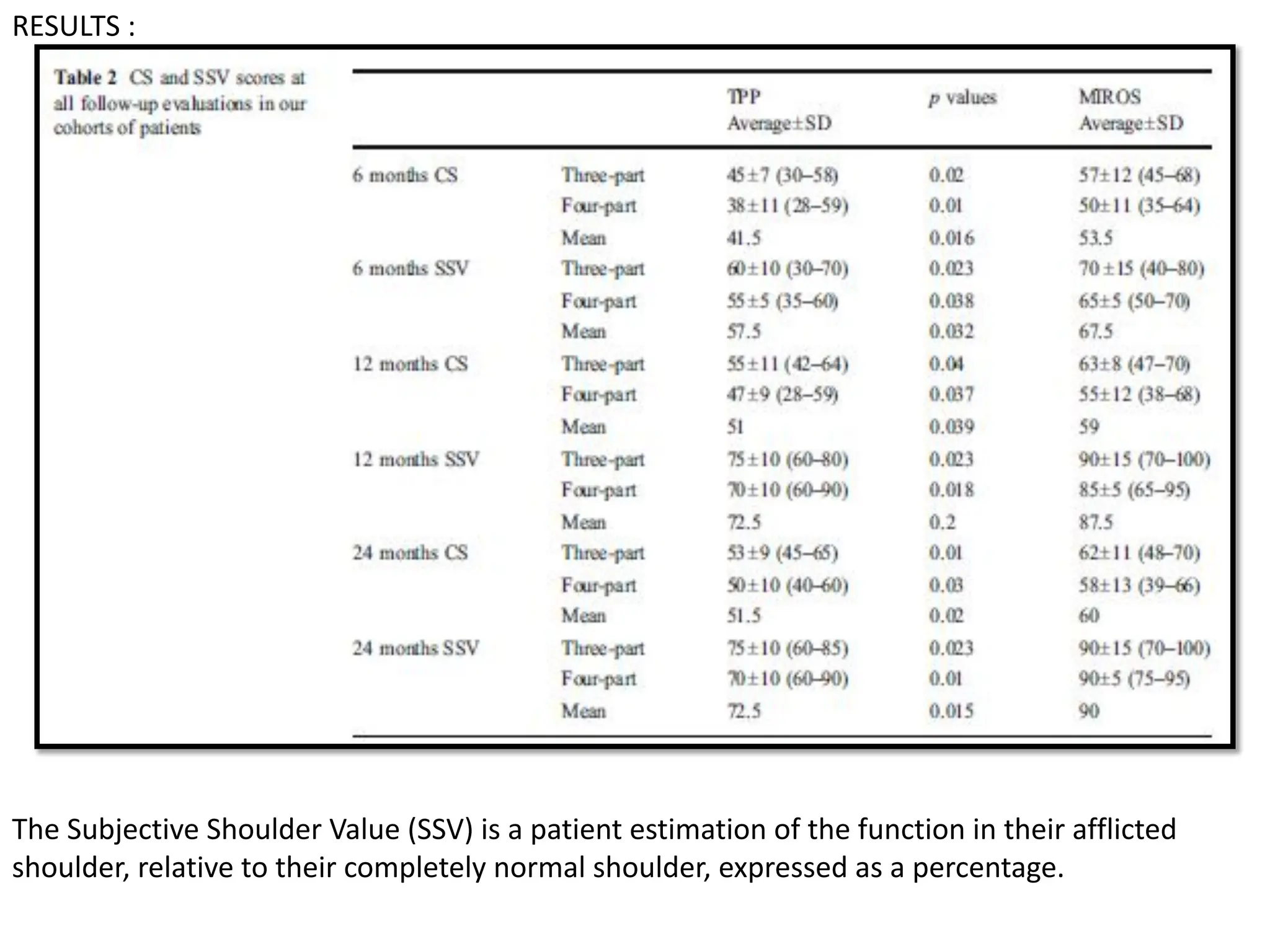
3). CS SCORE MORE+++ LESS++
4). SSV SCORE MORE+++ LESS++
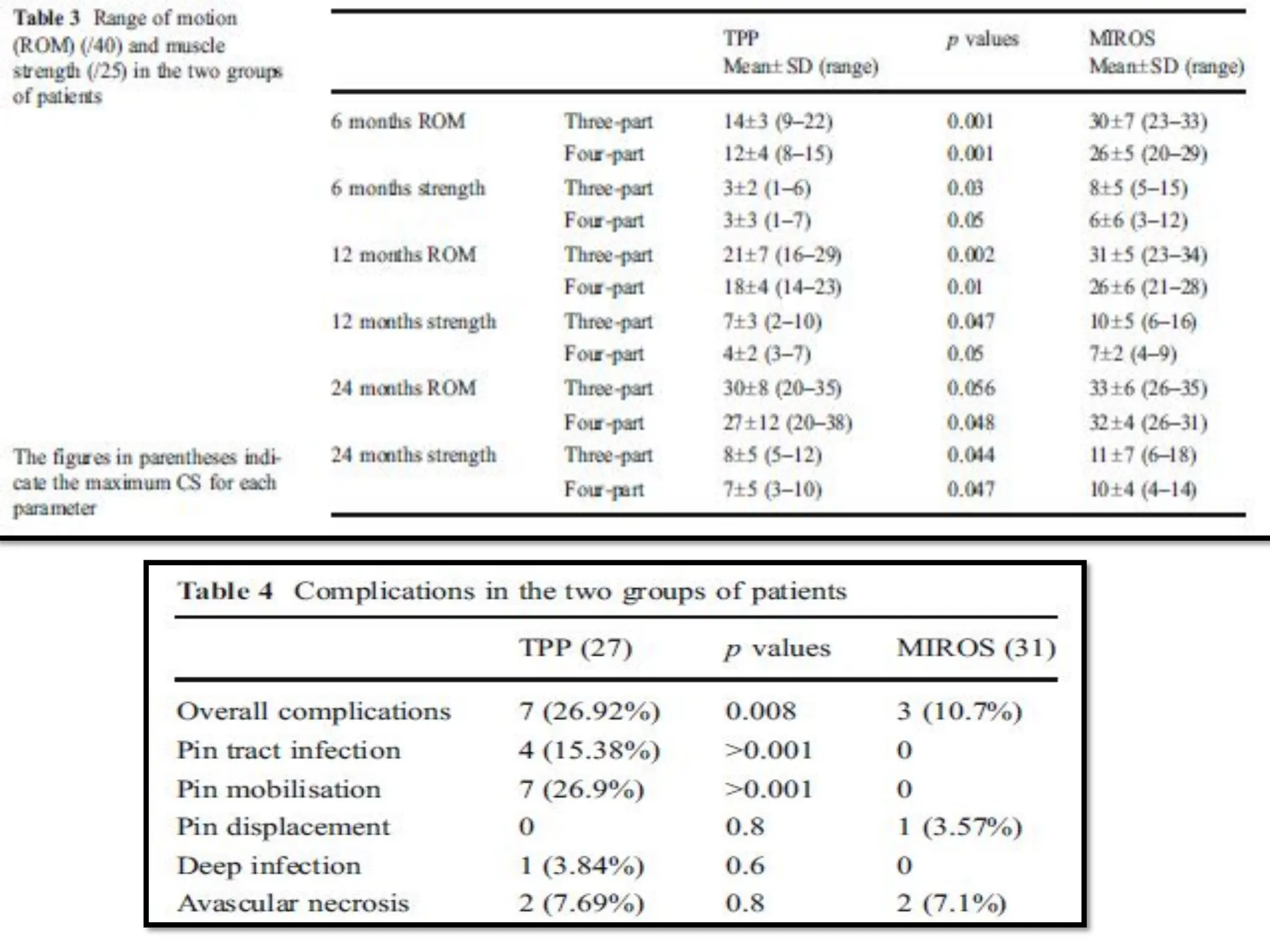
5). COMPLICATION RATE 10.7 26.9
6). ROM OF MIROS IN FOLLOW UP MORE THAN TPP
7). ABDUCTION STRENGTH OF MIROS IN FOLLOW UP MORE THAN TPP
8). 1/2 PINS COME OUT PARTIALLY FROM HUMRUS IN 5 PTS – REMOVED WITHOUT LOSS OF REDUCTION
9). MIROS – 1 PT HAS MODERATE LOSS OF FRACTURE REDUCTION
10). TPP- 1 PT HAS INFECTION-ANTIBIOTICS
11). 4 PT HAS AVN – 3 DO NOT ASK FOR OPERATIVE BCZ ACCEPTABLE CONDITION
12). A STATISTICALLY SIGNIFICANT DIFFERENCE BETWEEN THE TWO GROUPS WAS FOUND
FOR OVERALL COMPLICATIONS, PIN MOBILISATION AND PIN TRACT INFECTION (P<0.05).
13). IN BOTH GROUPS, THE MULTIPLE REGRESSION ANALYSIS SHOWED THAT THE VARIABLES THAT
INFLUENCED THE CS AT THE LATEST FOLLOWUP WERE THE TYPE OF FRACTURE [THREE- VS FOUR-PART
FRACTURES (P00.03)] AND COMPLICATIONS (P<0.001).
MIROS TPP
RESULTS :](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sharemirosseminar-231025204745-a72c05cf/75/MIROS-Minimally-Invasive-Reduction-and-Osteosynthesis-System-21-2048.jpg)