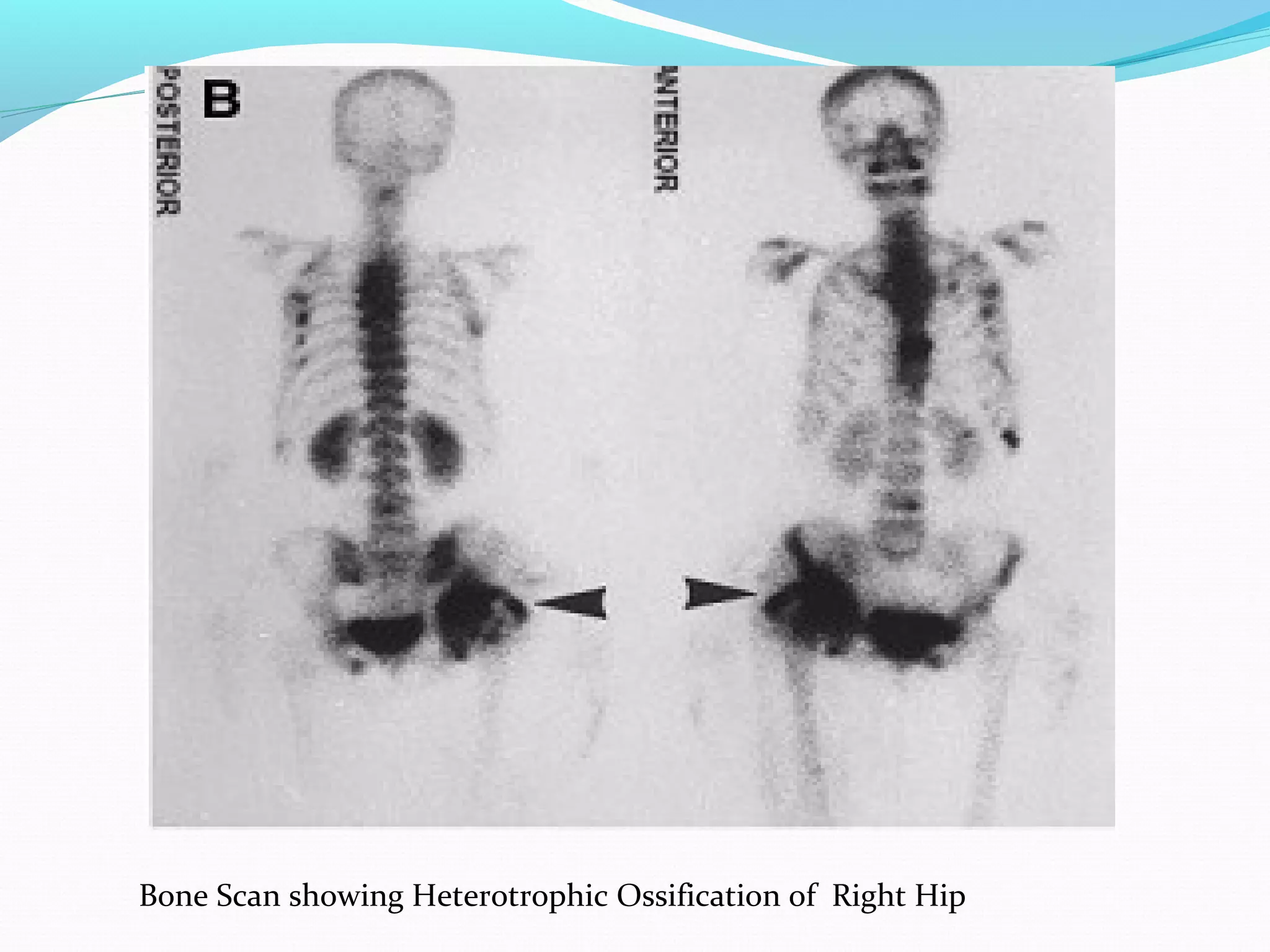
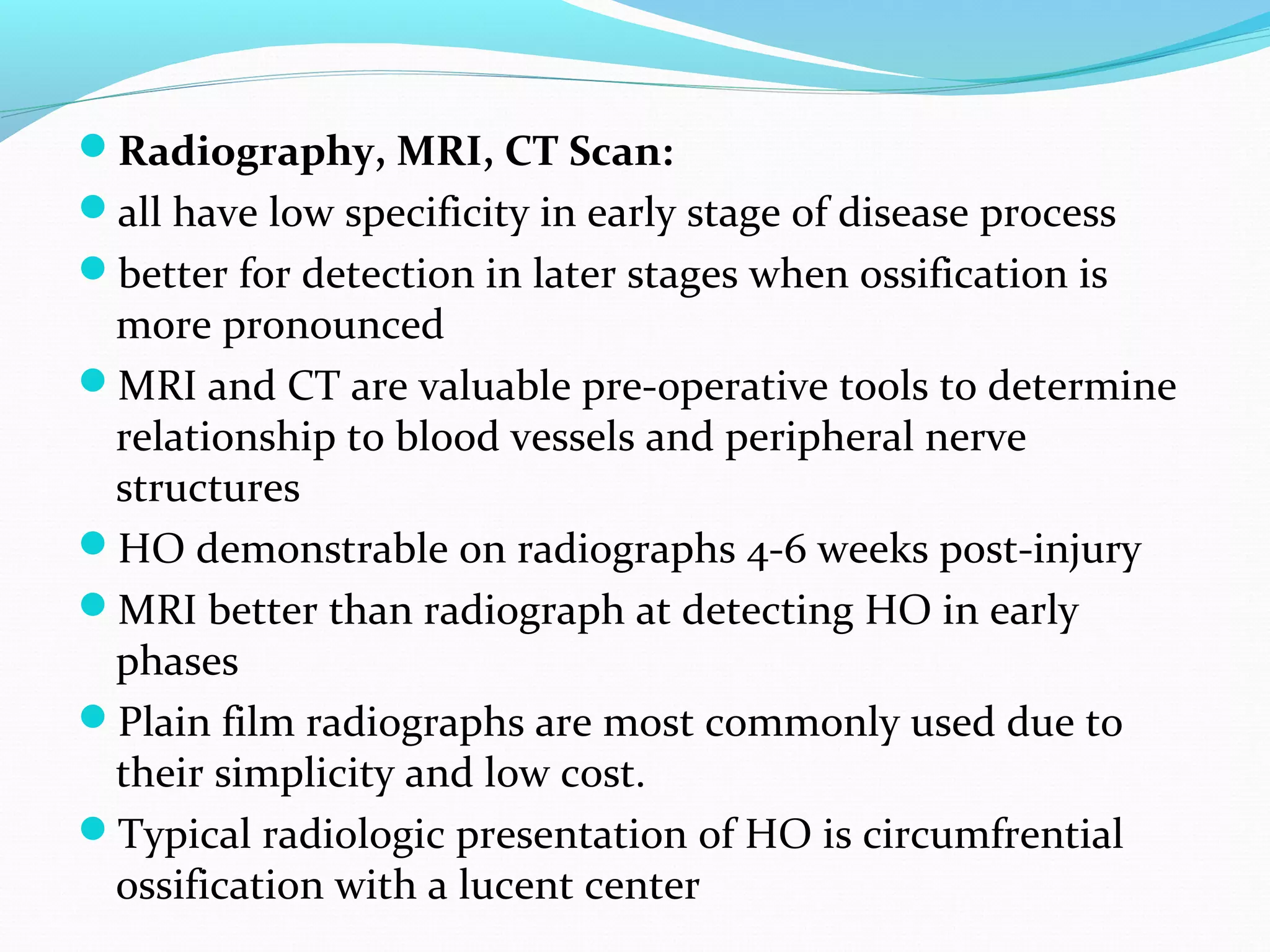
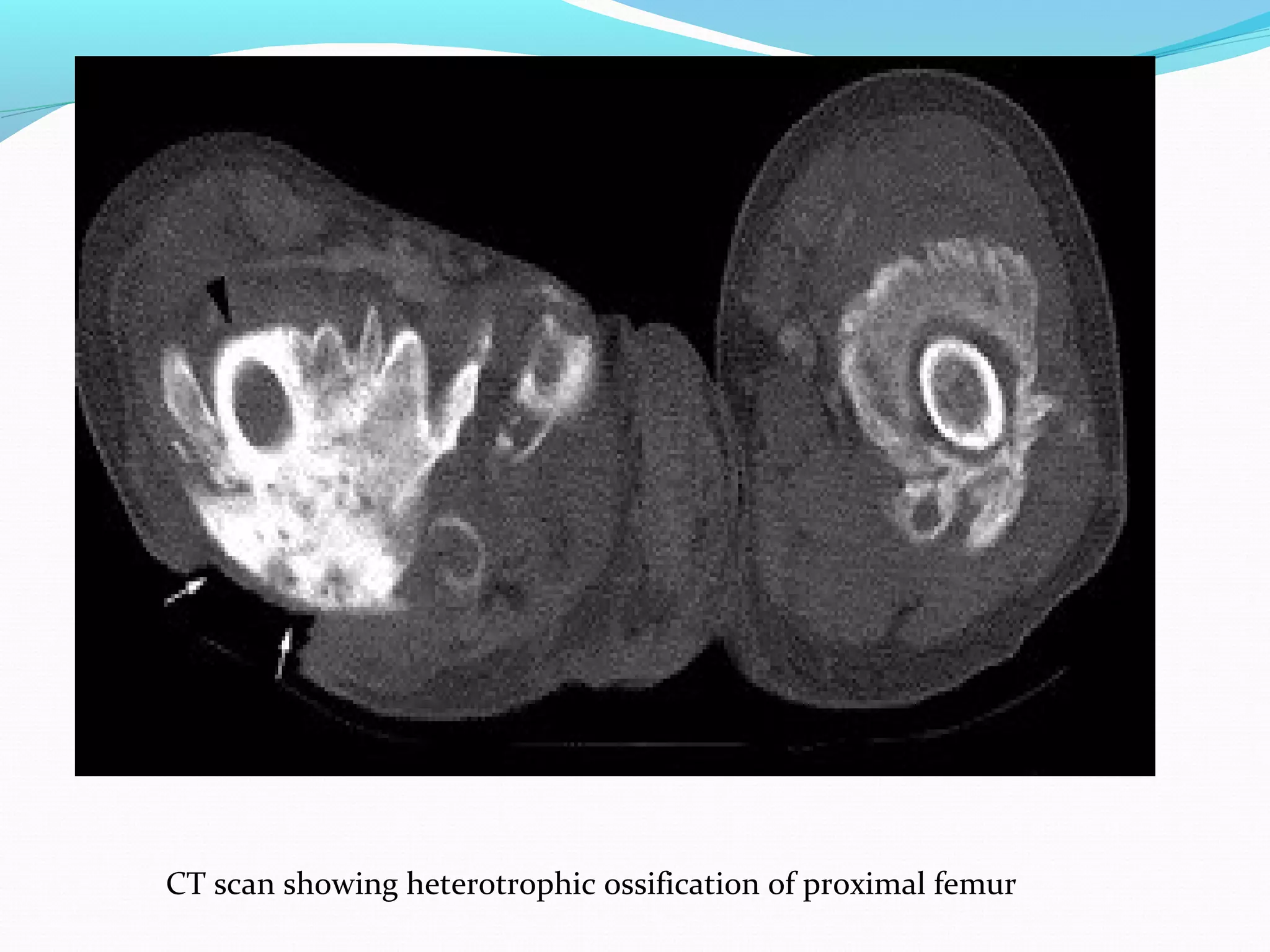
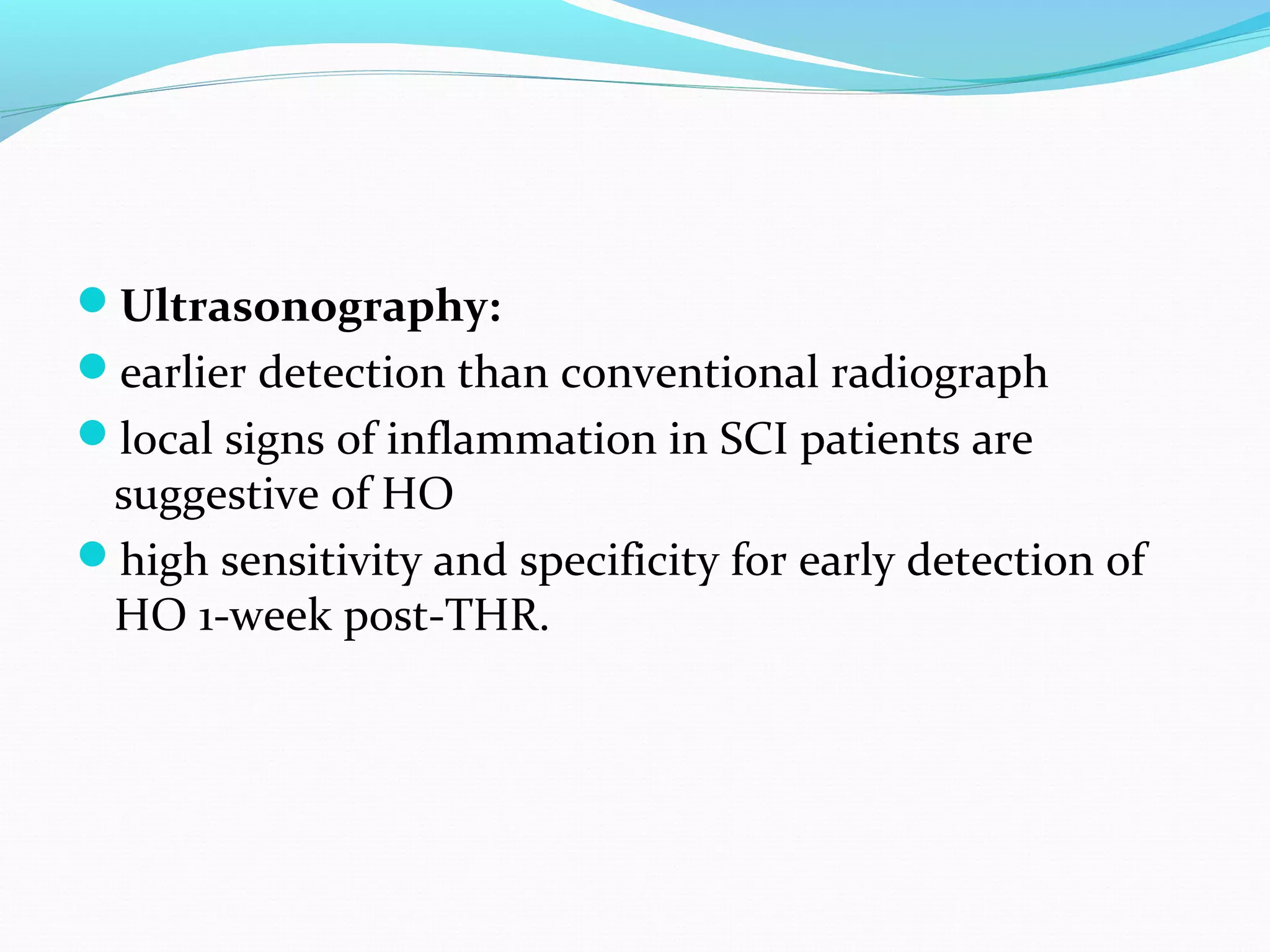
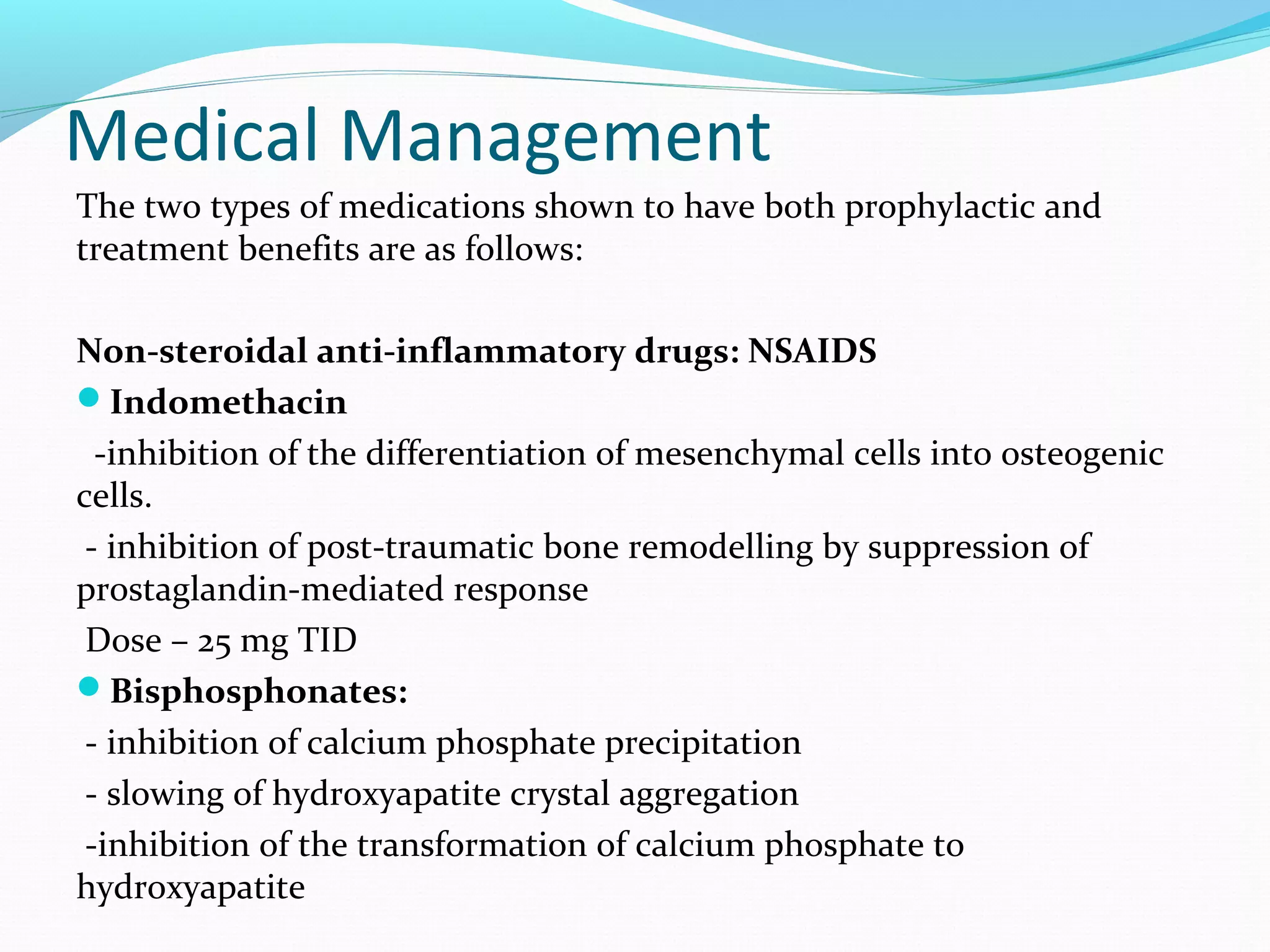
Heterotopic ossification (HO) is the formation of bone in soft tissues near a joint. It commonly occurs after injuries like traumatic brain or spinal cord injuries. Risk factors include older age, complete neurological lesions, male gender, and spasticity. While the exact cause is unknown, damage to sympathetic nerves may increase blood flow and promote HO. Diagnosis involves imaging like bone scans and x-rays. Treatment includes NSAIDs, bisphosphonates, radiation, surgery if limiting range of motion, and physical therapy to preserve joint mobility. Rehabilitation follows phases focusing on edema control, range of motion, and returning to prior activity levels.