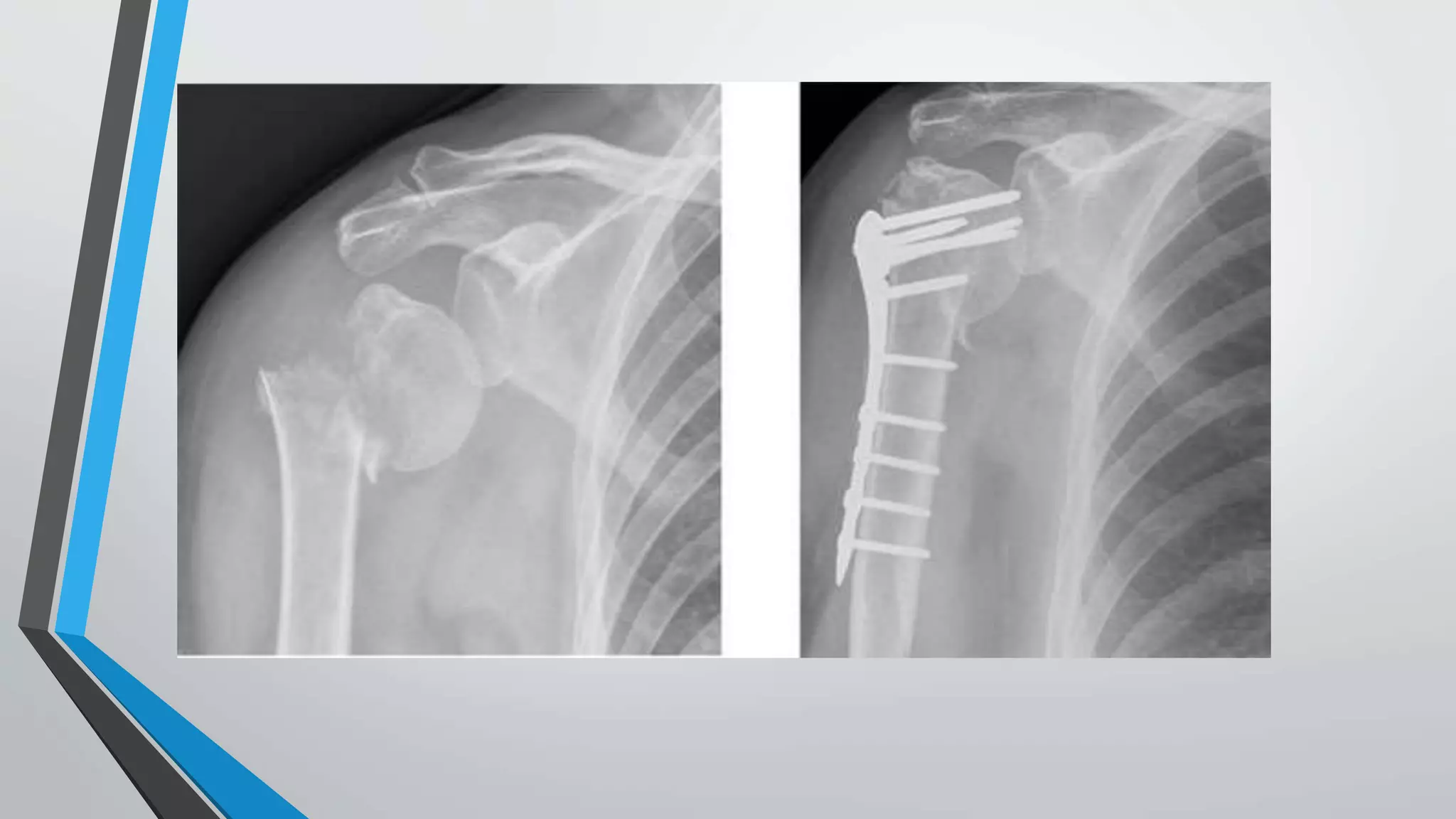
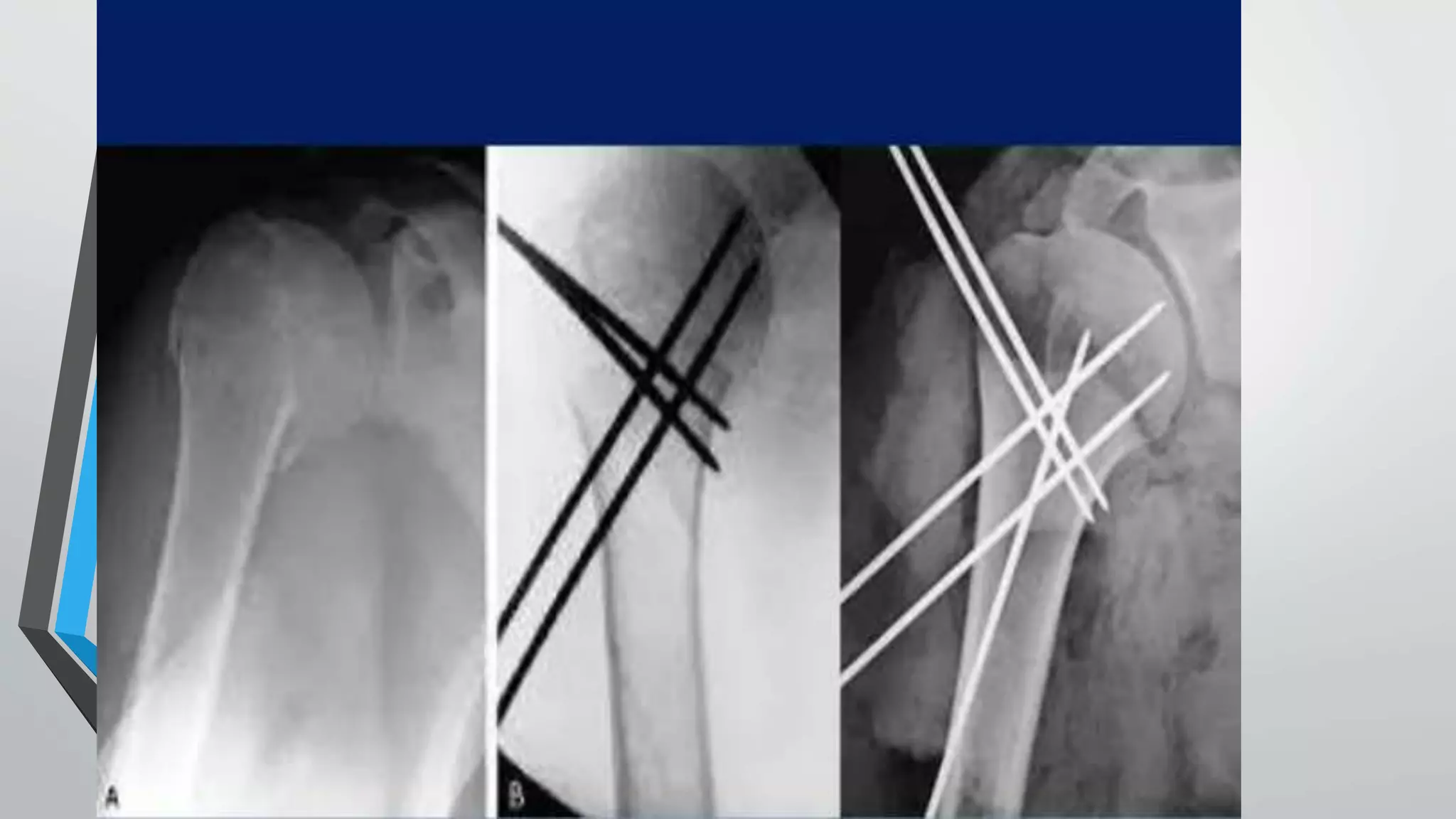
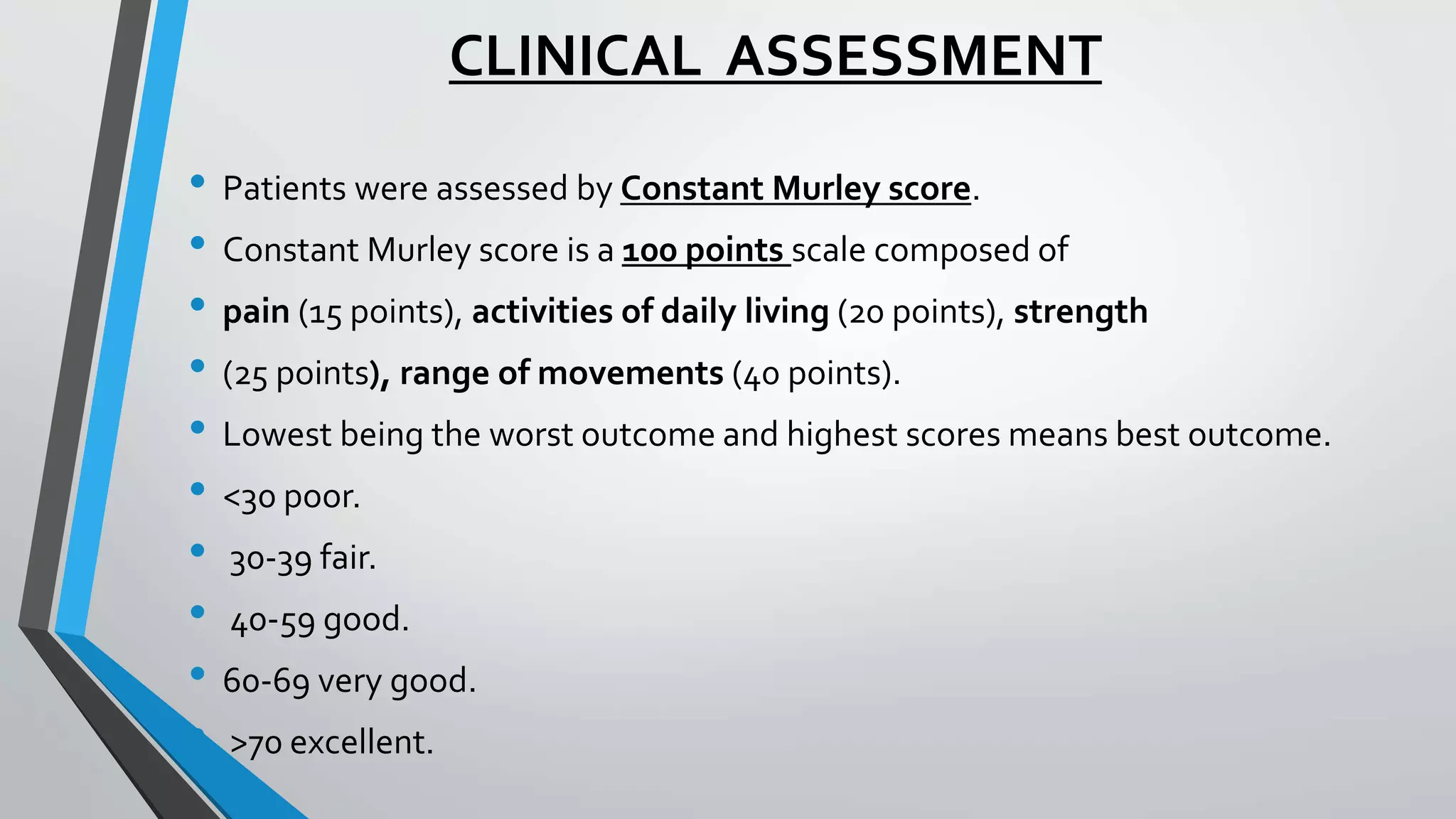
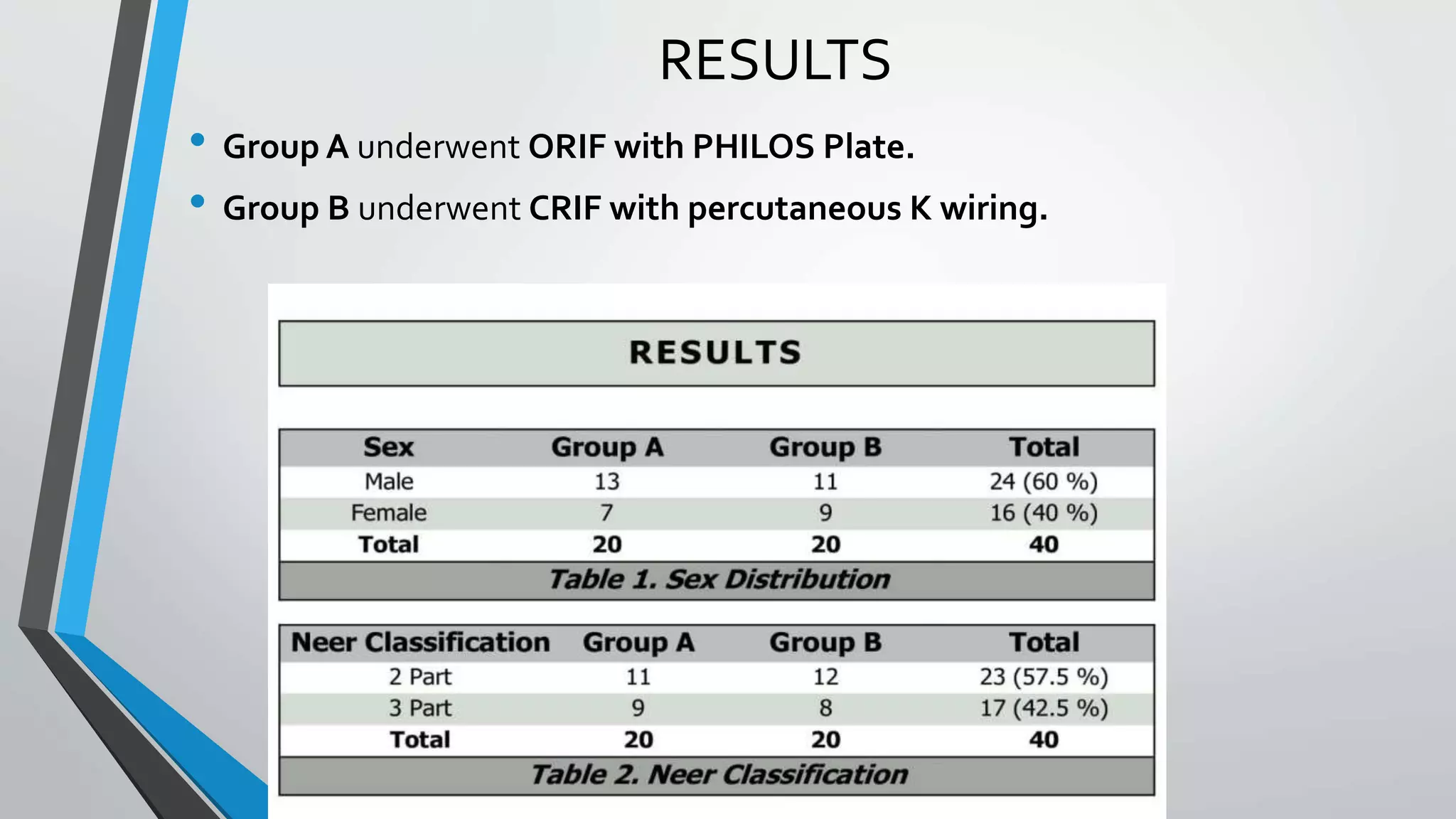
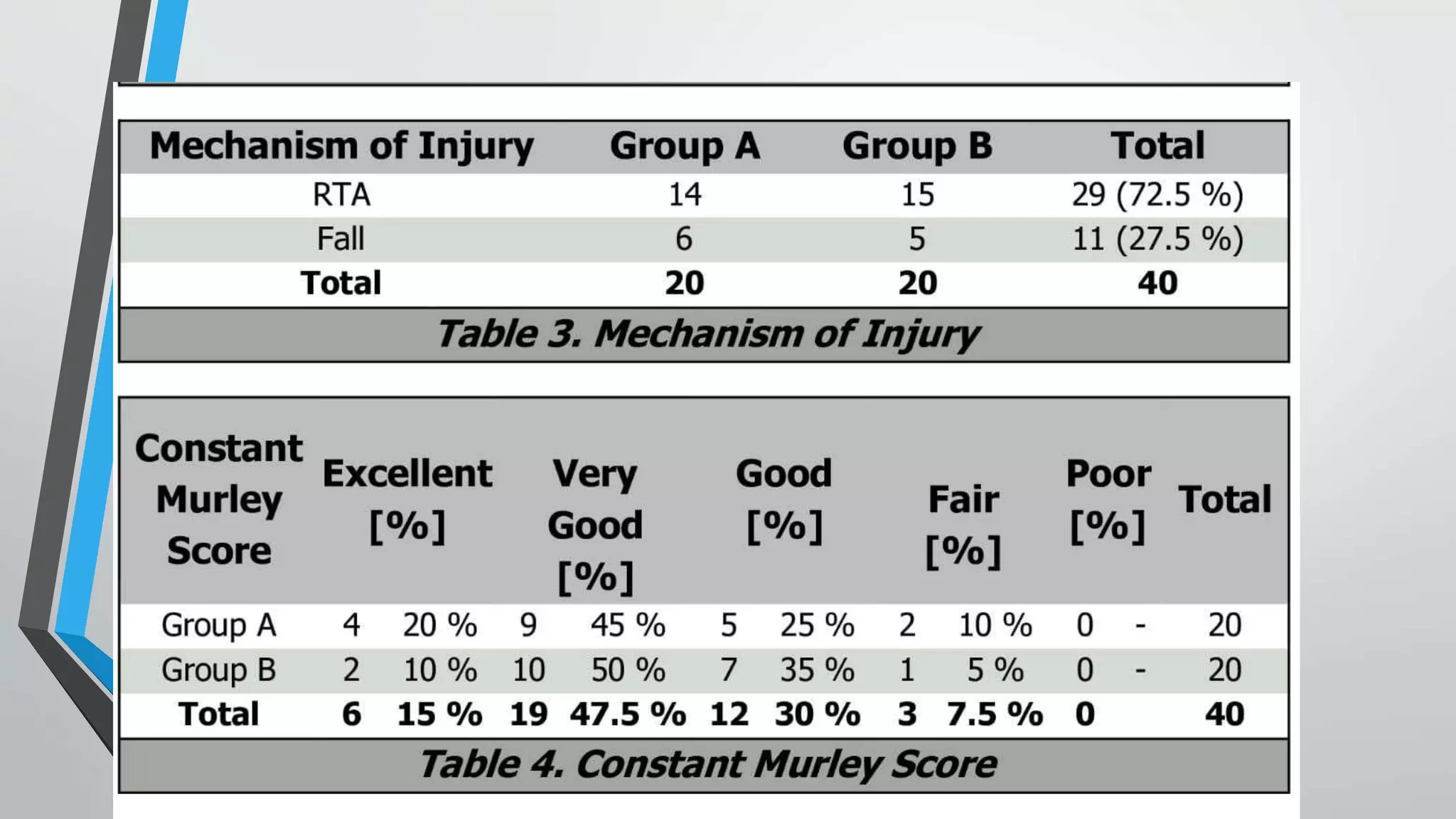
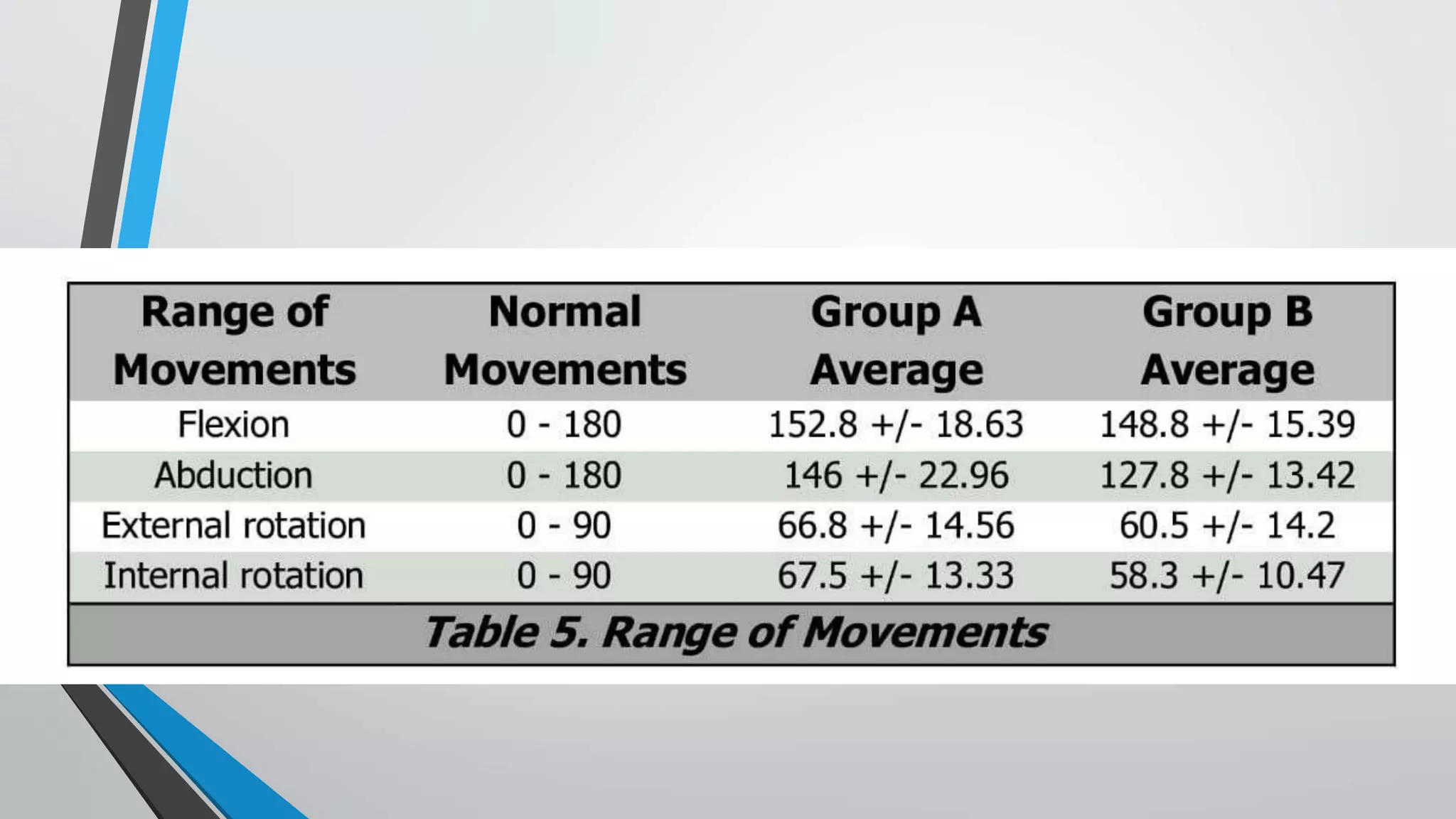
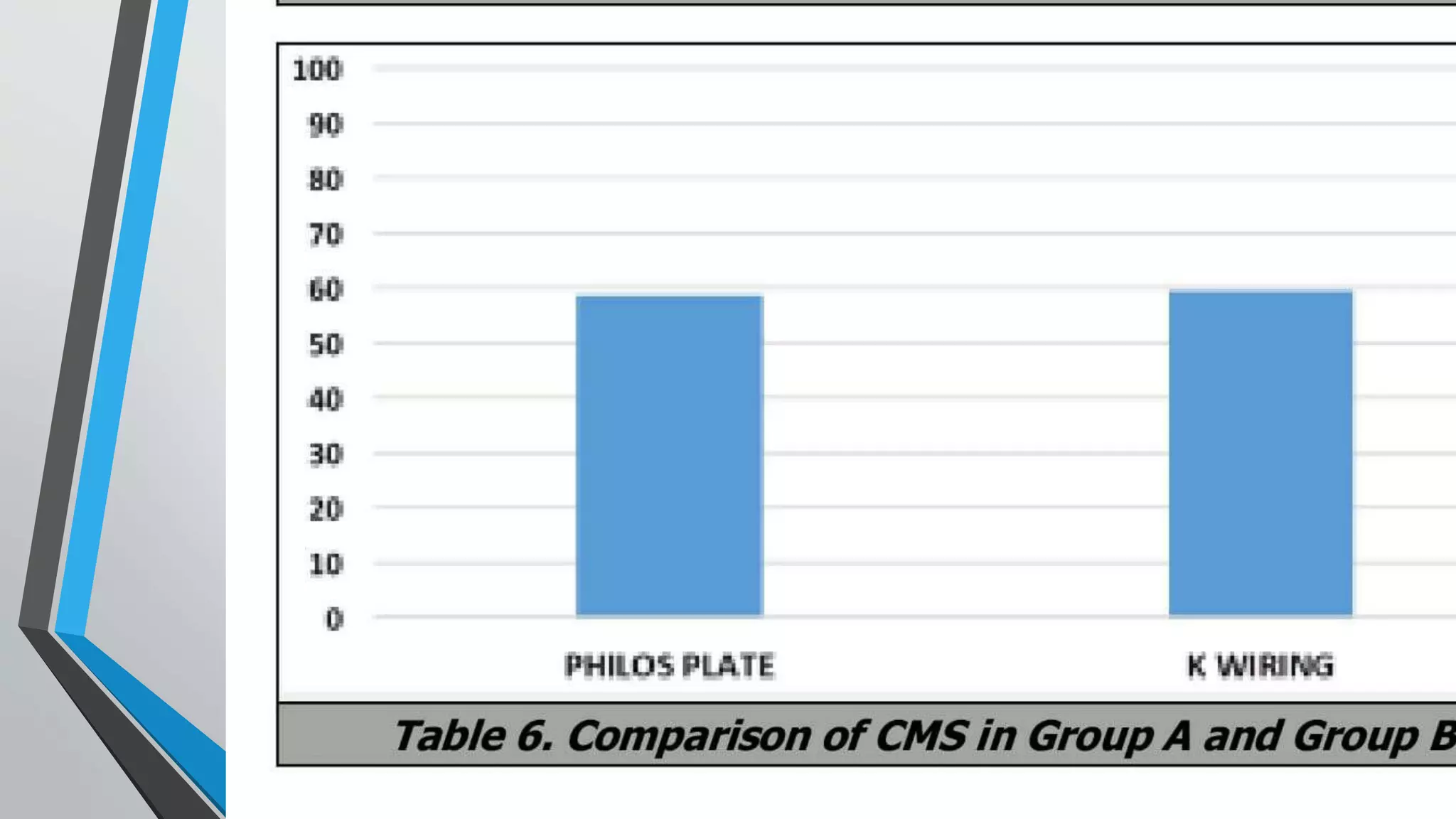
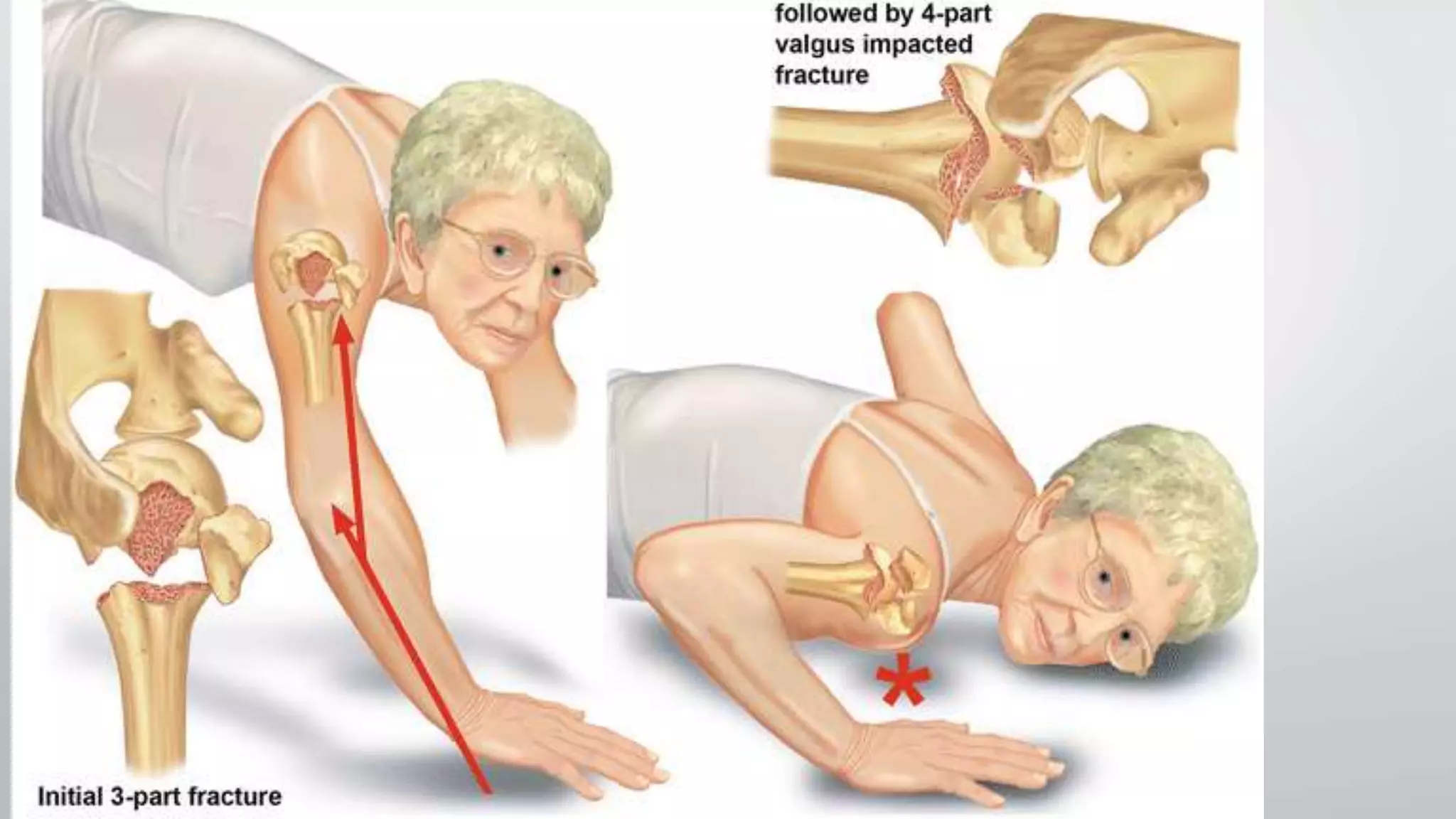
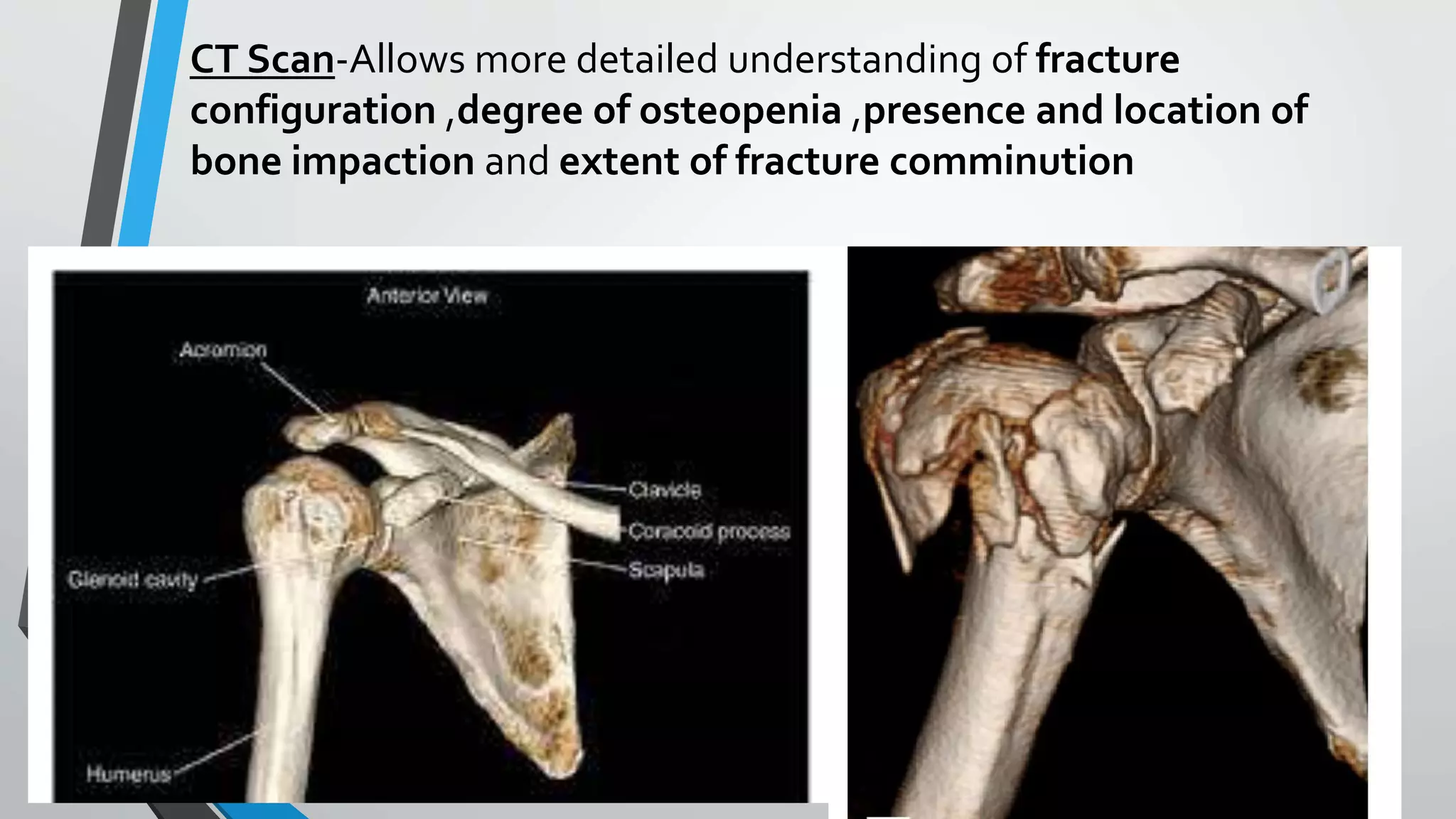
This document presents a comparative study of open reduction with internal fixation (ORIF) using a Philos plate versus closed reduction with percutaneous K-wiring for treating Neer's 2-part and 3-part proximal humerus fractures. The study involved 40 cases and evaluated clinical, functional, and radiological outcomes, ultimately finding no significant difference in scores between the two methods, although Philos plate fixation allowed for better radiological results. The study concludes that both techniques are effective, with K-wire fixation being preferred due to its less invasive nature and reduced surgical trauma.

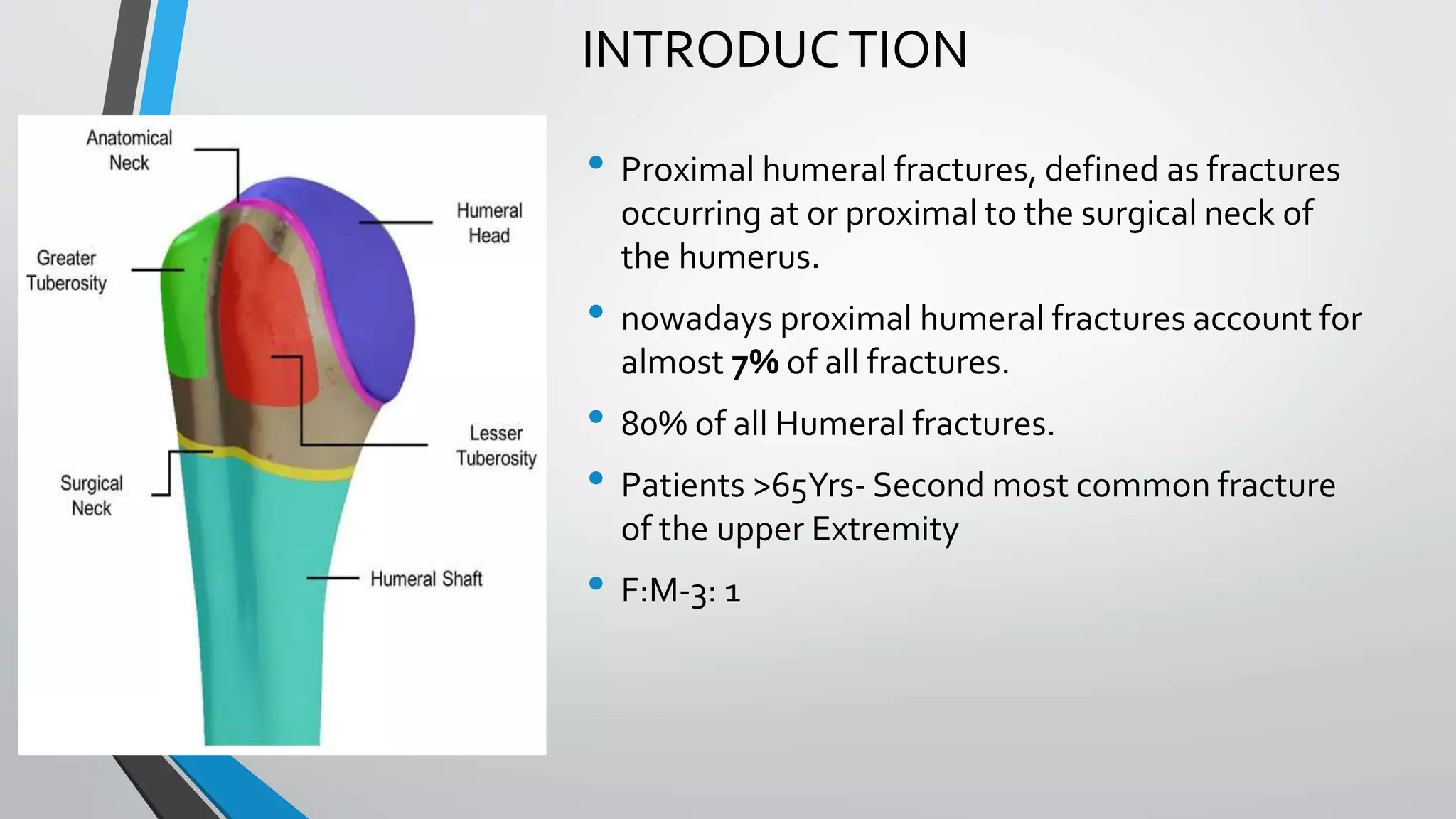
![PATHOANATOMY
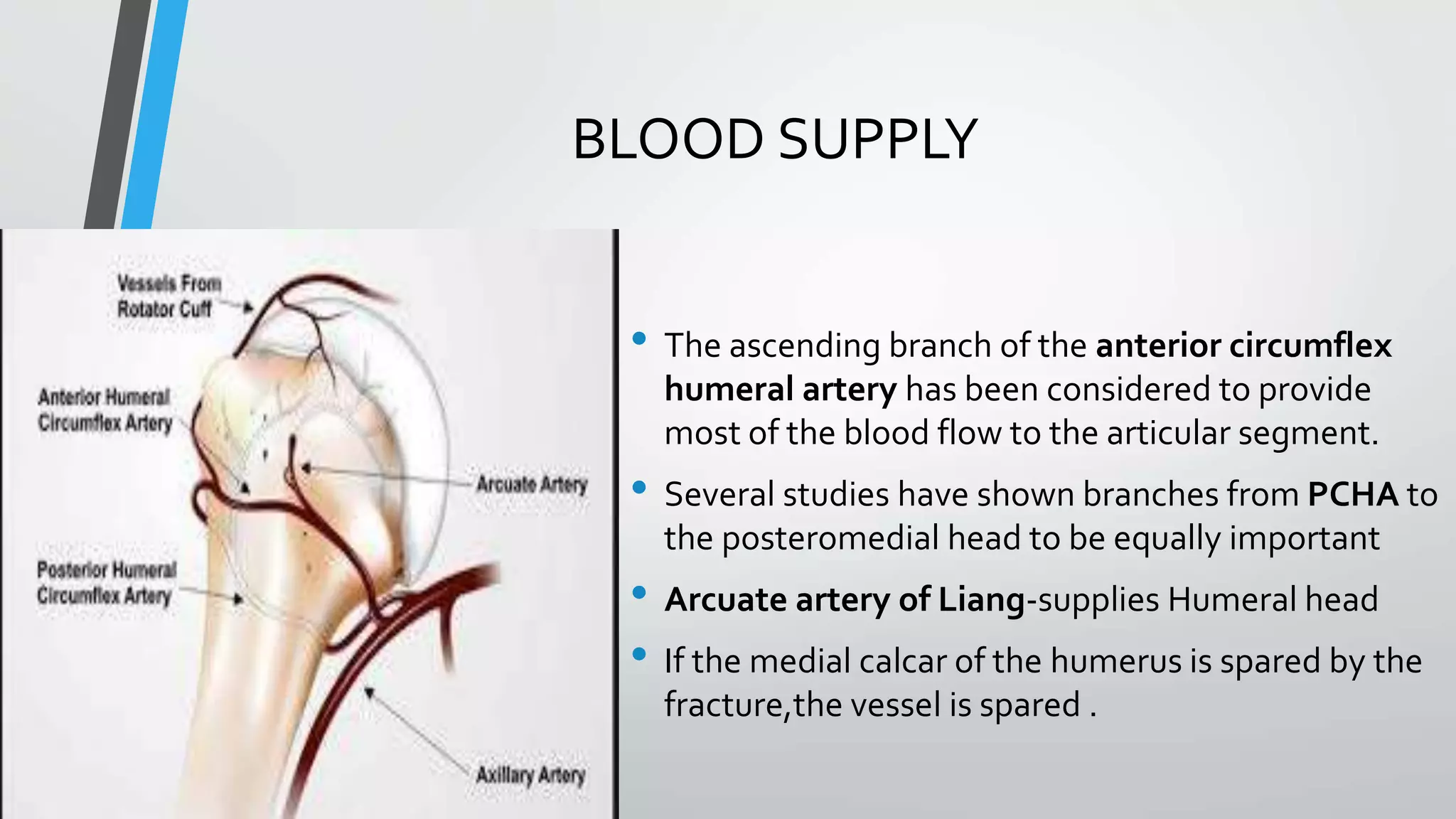
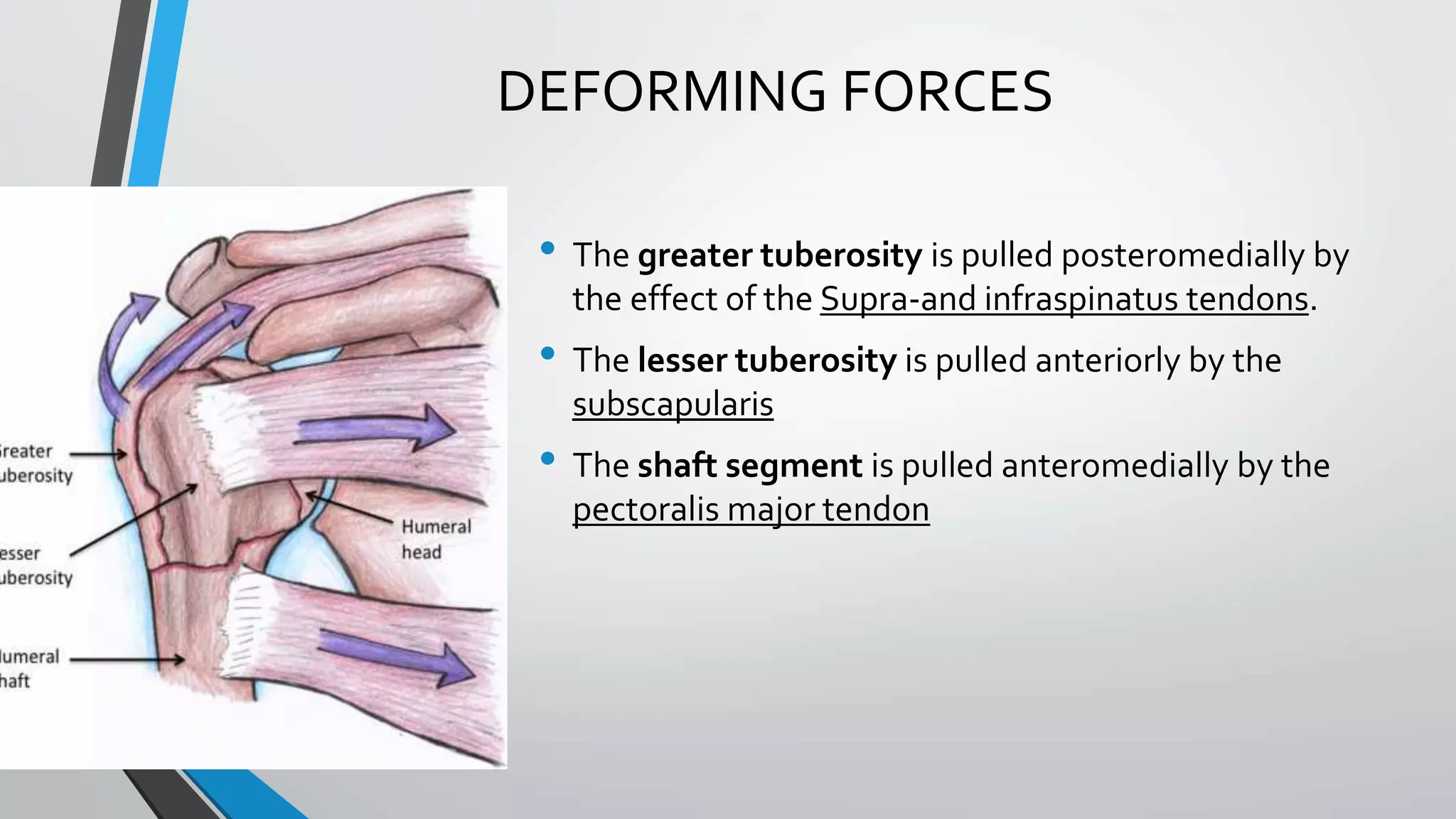
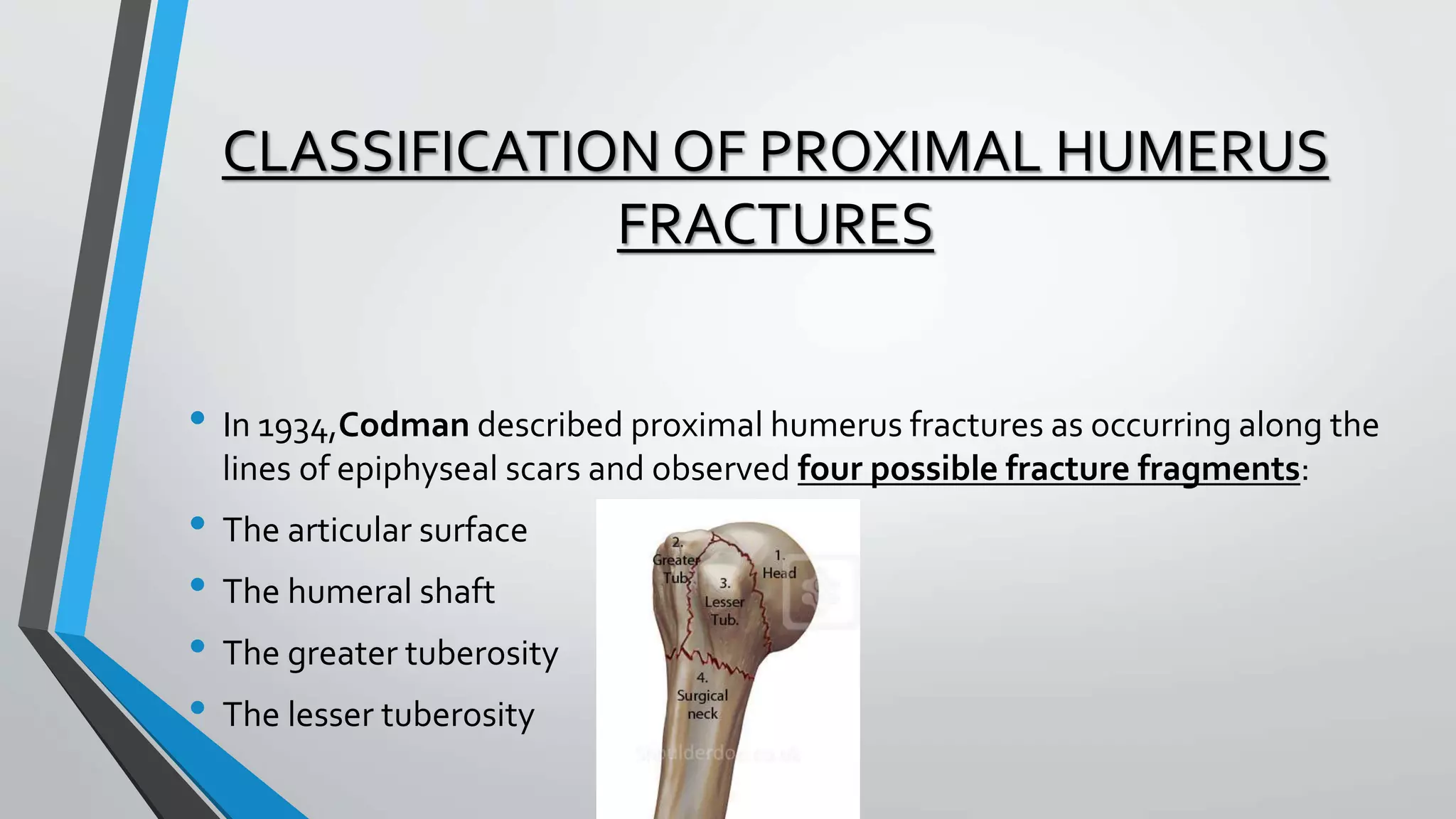
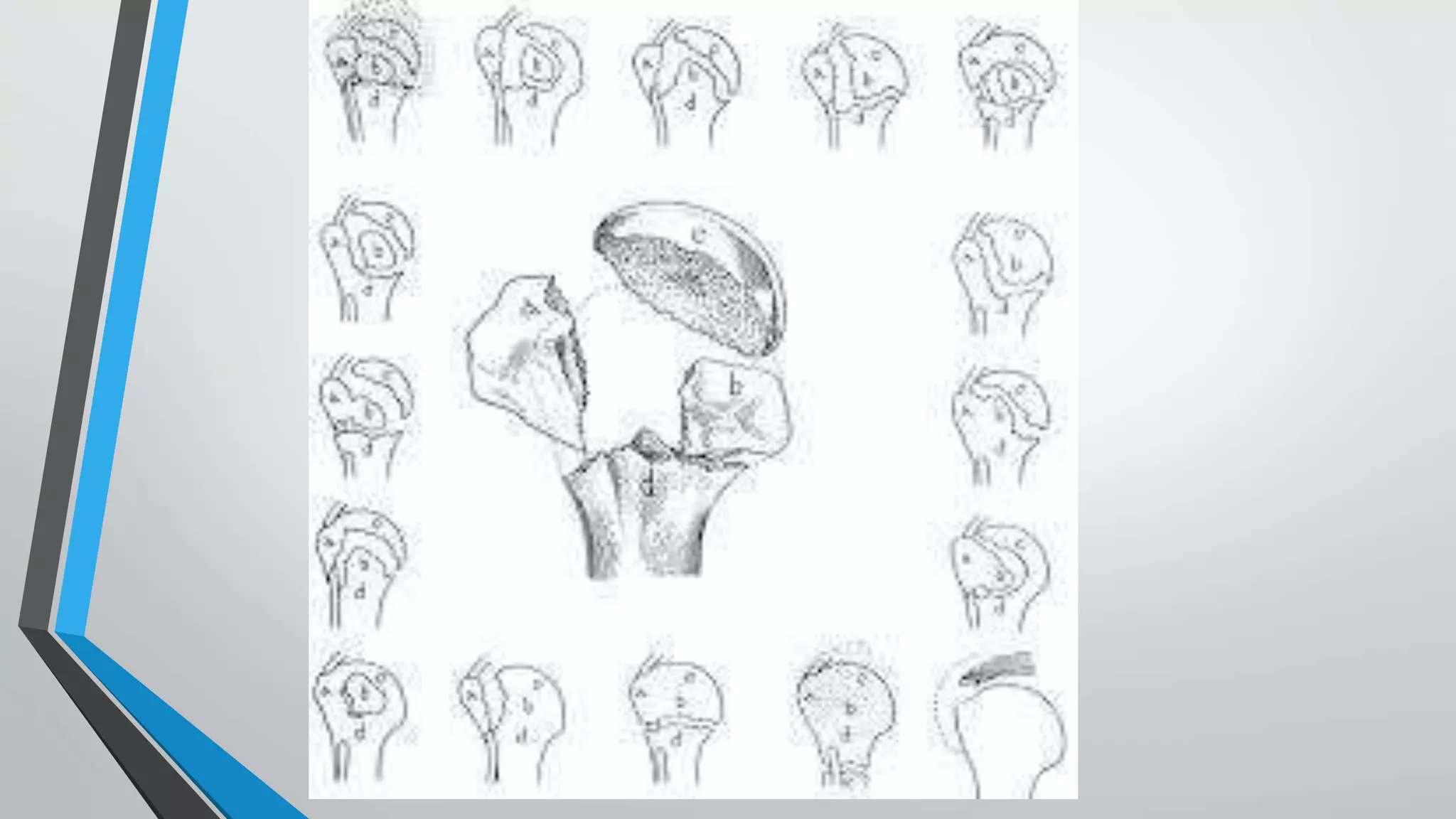
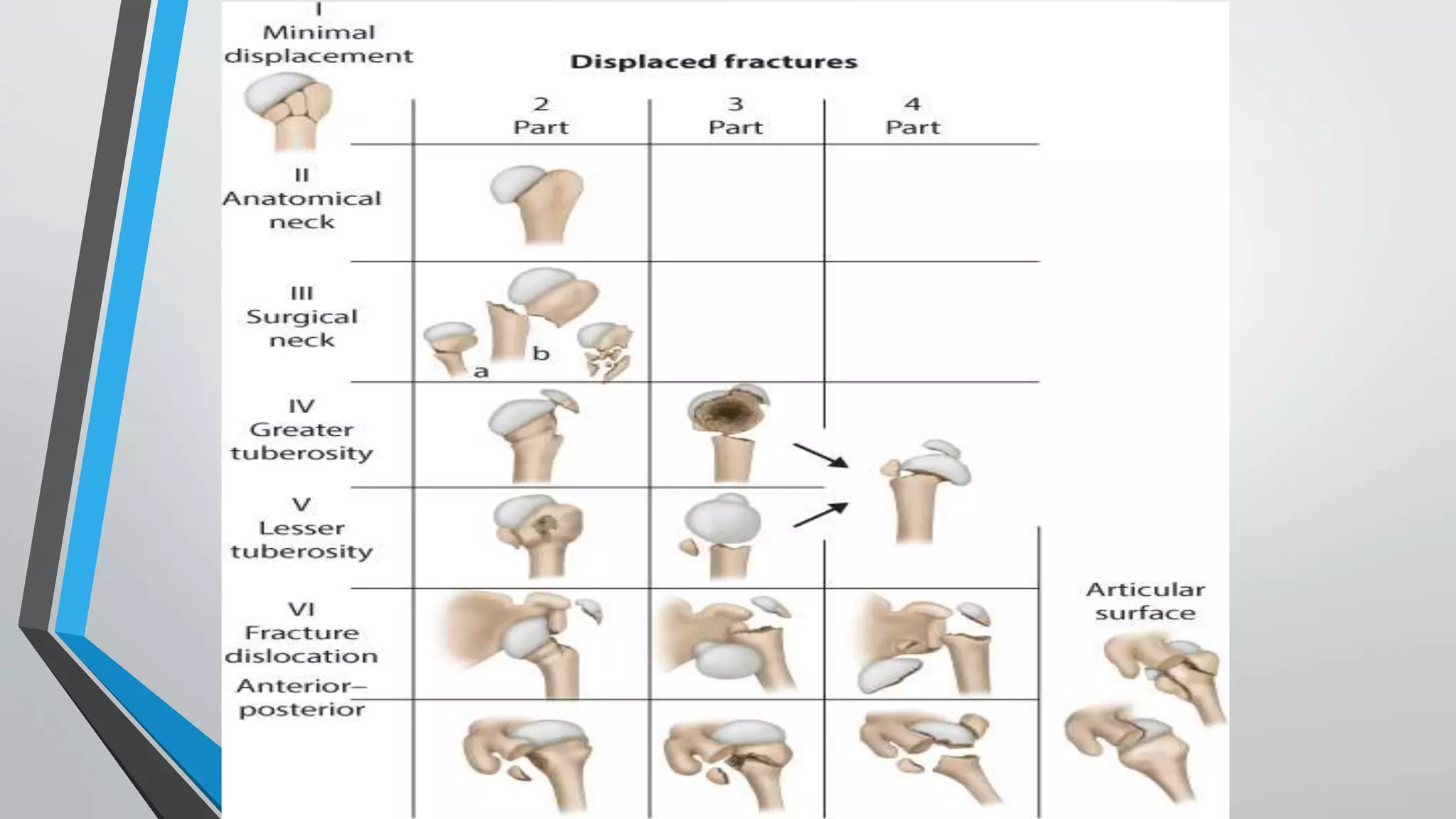
• The region of transition between the articular cartilage and
surrounding bone is defined as the anatomic neck
• whereas the region immediately inferior to the
tuberosities is termed the surgical neck
• Articular Segment is almost spherical, with a diameter of
curvature averaging 46 mm (Ranging from 37 to 57 mm)
• Inclination of the humeral head relative to the Shaft
averages 130°(centrum collum diaphyseal angle[CCD]
• Retroversion of the head varies from 18 to 40°](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bbala20a20comparative20study20of20orif20with20philos20plate-230701044335-29535636/75/Comparative-study-of-ORIF-with-philos-plate-vs-CRIF-with-k-wiring-of-Neers-2part-and-3part-proximal-humerus-fractures-3-2048.jpg)
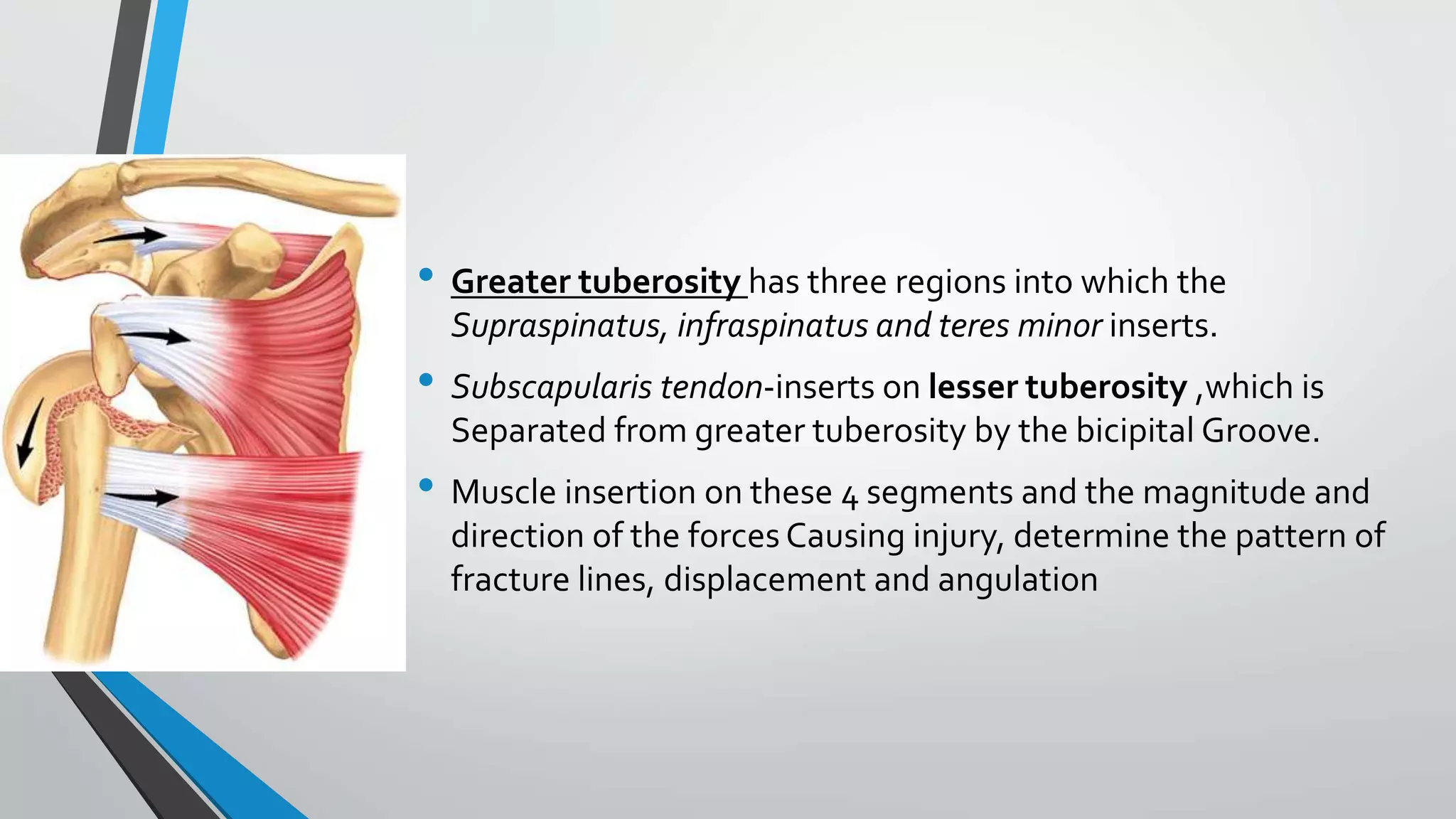














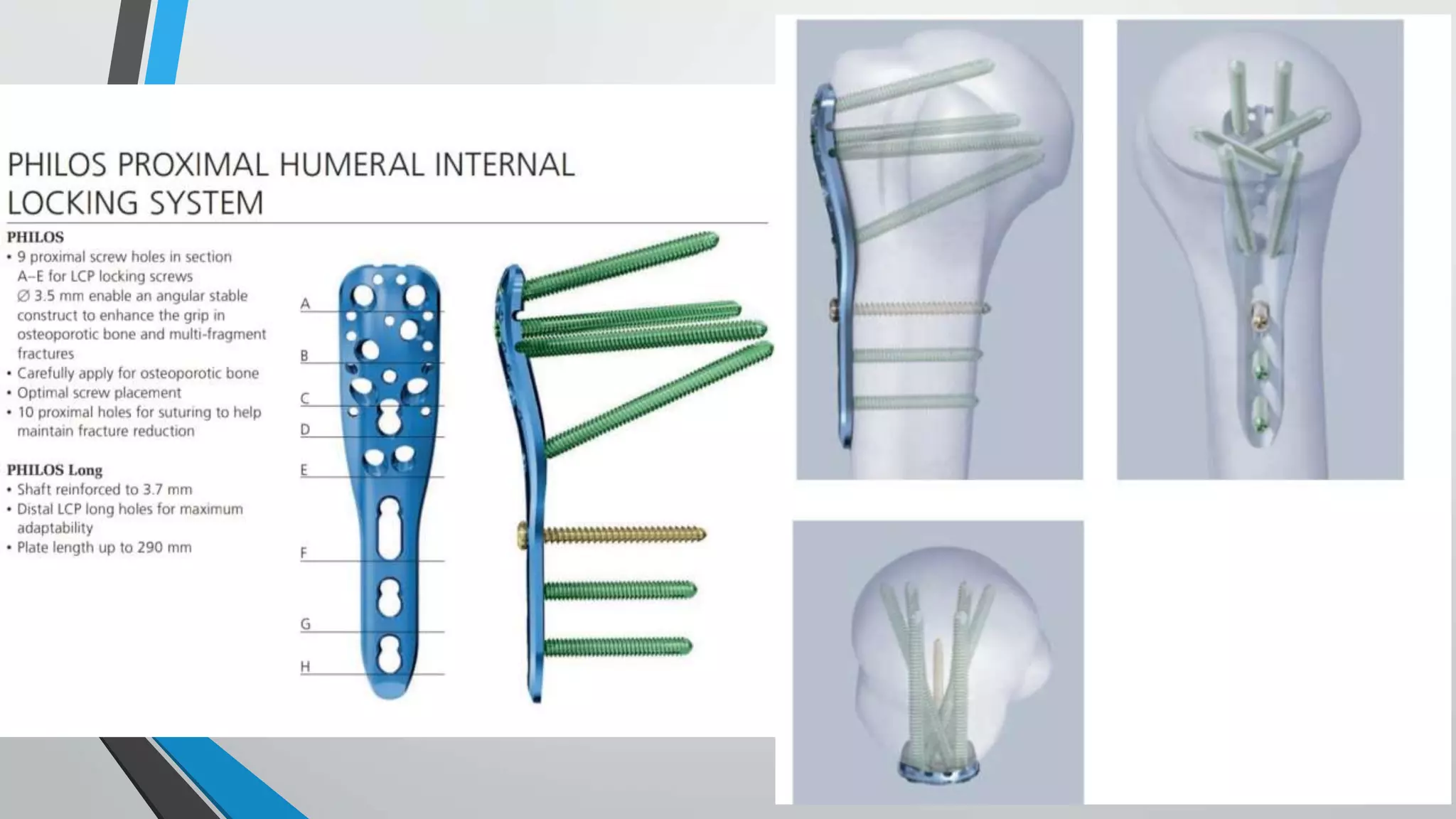
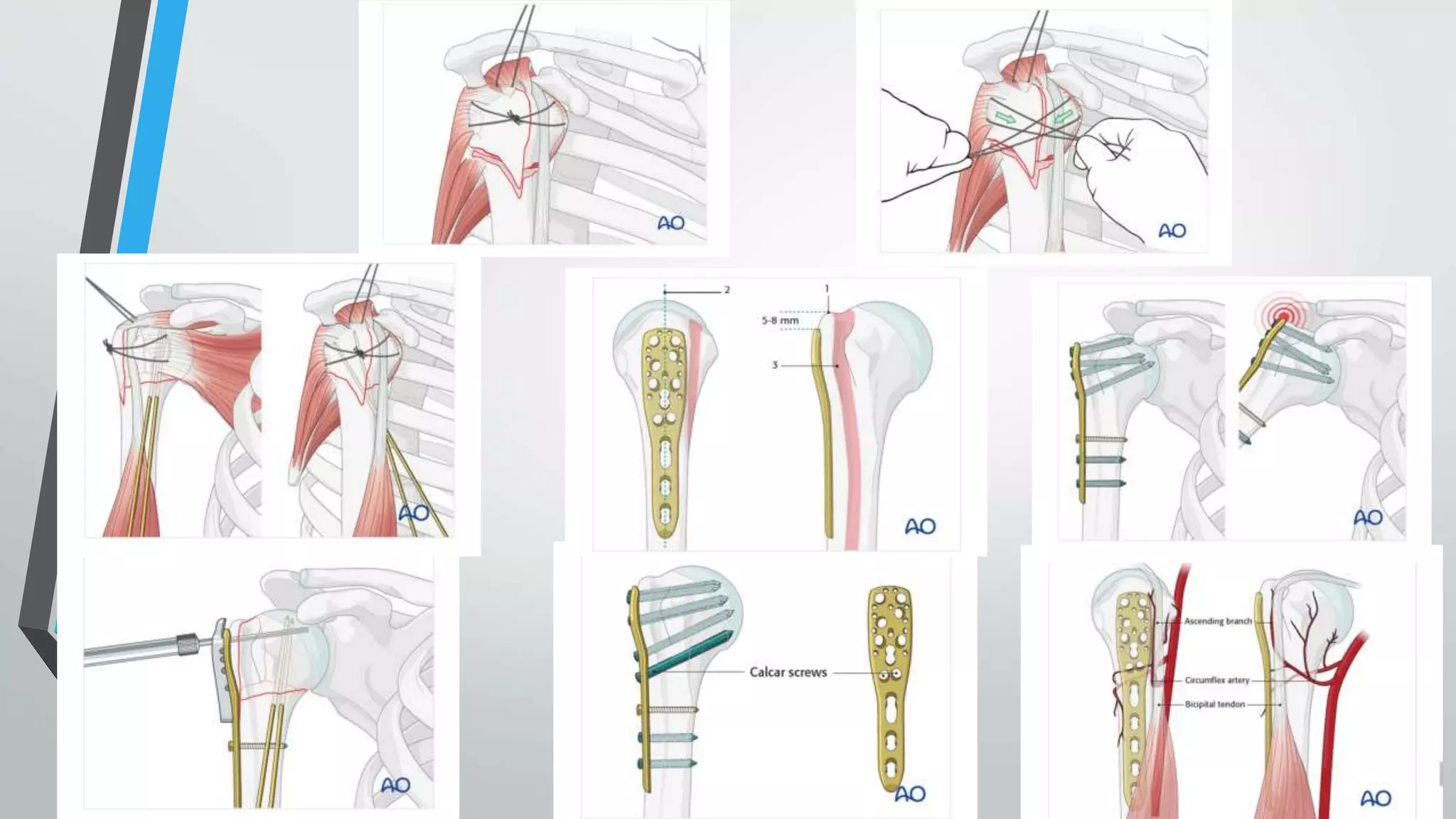
![Fixation using proximal humerus locking
plate[PHILOS PLATING]
• The inability of conventional plates and screws to resist varus deforming forces in the
proximal humerus,particularly if the bone is osteoporotic ,has led to locking plate fixation
being used for these fractures
• Several clinical studies have shown high rates of healing and excellent functional
recovery with proximal humerus locking plates.
• Plate designs vary in terms of the number of proximal screws and their arrangement ,as
well as the ability to place screws at different angles with regard to the plate
• A plate is selected to allow at least three screws to be placed into the distal shaft
segment .the plate position is also selected to avoid subacromial impingement and to
allow two screws to be placed into inferomedial aspect of the humeral head
• A minimum of five or six screws are routinrly placed into the proximal segment .screw
placement should be performed by drilling through the near cortex only,this avoids
perforation of the articular surface.
• Once the plate and the screws have been placed transtendinous sutures are tied onto
the plate to provide additional fixation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bbala20a20comparative20study20of20orif20with20philos20plate-230701044335-29535636/75/Comparative-study-of-ORIF-with-philos-plate-vs-CRIF-with-k-wiring-of-Neers-2part-and-3part-proximal-humerus-fractures-35-2048.jpg)