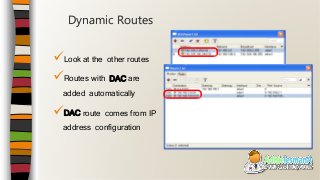
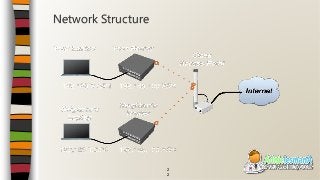
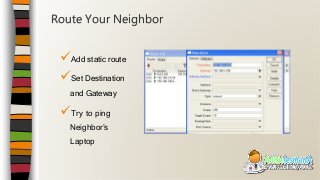
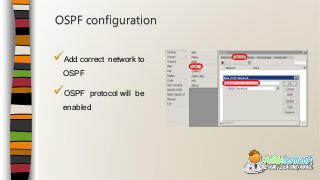
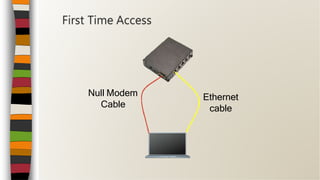
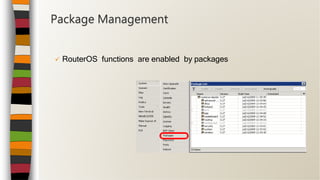
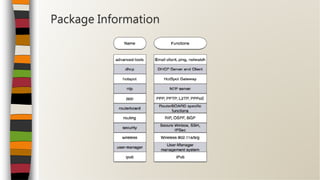
This document provides an overview of an introductory training class on MikroTik router configuration. It discusses MikroTik's history as a router software and hardware manufacturer, the capabilities of their RouterOS software and RouterBoard hardware, and how to connect to and configure a MikroTik router using Winbox. The training covers topics like the MikroTik interface, network addressing, static and dynamic routing, and basic router management tools.







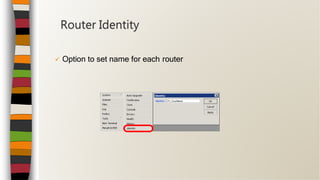
![• Click on the [...] button to see your router
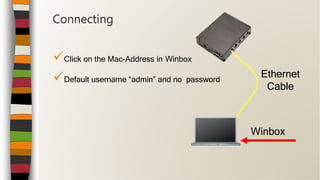
Connecting](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mikrotikbasictrainingclass-170903100040/85/MikroTik-Basic-Training-Class-Online-Moduls-English-14-320.jpg)










![Additionally use export and import commands in CLI
Export files are editable
Passwords are not saved with export
/export file=conf-august-2009
/ ip firewall filter export file=firewall-aug-2009
/ file print
/ import [Tab]
Configuration Backup](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mikrotikbasictrainingclass-170903100040/85/MikroTik-Basic-Training-Class-Online-Moduls-English-33-320.jpg)