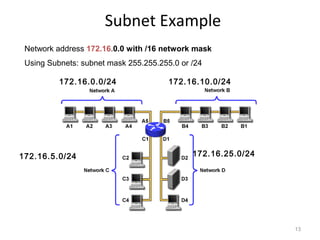
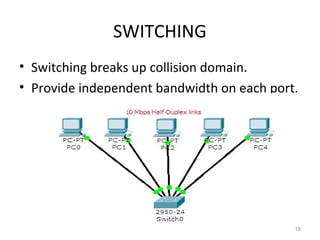
This document provides an overview of managing a Cisco network. It discusses CCNA certification which validates skills in installing, configuring, operating and troubleshooting switched and routed networks. It also covers topics like internetworking which connects different networks, IP addressing classes, subnetting to increase networks, routing protocols like RIP, EIGRP, OSPF, switching, VLANs, interVLAN routing, and STP to prevent network loops.