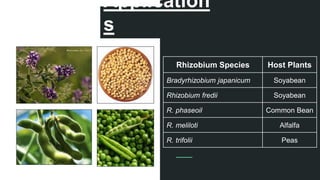
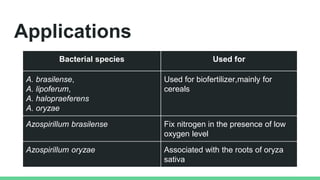
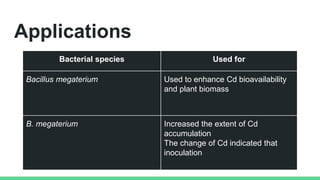
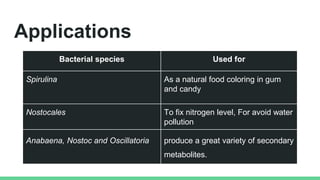
This document discusses various types of microorganisms used in biofertilizers, including their functions, mechanisms, and applications. It describes rhizobium bacteria that fix atmospheric nitrogen through a symbiotic relationship with legumes. Azotobacter are free-living nitrogen fixers that also produce plant hormones. Azospirillum fix nitrogen in low-oxygen environments and enhance mineral uptake in plants. Phosphate solubilizing bacteria convert insoluble phosphate into a soluble form through organic acid production. Blue-green algae, or cyanobacteria, can fix carbon and nitrogen through photosynthesis. These microorganisms improve soil properties and provide nutrients to plants, though biofertilizers have a shorter shelf life than chemical fertil