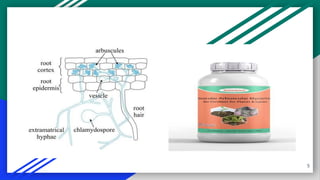
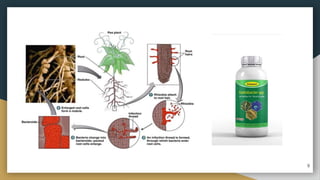
The document discusses biofertilizers, substances containing living microorganisms that enhance plant growth by improving nutrient availability. It covers various types of biofertilizers such as vesicular arbuscular mycorrhiza, phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms, azotobacter, phosphorus biofertilizers, and compost biofertilizers, detailing their roles and benefits to crop yields and soil health. The information is presented as part of an academic curriculum in sericulture.