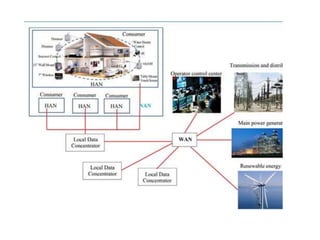
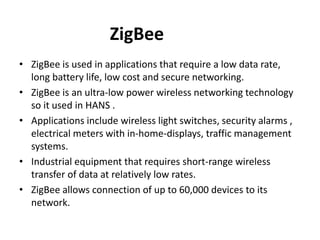
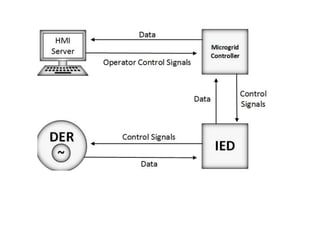
The microgrid communication system uses three types of networks - the Home Area Network (HAN), Neighborhood Area Network (NAN), and Wide Area Network (WAN). The HAN connects smart home devices and meters within a home. The NAN connects multiple HANs within a neighborhood and transmits energy usage data to local data centers. The WAN connects various microgrid components like generation and distribution over a wide area. Communication technologies used include ZigBee for low data HANs, WiFi/PLC for NANs, and Ethernet/WiMAX for high data WANs. Intelligent electronic devices receive DER data and control signals from the microgrid controller.