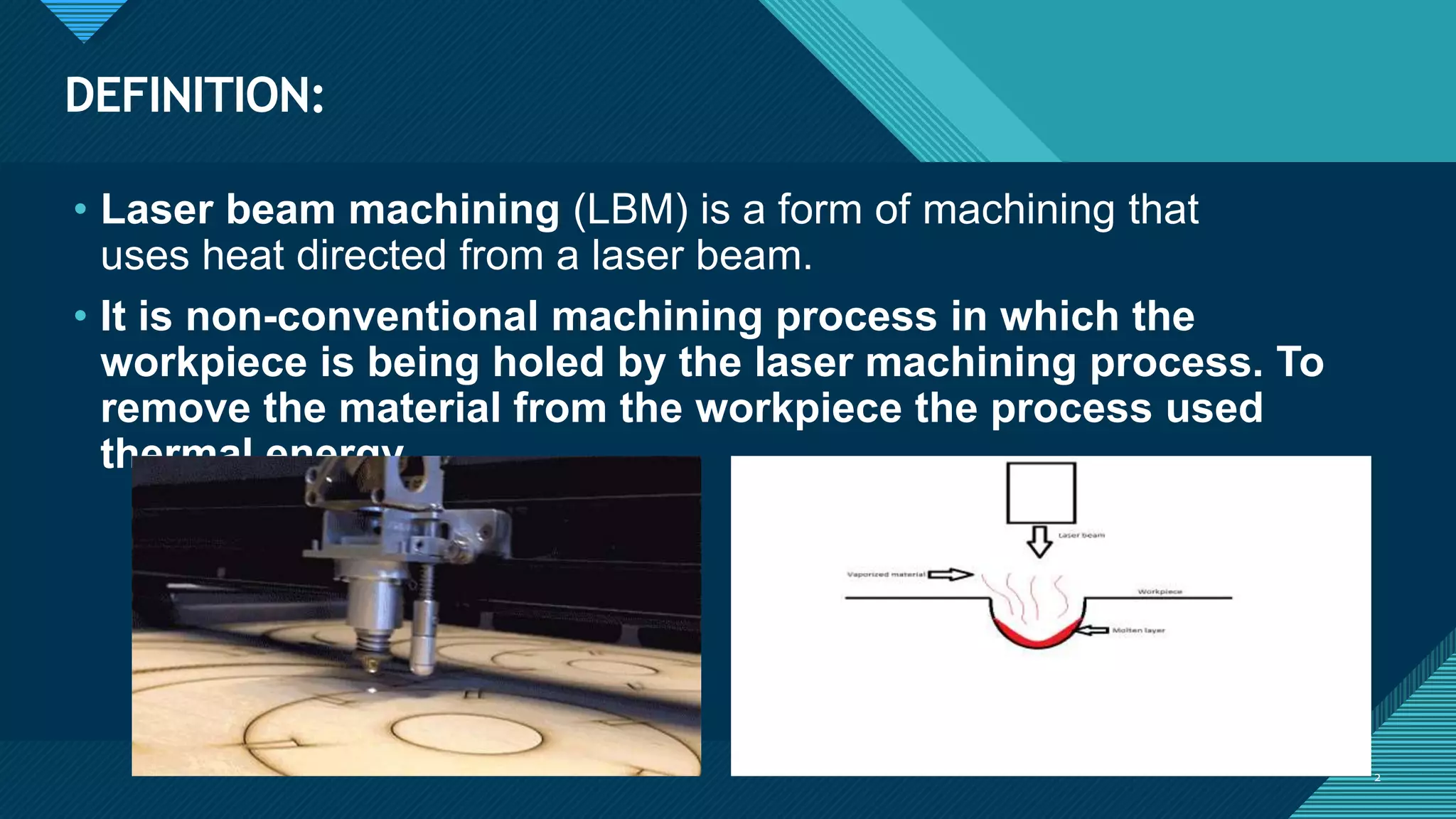
1. Laser beam machining is a non-conventional machining process that uses a laser beam directed by mirrors to remove material from a workpiece through thermal energy.
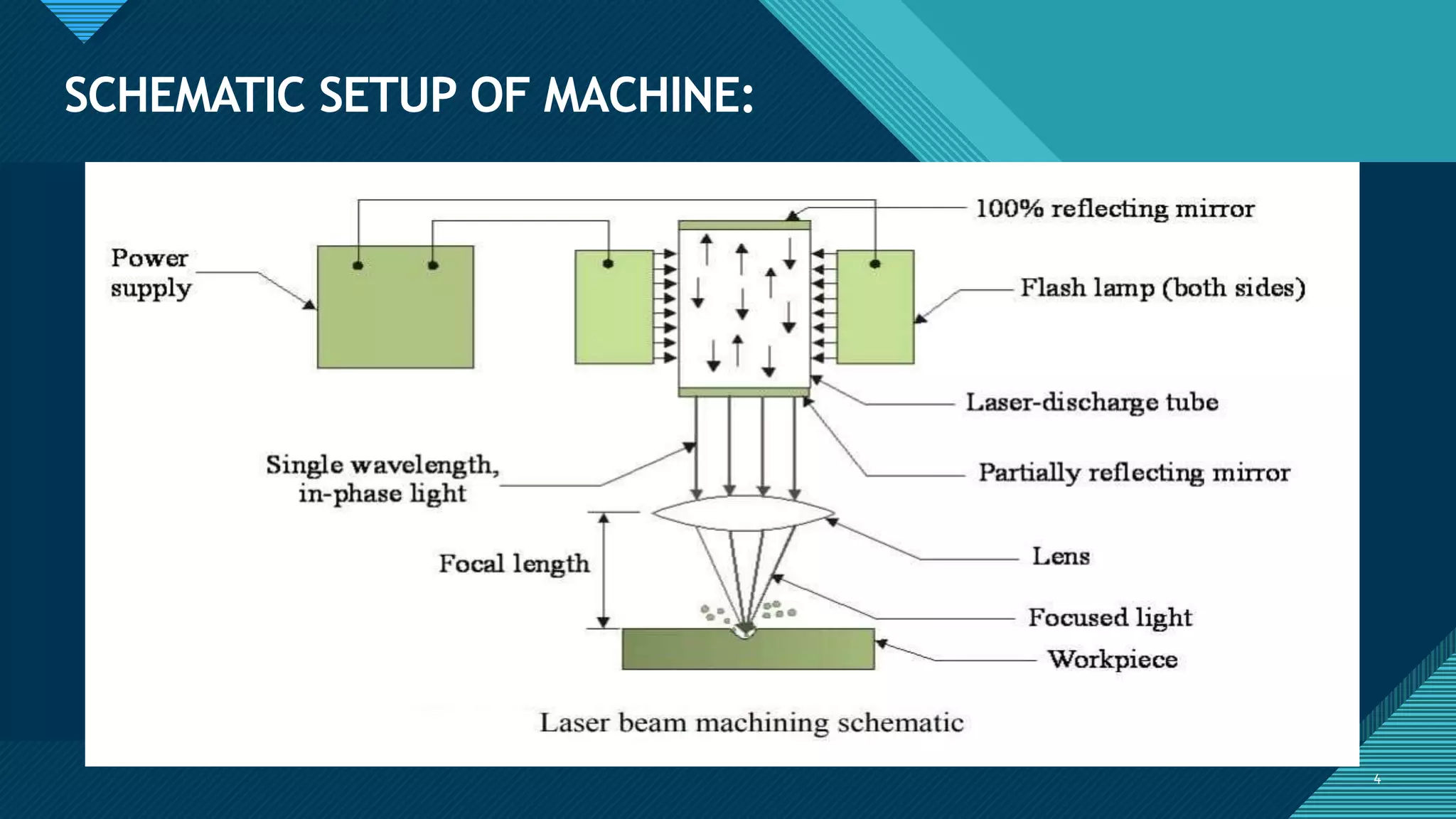
2. The laser beam machining process involves using a power supply to energize flash lamps, which produce intense light to energize lasing materials like ruby crystals. The coherent laser light is focused by lenses onto the workpiece.
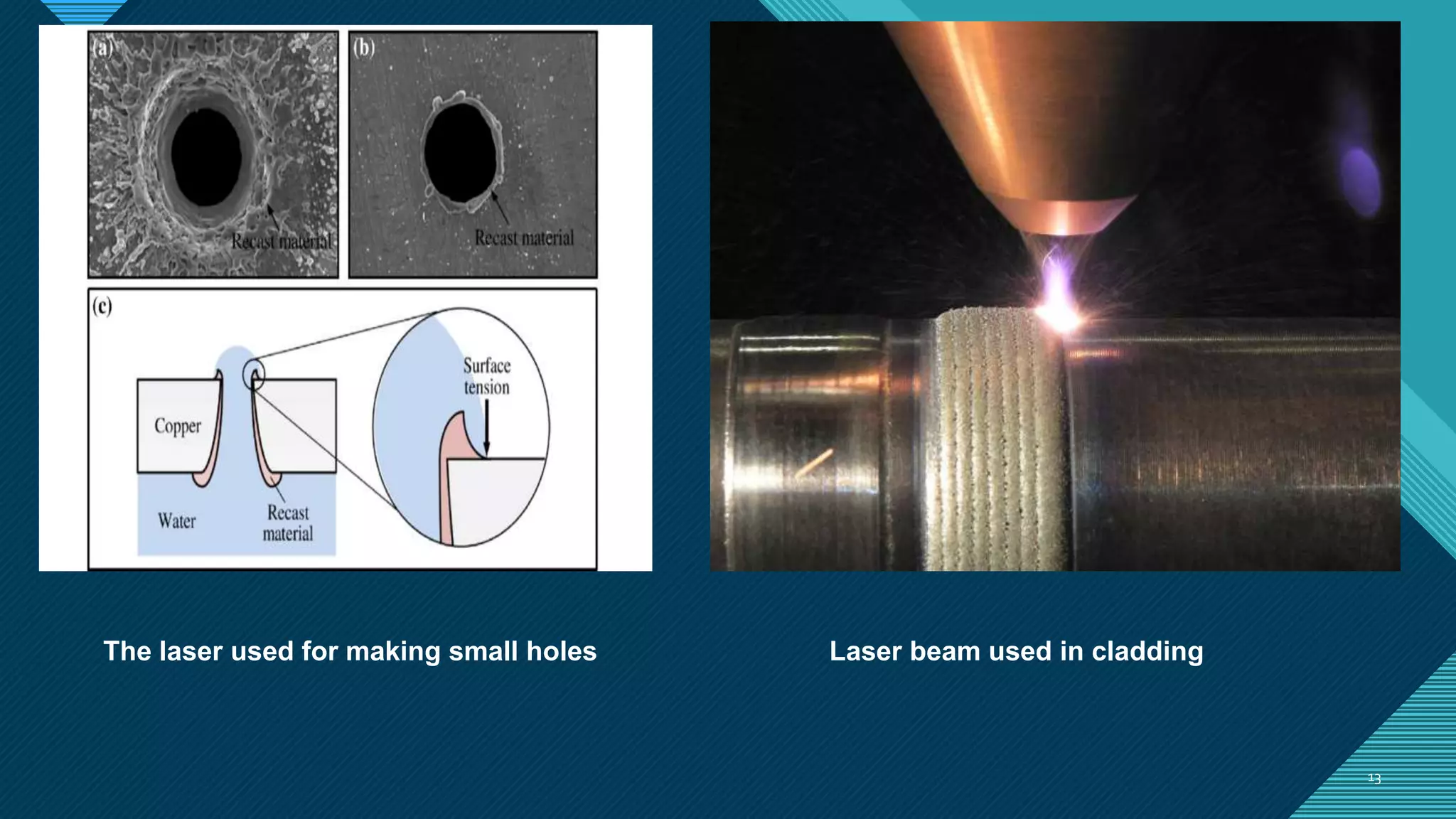
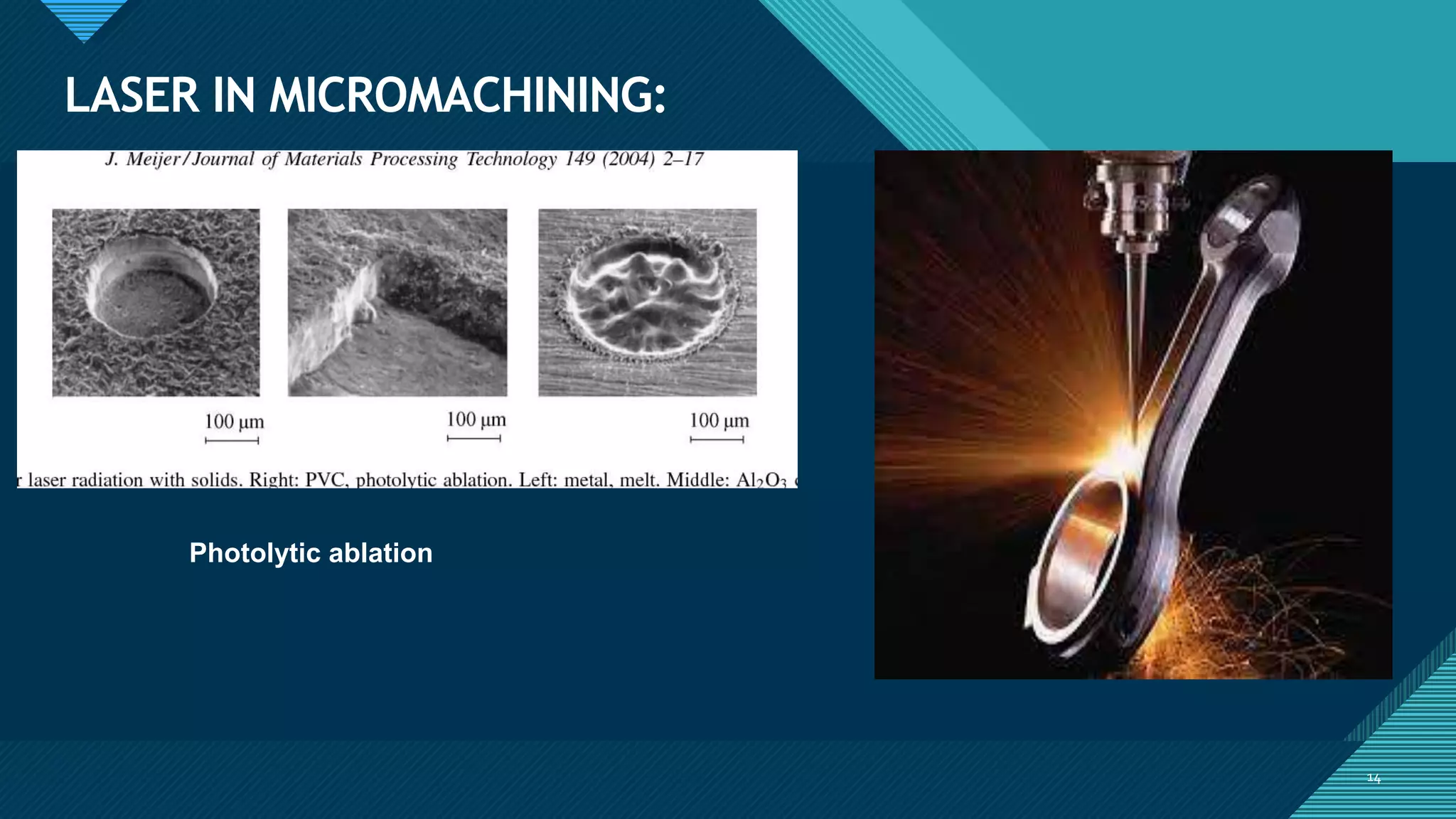
3. Laser beam machining can machine any material with high accuracy and a small heat affected zone. It is used to make small holes and for applications like micro-drilling, welding specialty materials, and medical procedures.