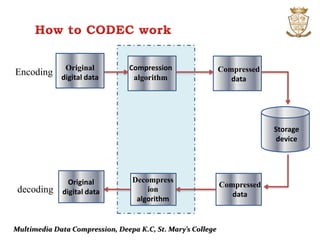
This document discusses multimedia data compression. It explains that multimedia files like images, audio, and video take up significantly more storage space than text files. Data compression reduces the size of files by removing redundant data, saving storage space and allowing faster transfers. Compression is achieved through codecs, which are hardware or software that compresses and decompresses data. Compression can be lossless, allowing exact reconstruction of the original data, or lossy, which sacrifices some quality to achieve greater compression but does not allow exact reconstruction.