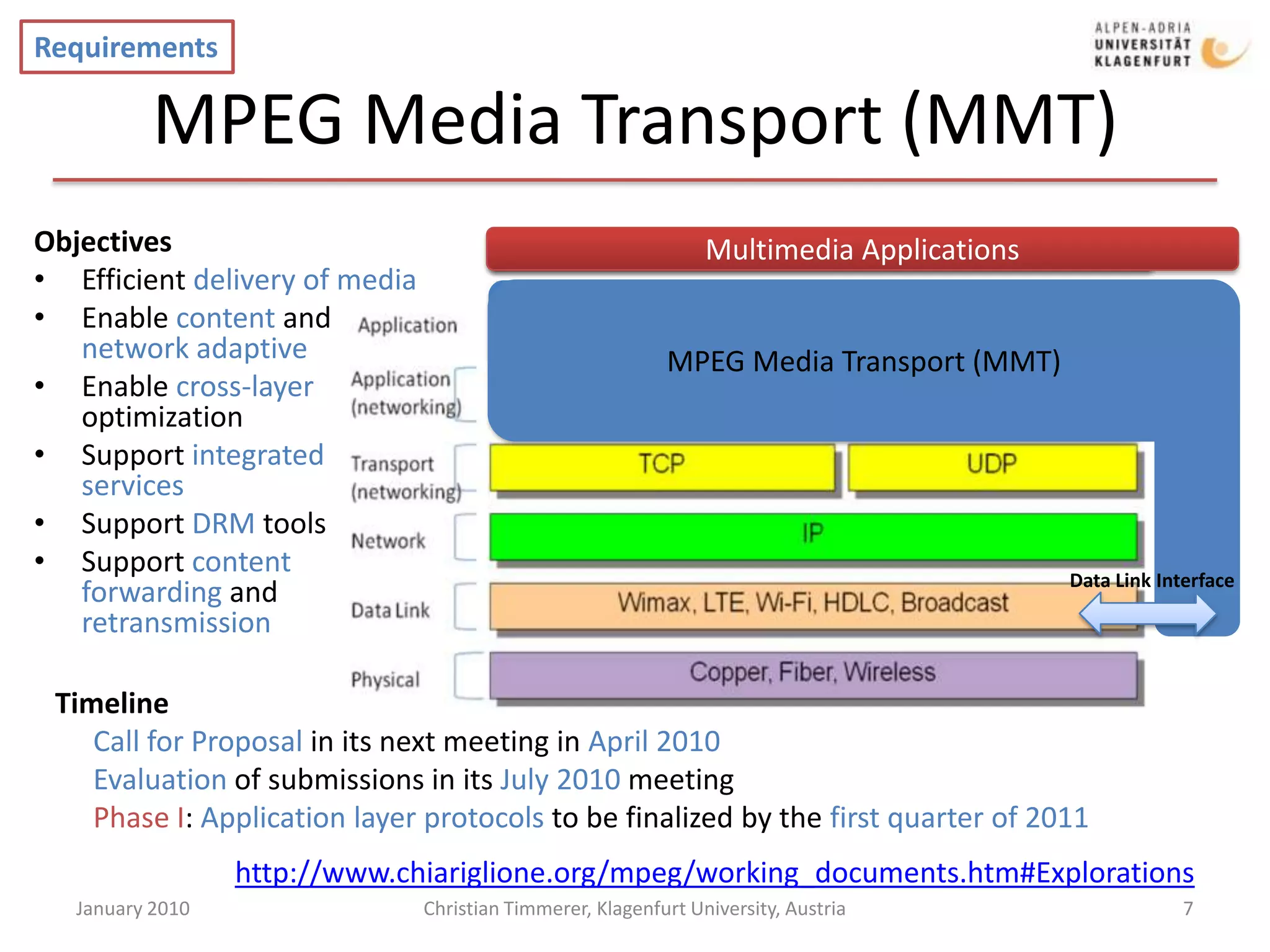
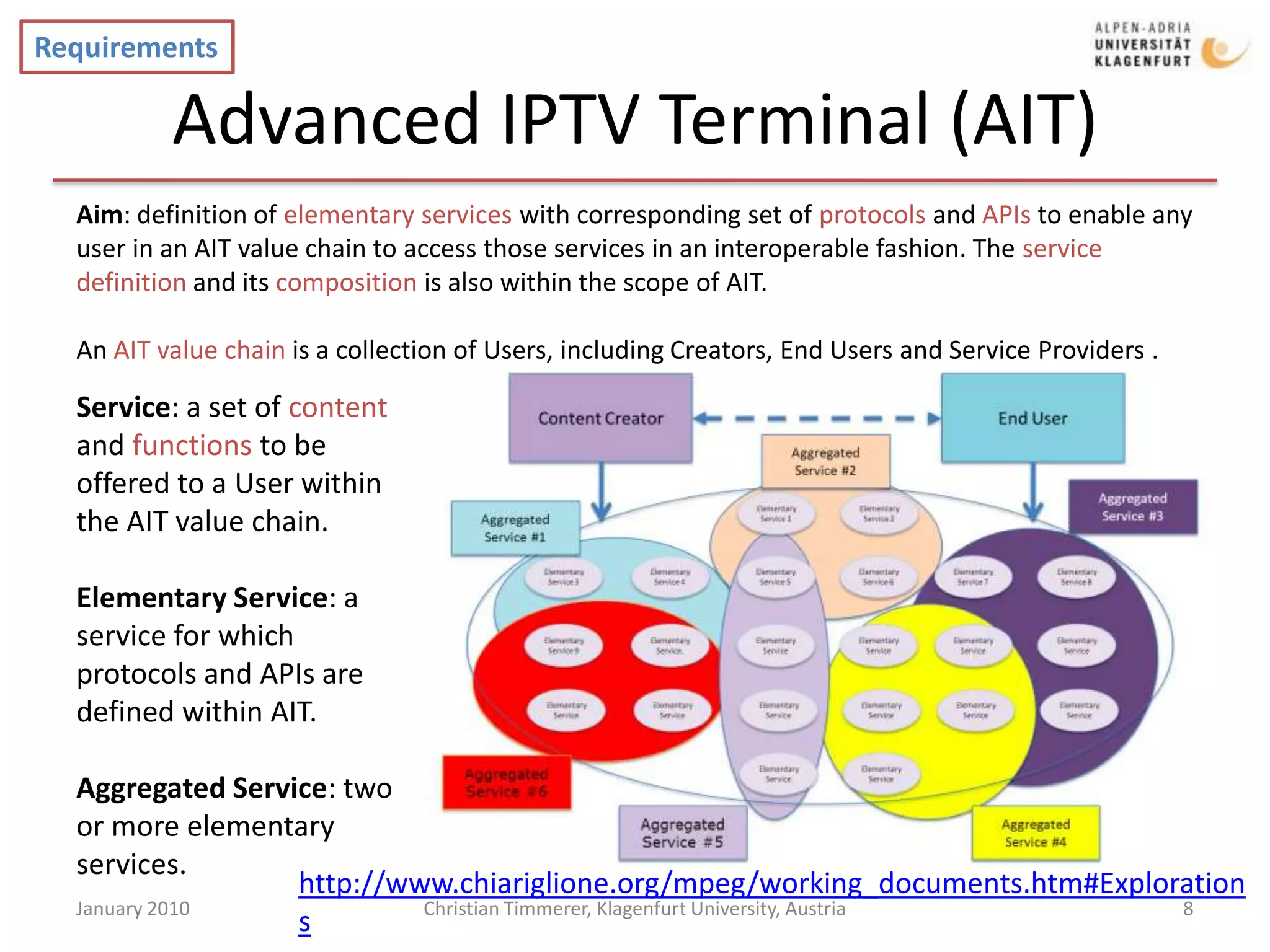
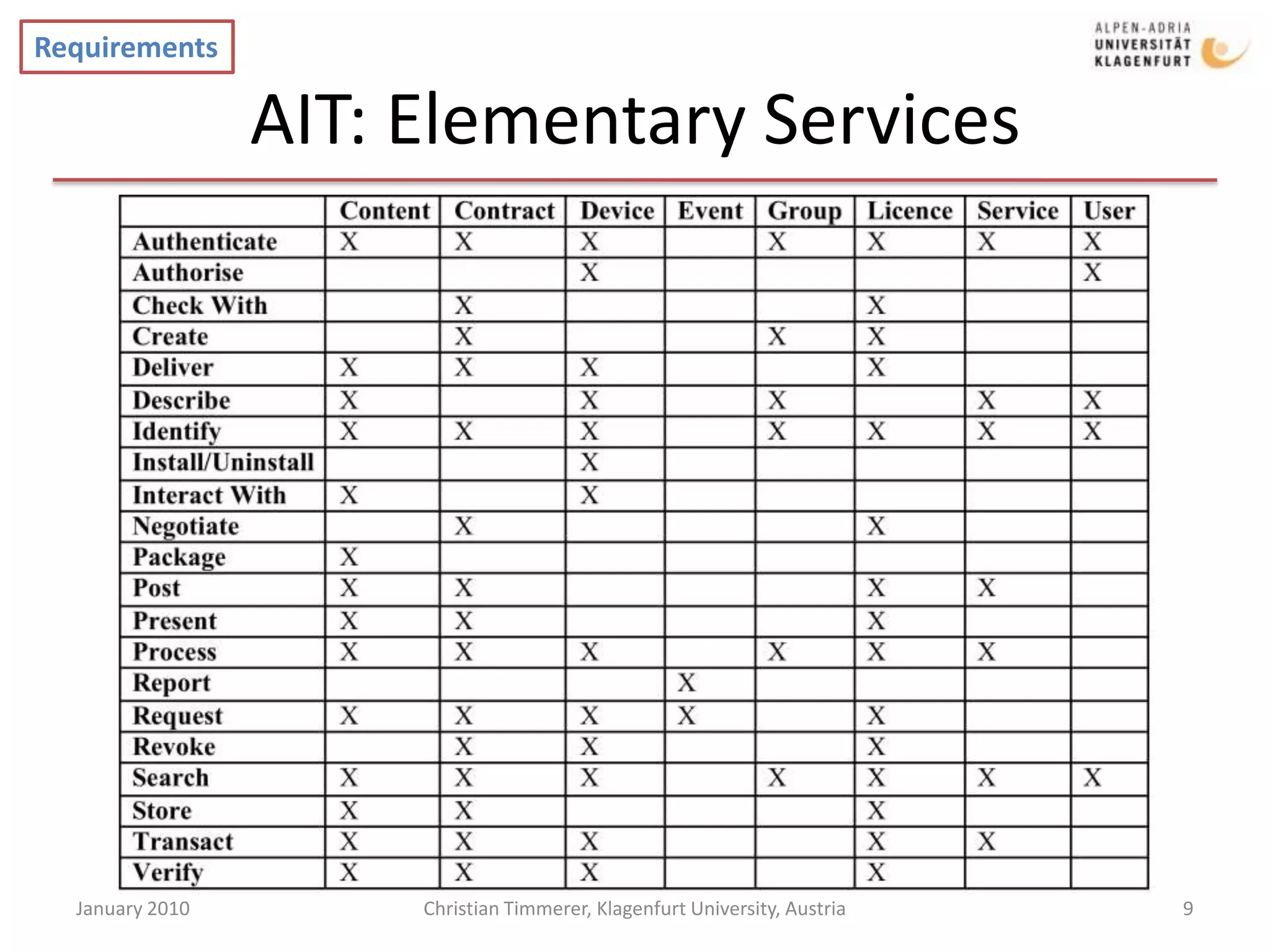
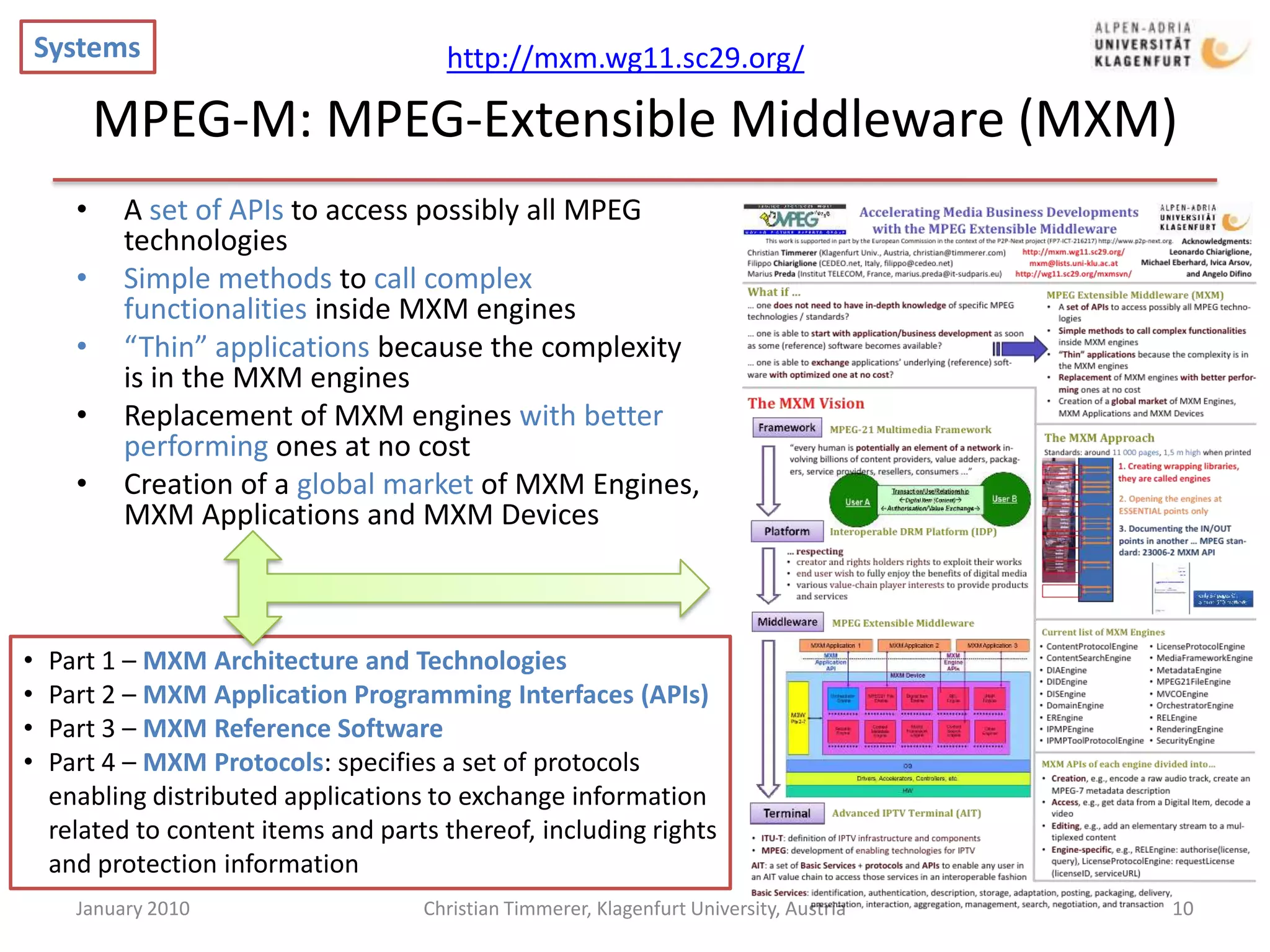
The document provides an overview of selected current activities within MPEG, including requirements and timelines. It discusses the Mobile Visual Search work item which aims to enable efficient transmission of local image features for mobile visual search applications. It also outlines the MPEG Media Transport work item which focuses on efficient delivery of media to enable content and network adaptive streaming. Additionally, it summarizes the Advanced IPTV Terminal work item and its goal of defining elementary services and protocols to enable interoperability.