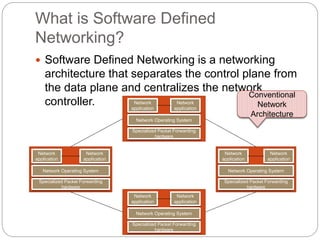
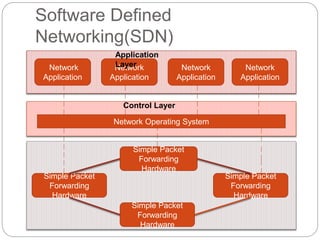
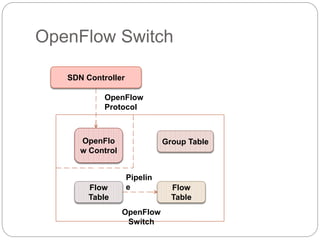
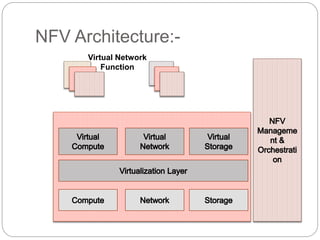
This document discusses the concepts of Software Defined Networking (SDN) and Network Function Virtualization (NFV), highlighting the limitations of conventional network architectures, such as complexity and management overhead. It explains how SDN separates the control and data planes for better manageability and introduces OpenFlow as a key communication protocol. NFV is described as a technology that allows virtualization of network functions, making them independent of the underlying hardware, thus improving efficiency and reducing costs.