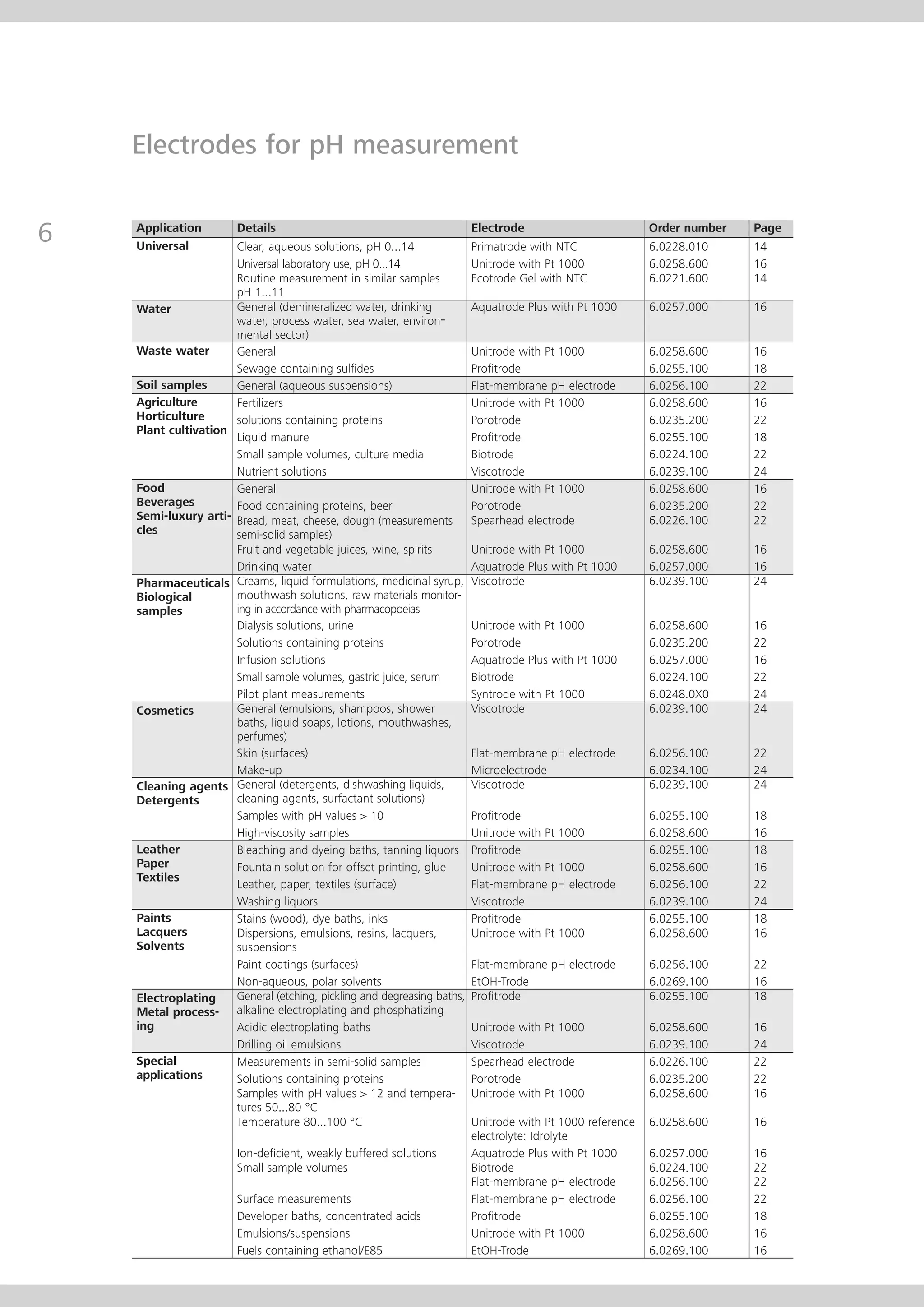
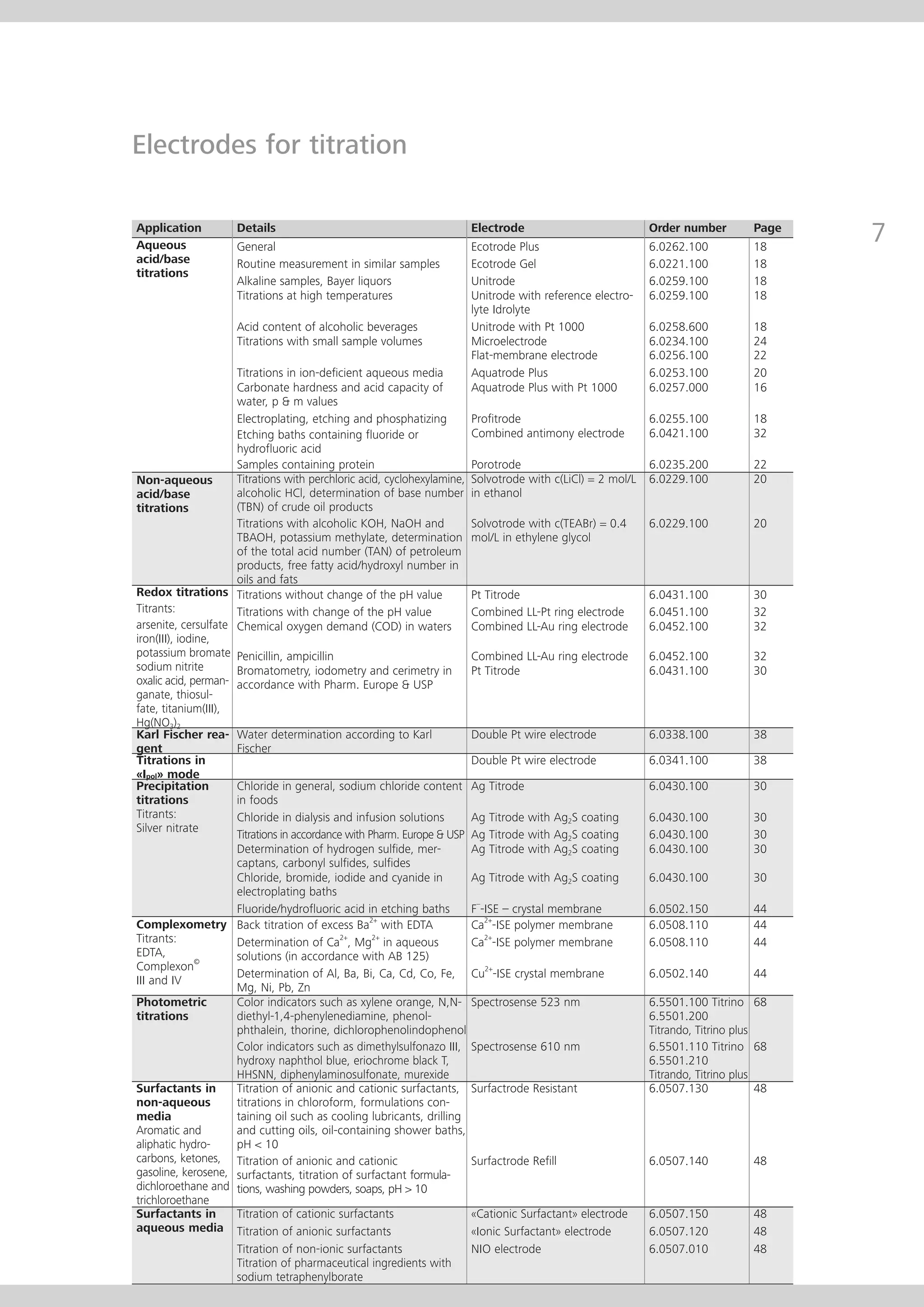
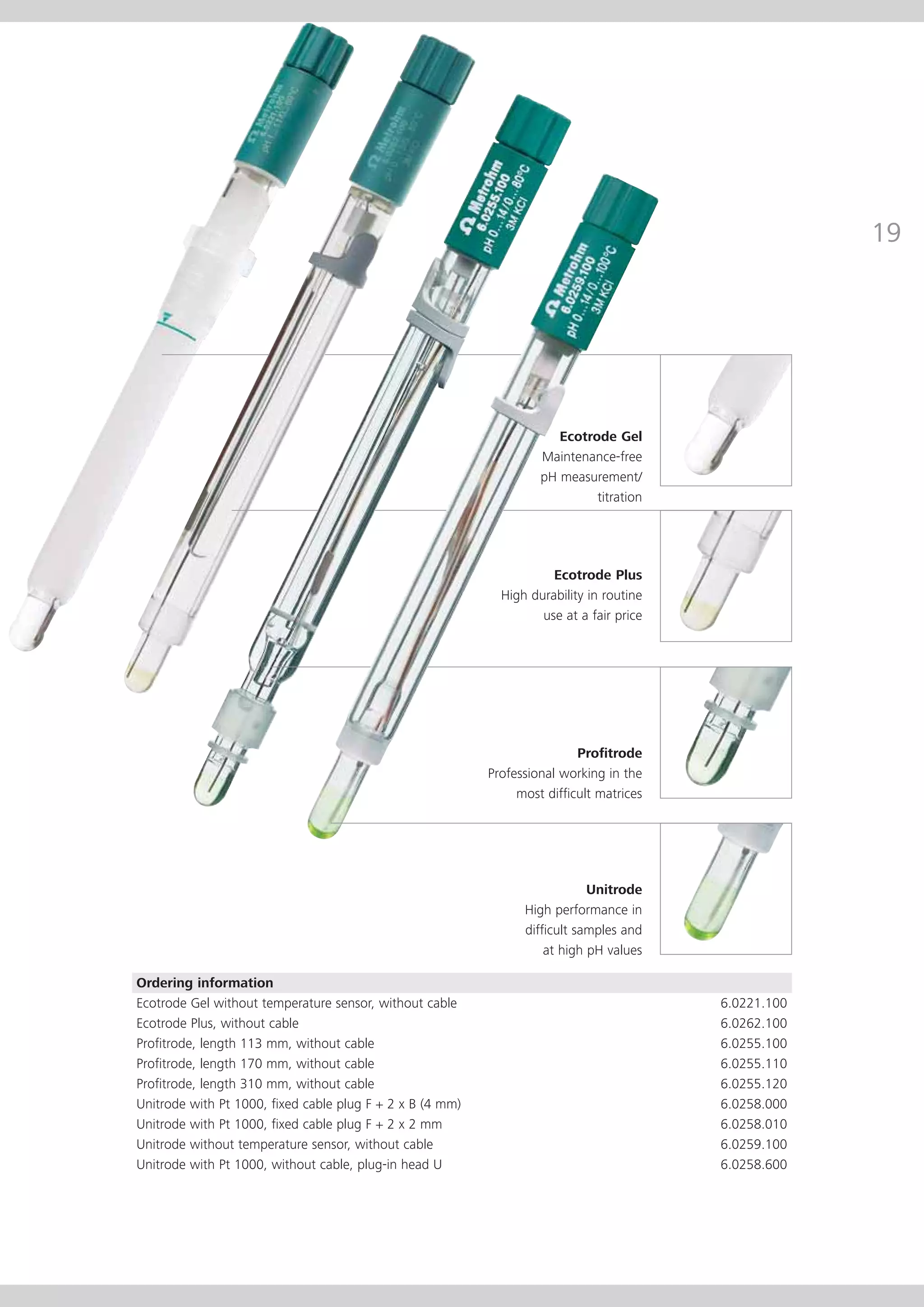
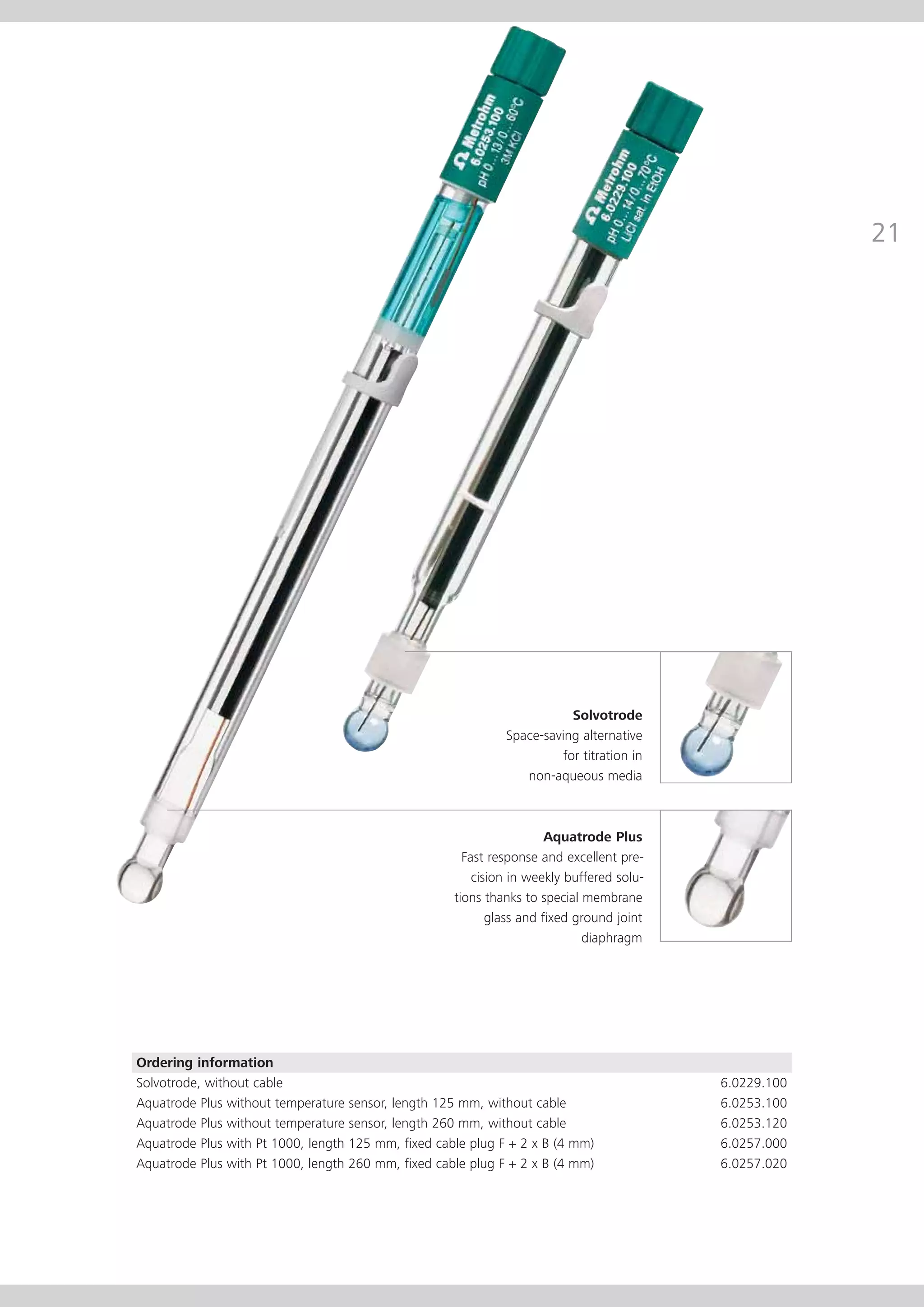
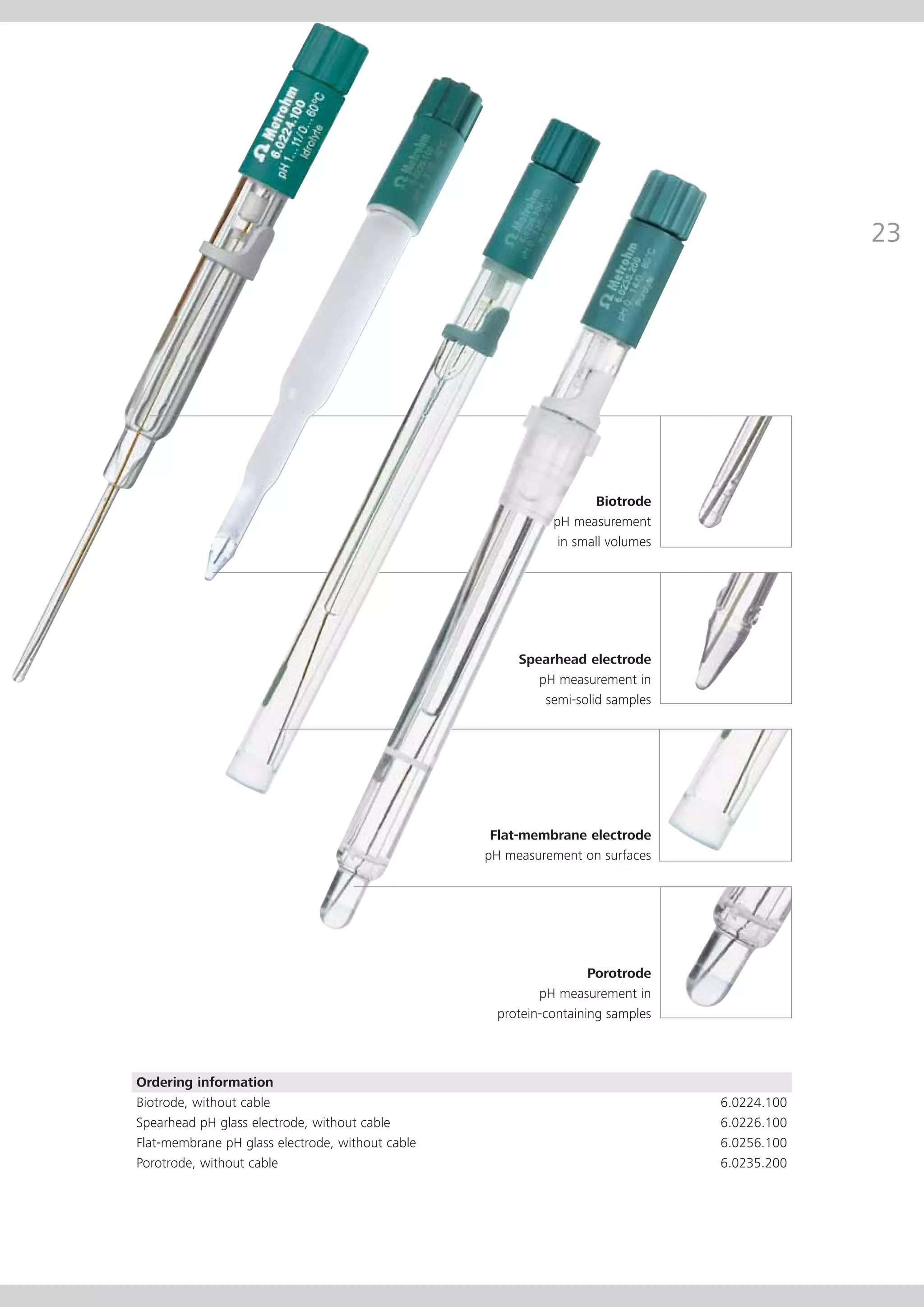
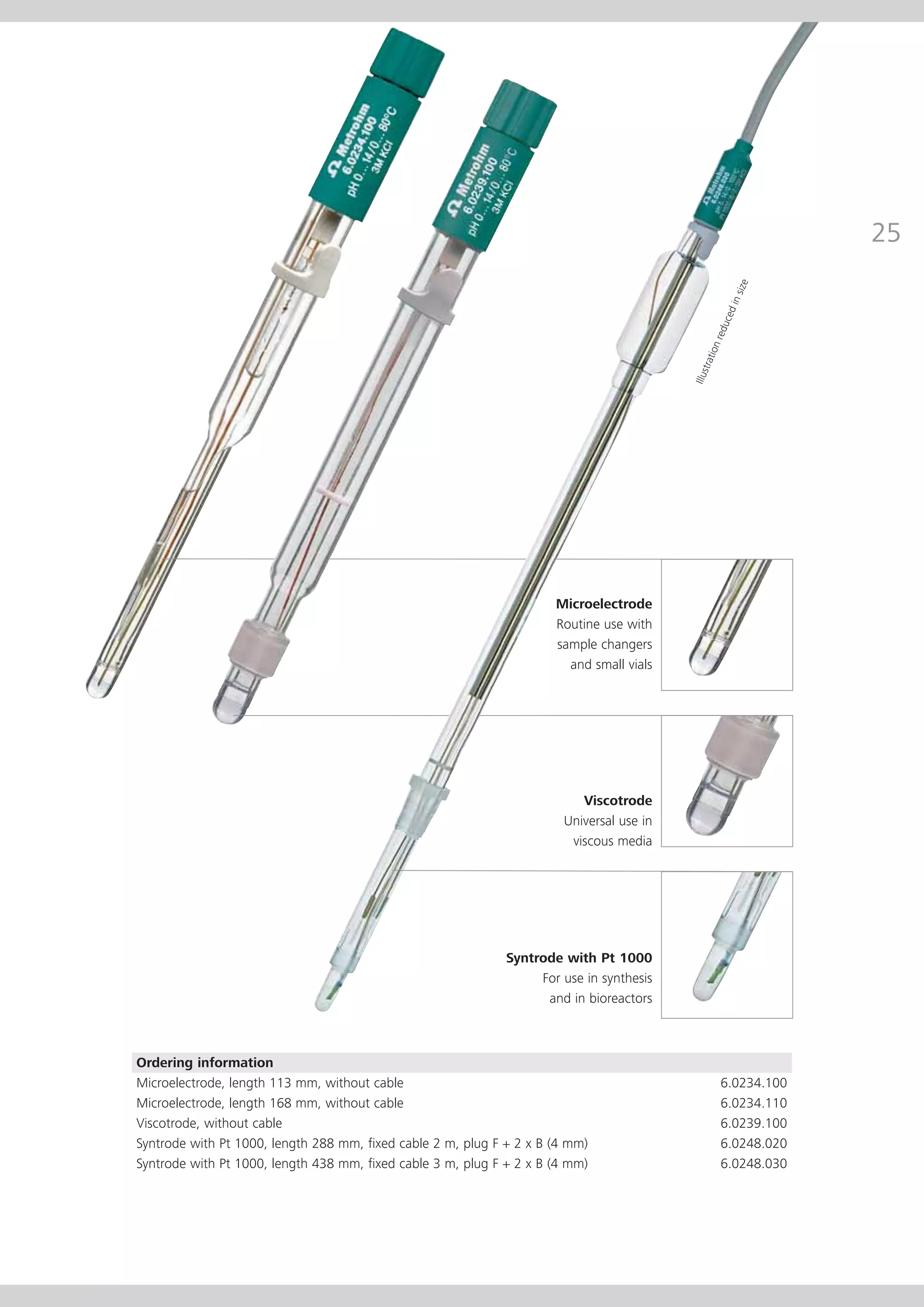
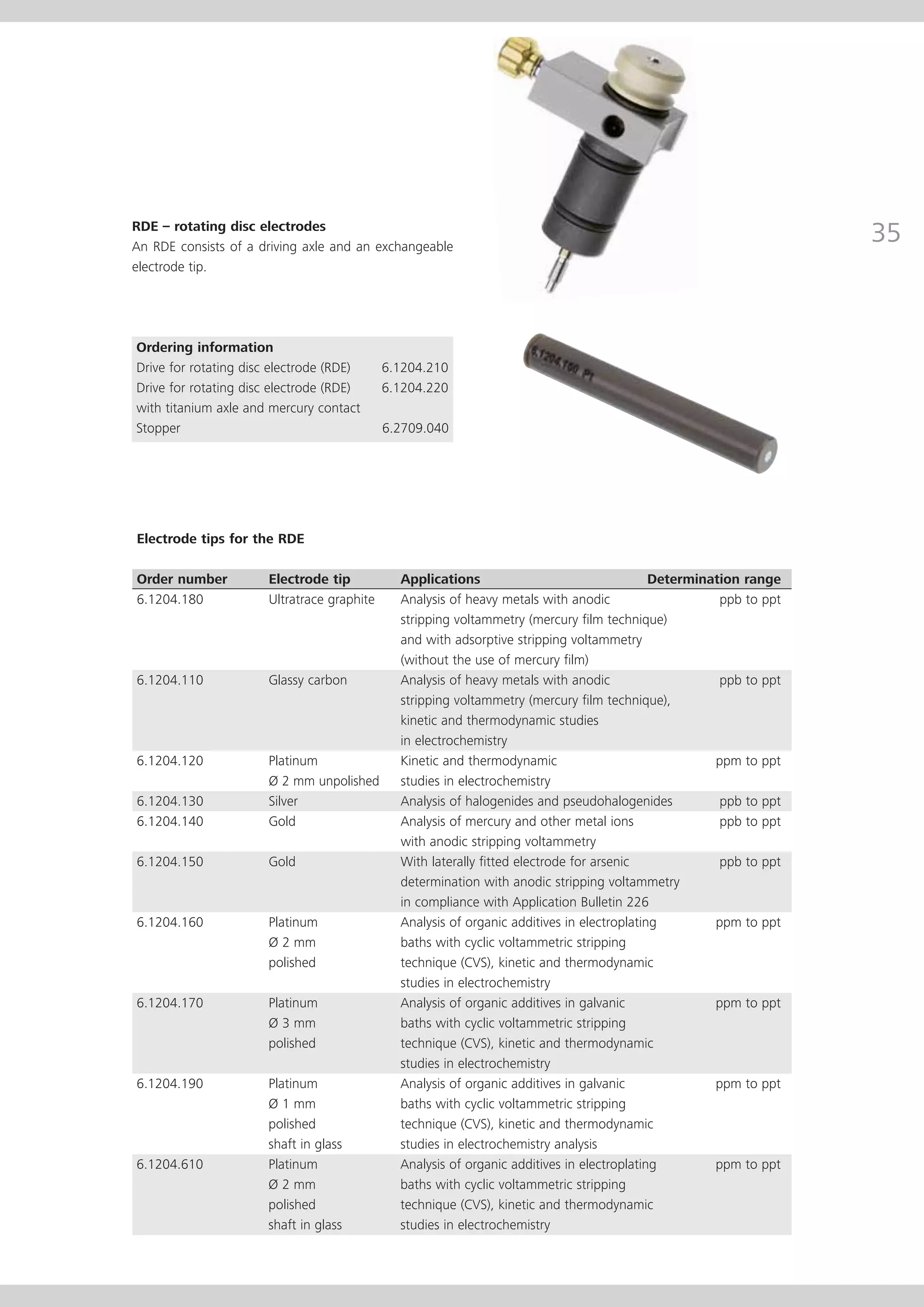
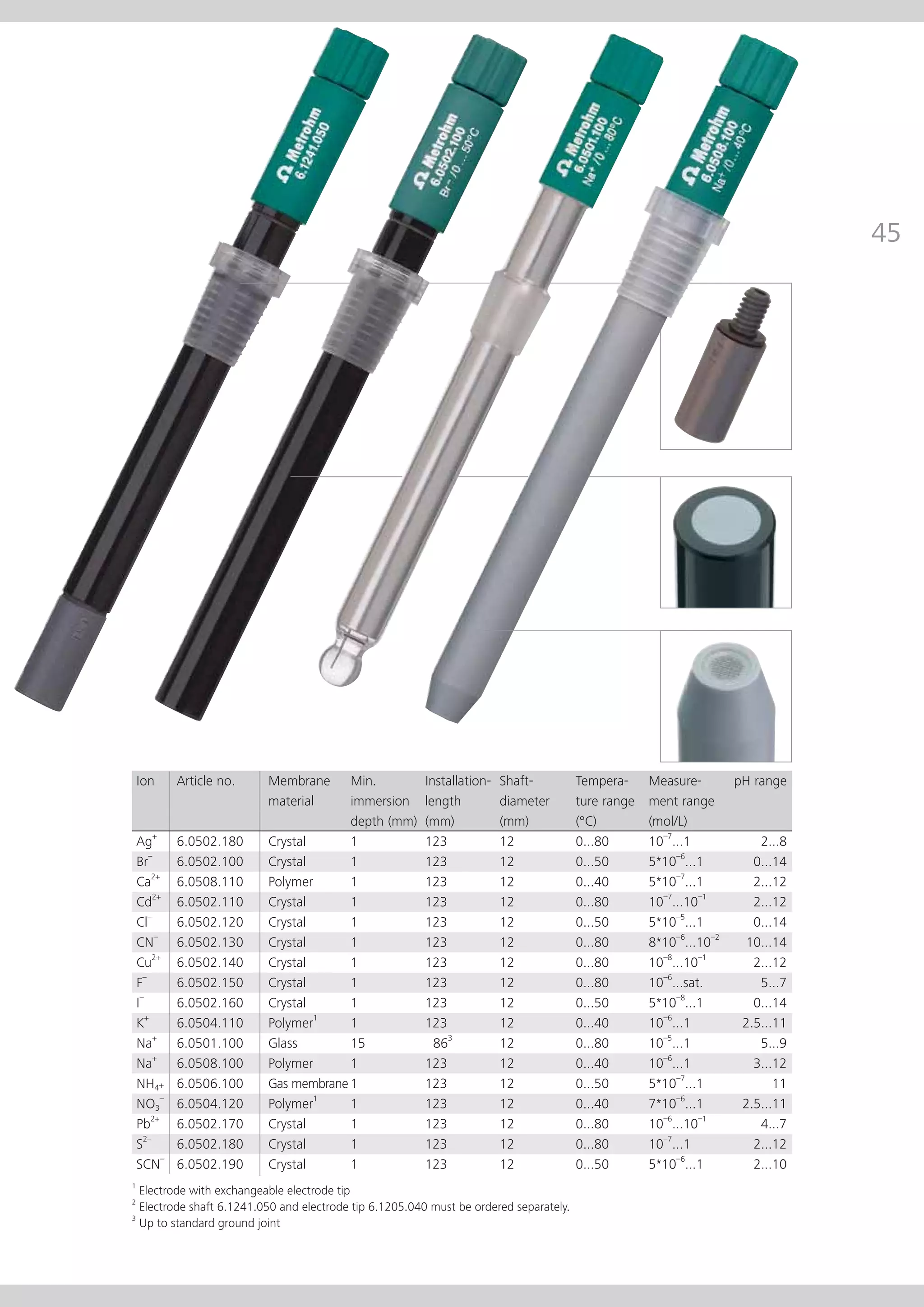
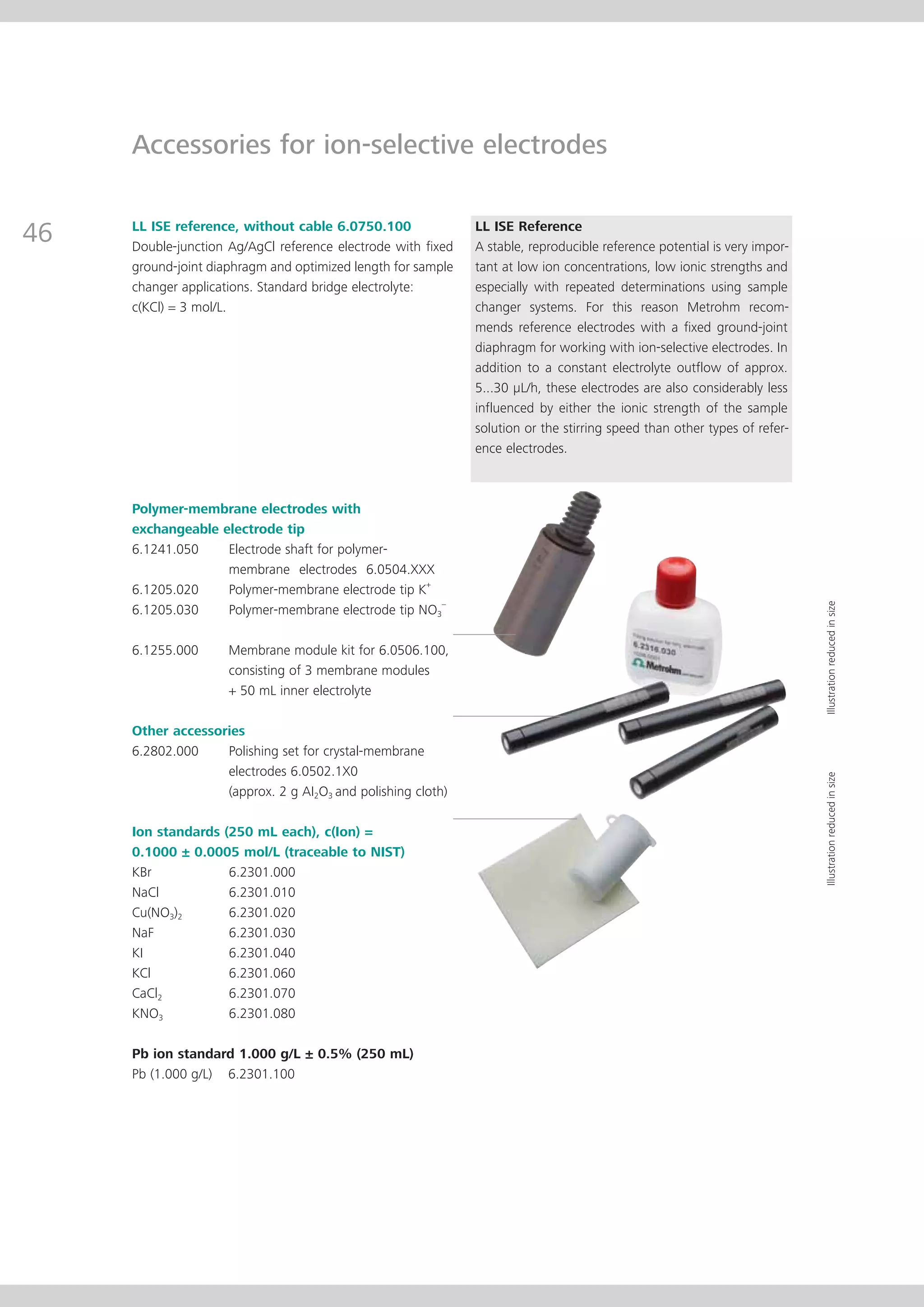
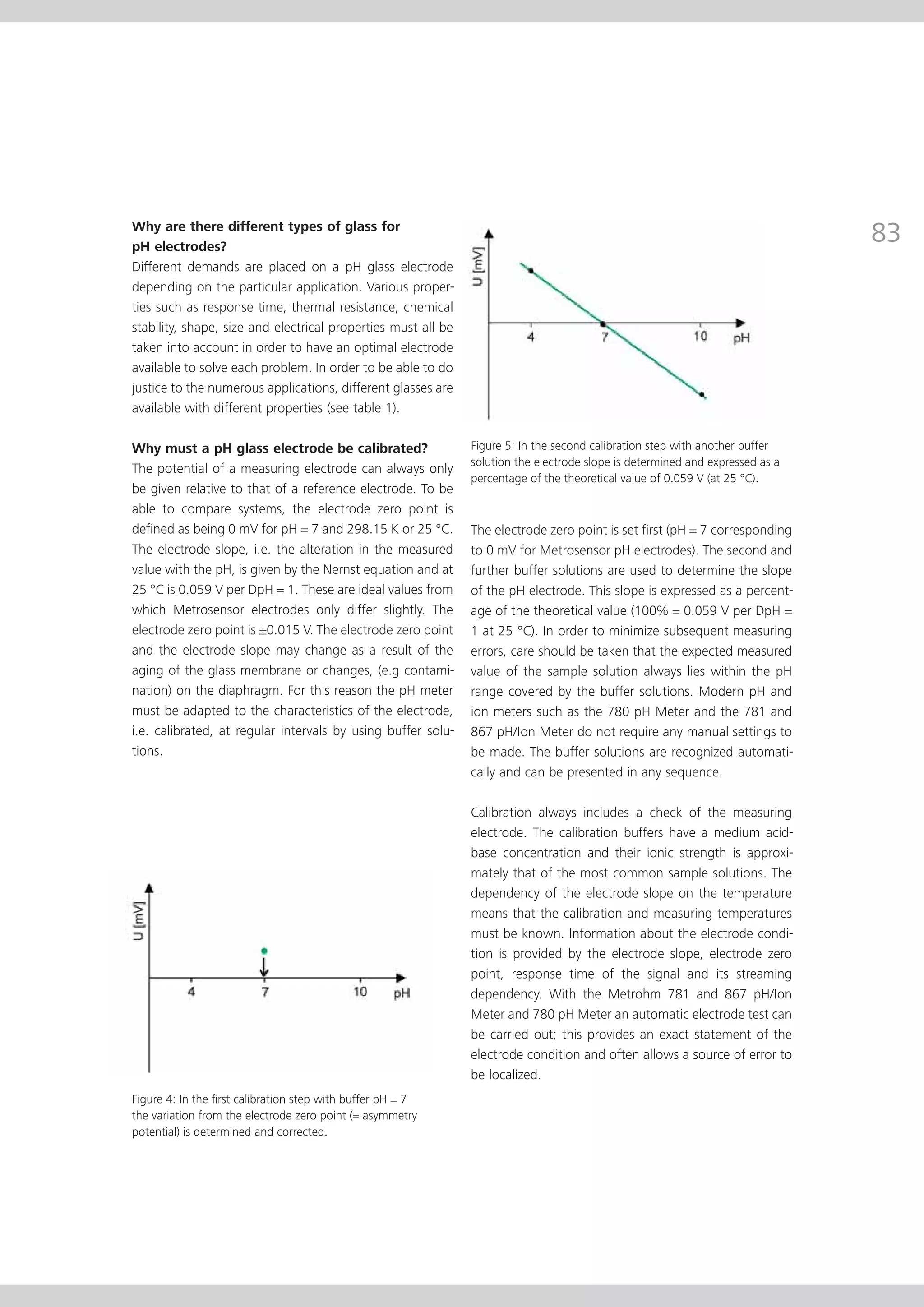
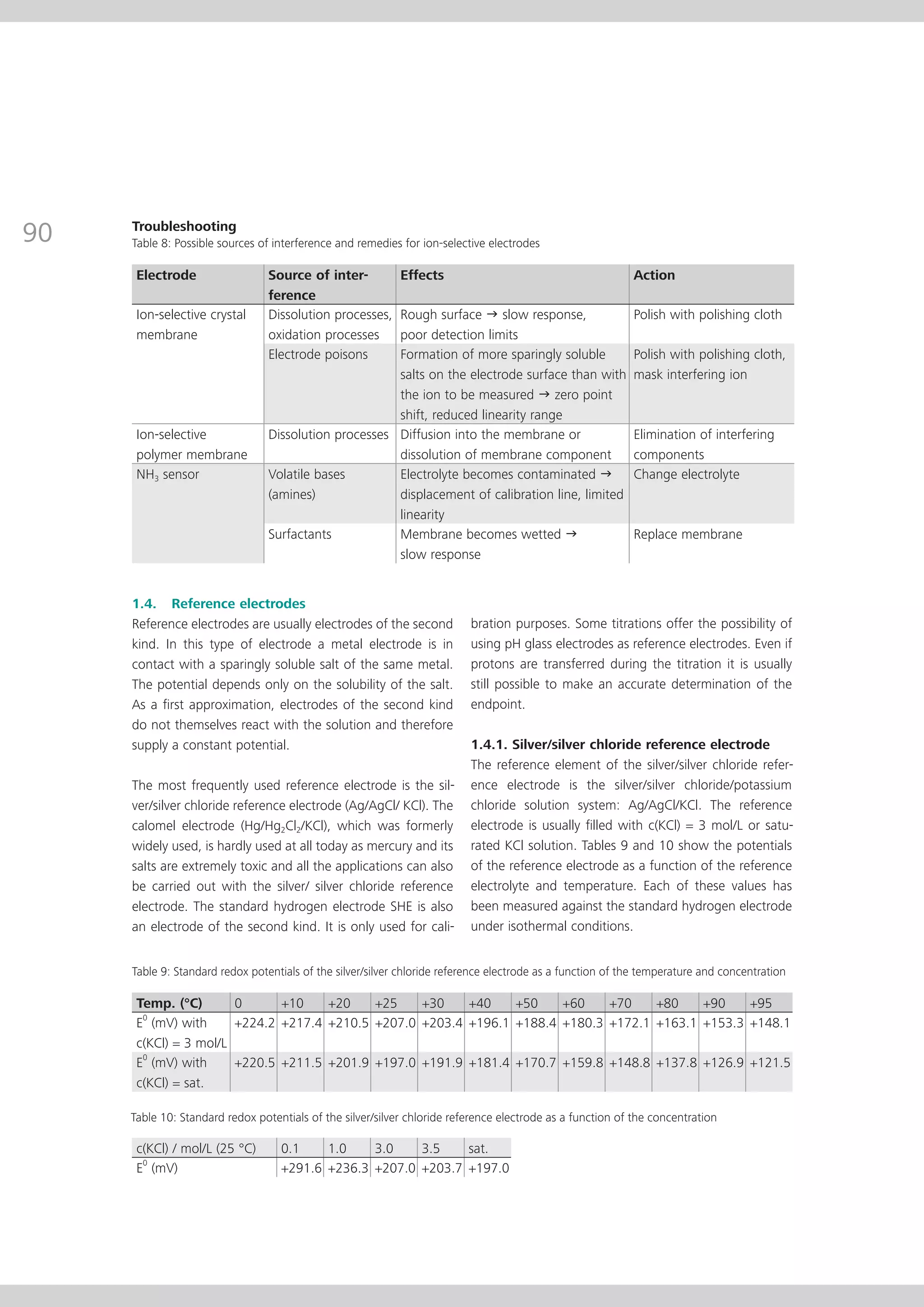
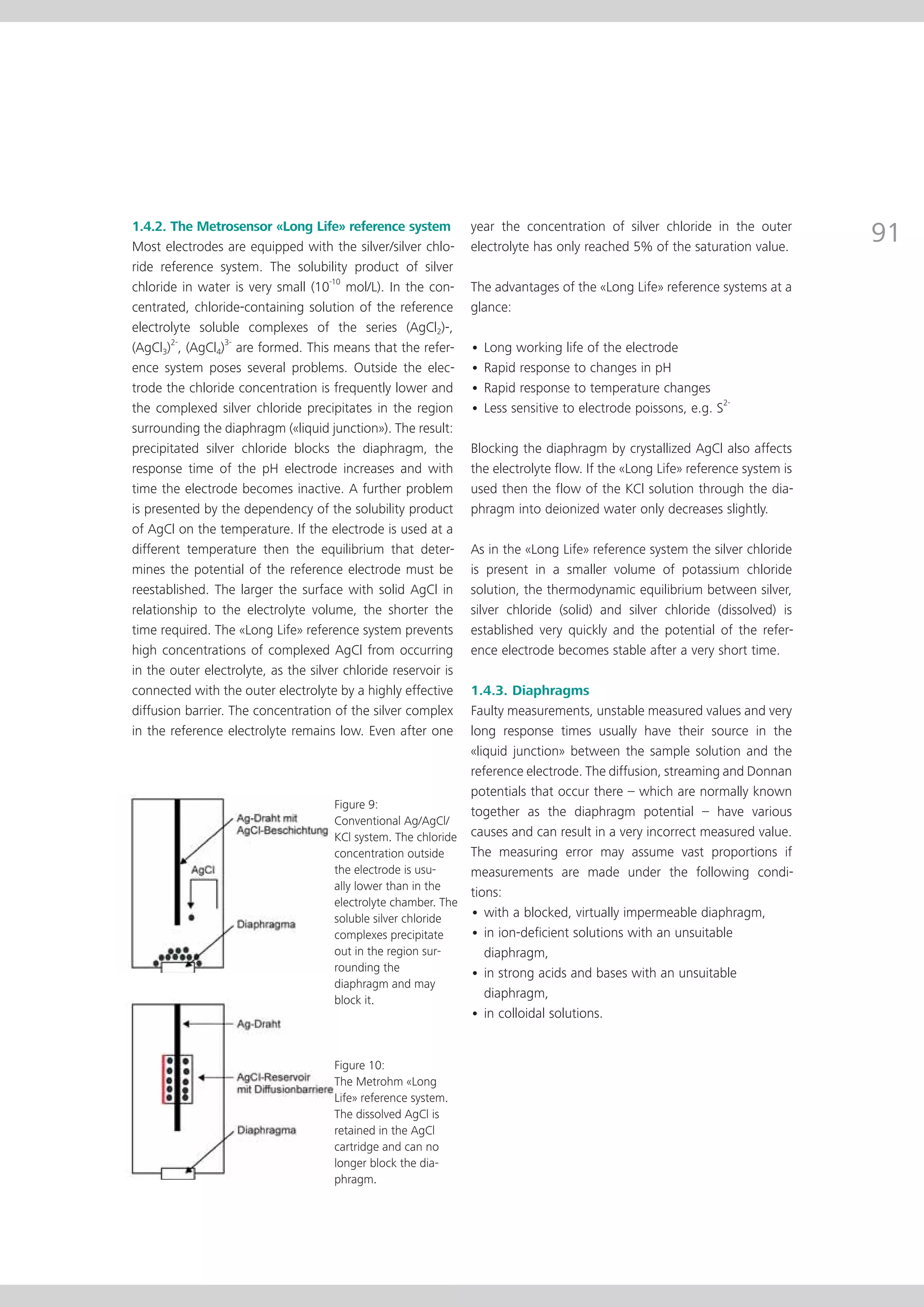
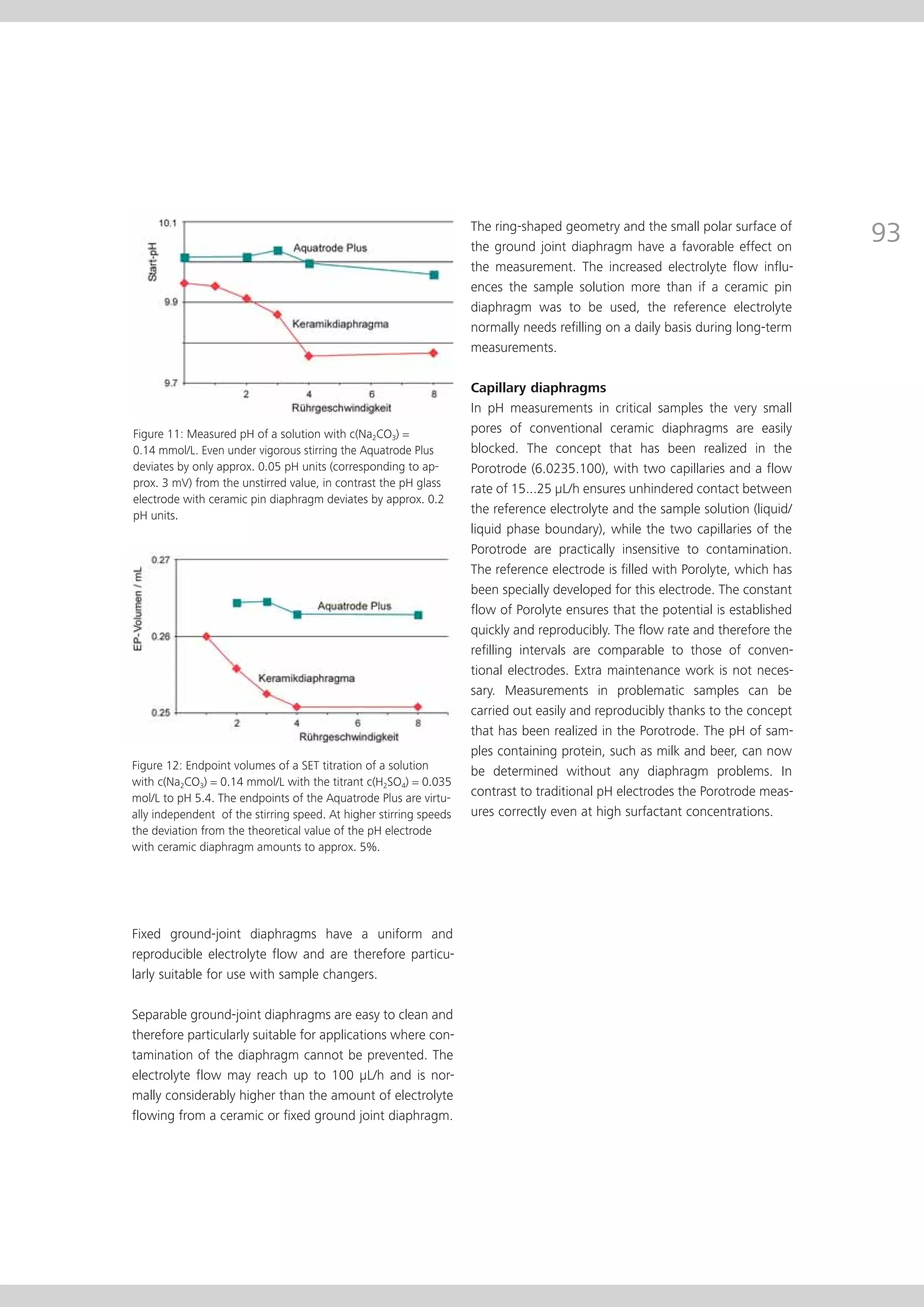
This document provides an electrode catalog with recommendations for which Metrosensor electrodes to use for various pH measurement and titration applications. It lists electrodes for general and specialized pH measurement in areas like water, wastewater, agriculture, food, pharmaceuticals, and more. It also lists electrodes for different types of titrations including acid/base, redox, Karl Fischer, precipitation, and complexometric titrations. The catalog provides details on each electrode model including its order number and the page in the catalog where its specifications can be found.














































































![2. Basics of conductometry
96 2.1. General
Conductometry means measuring the conductivity – a
c = distance between Pt sheets [cm–1]
conductometer measures the electrical conductivity of electrode surface area
ionic solutions. This is done by applying an electric field
between two electrodes. The ions wander in this field. Cell constant (11)
The anions migrate to the anode and the cations to the
cathode. In order to avoid substance conversions and the must be known. The result of the measurement is there-
formation of diffusion layers at the electrodes (polariza- fore always given as the specific conductivity with the
tion), work is carried out with alternating voltage. The unit Siemens per cm (S·cm–1).
rule of thumb is that the frequency of the alternating
voltage must be increased as the ion concentration L * c [S cm–1]
increases. Modern conductometers automatically adapt
the measuring frequency to the particular measuring Specific conductivity (12)
conditions.
This means that the conductometer must be calibrated
Ion migration in an electric field depends on many fac- before each measurement by determining the cell con-
tors. The temperature has a decisive influence on the stant in a solution of known specific conductivity. The
viscosity of the solution and therefore on the mobility of specific conductivity for various concentrations of many
the ions. As the temperature increases the viscosity salts is given in tables. The specific conductivity is
decreases and the conductivity increases. Dissociation linked with the concentration ci of the individual ion i via
constants are also temperature-dependent quantities. the concentration-dependent equivalent conductivity i.
This is why it is important to make measurements at a The equivalent conductivity i is similar to the activity
constant temperature or to compensate for changes of coefficient (see Section 1.2.) and is also a quantity that
temperature by using the so-called temperature coeffi- depends on the concentration.
cient. The temperature coefficient of most salt solutions
∑(
is approx. 2%/°C, but depends on the temperature in i i * zi * ci)
very dilute solutions.
Specific conductivity and concentration (13)
The measuring unit used in conductivity measurements is
At great dilutions, i.e. ci ≤0.001 mol/L, the equivalent
the electrical resistance of the solution. This means that
conductivity i can be equated with the equivalent con-
the conductivity is a sum parameter which includes all
ductivity shown in the tables for an infinite dilution.
dissolved ions. Conductivity cannot be used for the
determination of a single type of ion, unless the sample
is a solution of a single salt or the concentrations of the
other ions are known. The reciprocal value of the meas-
ured resistance of the solution, the so-called conduct-
ance L with the unit Siemens (S = Ω-1) is by itself less
meaningful, as the shape of the measuring cell must be
taken into account. The cell constant c of a conducto-
metric measuring cell](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metrosensorelectrodes-110520065504-phpapp01/75/Metrosensor-electrodes-from-Metrohm-96-2048.jpg)











