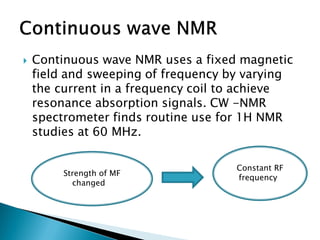
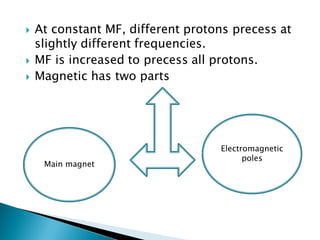
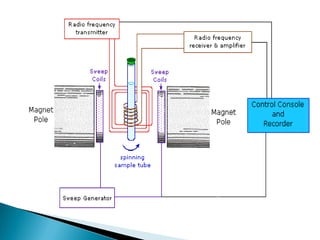
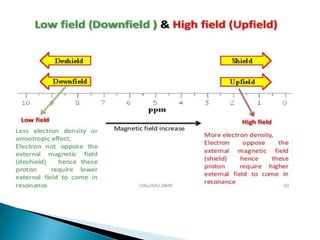
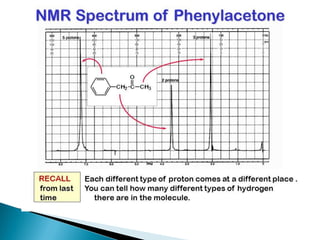
This document describes continuous wave (CW) NMR spectroscopy. It explains that CW-NMR uses a fixed magnetic field and varies the frequency coil current to achieve resonance signals. A typical CW spectrometer contains a sample tube spun between the poles of a powerful magnet. Radio frequency is broadcast into the sample while a receiver coil monitors the absorbed energy. By varying the magnetic field or radio frequency, an NMR spectrum is acquired showing signals from different proton types in the sample. While offering routine 1H NMR studies, CW spectroscopy has limitations such as low sensitivity, requirement for concentrated samples, and production of high noise.