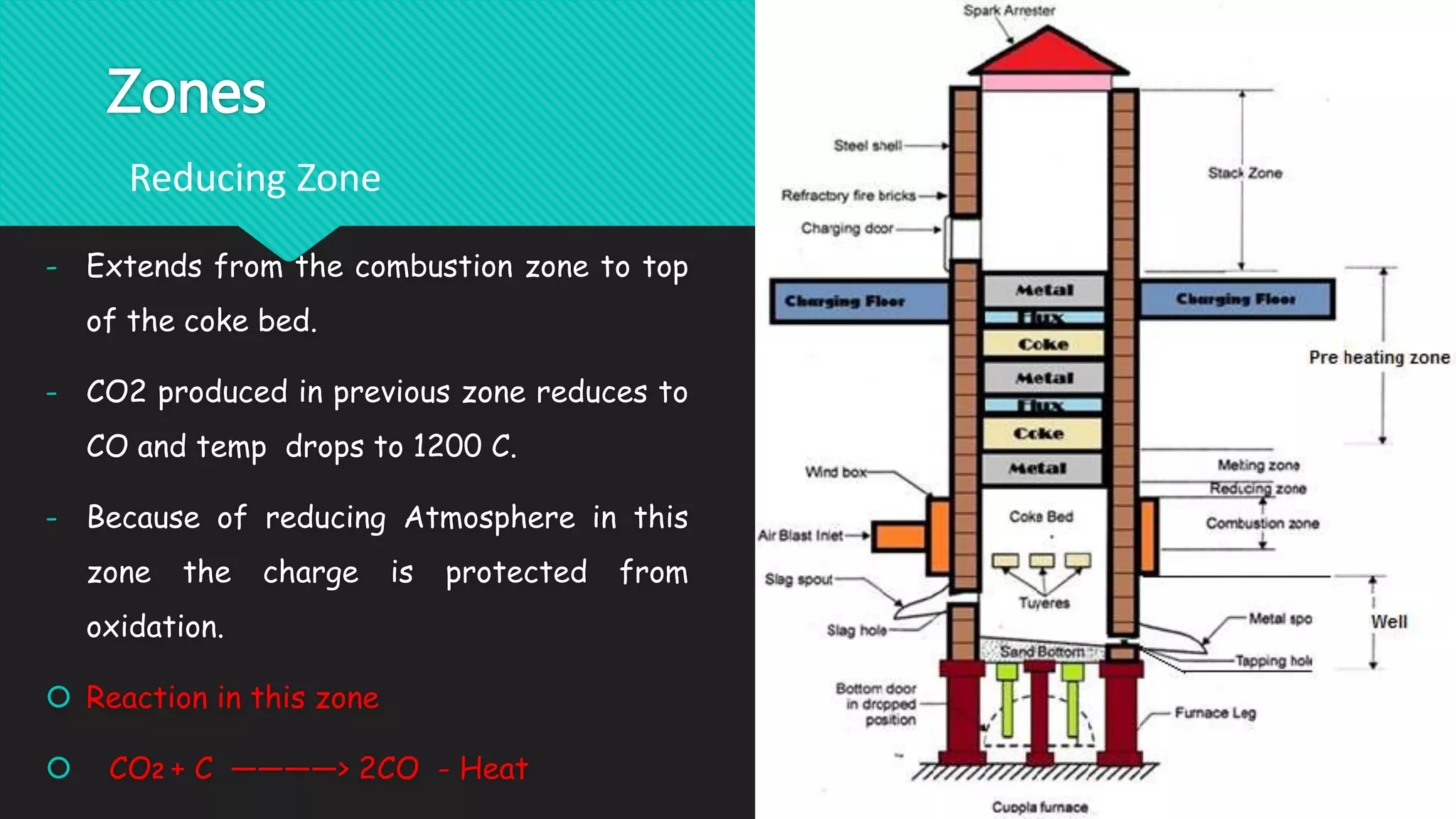
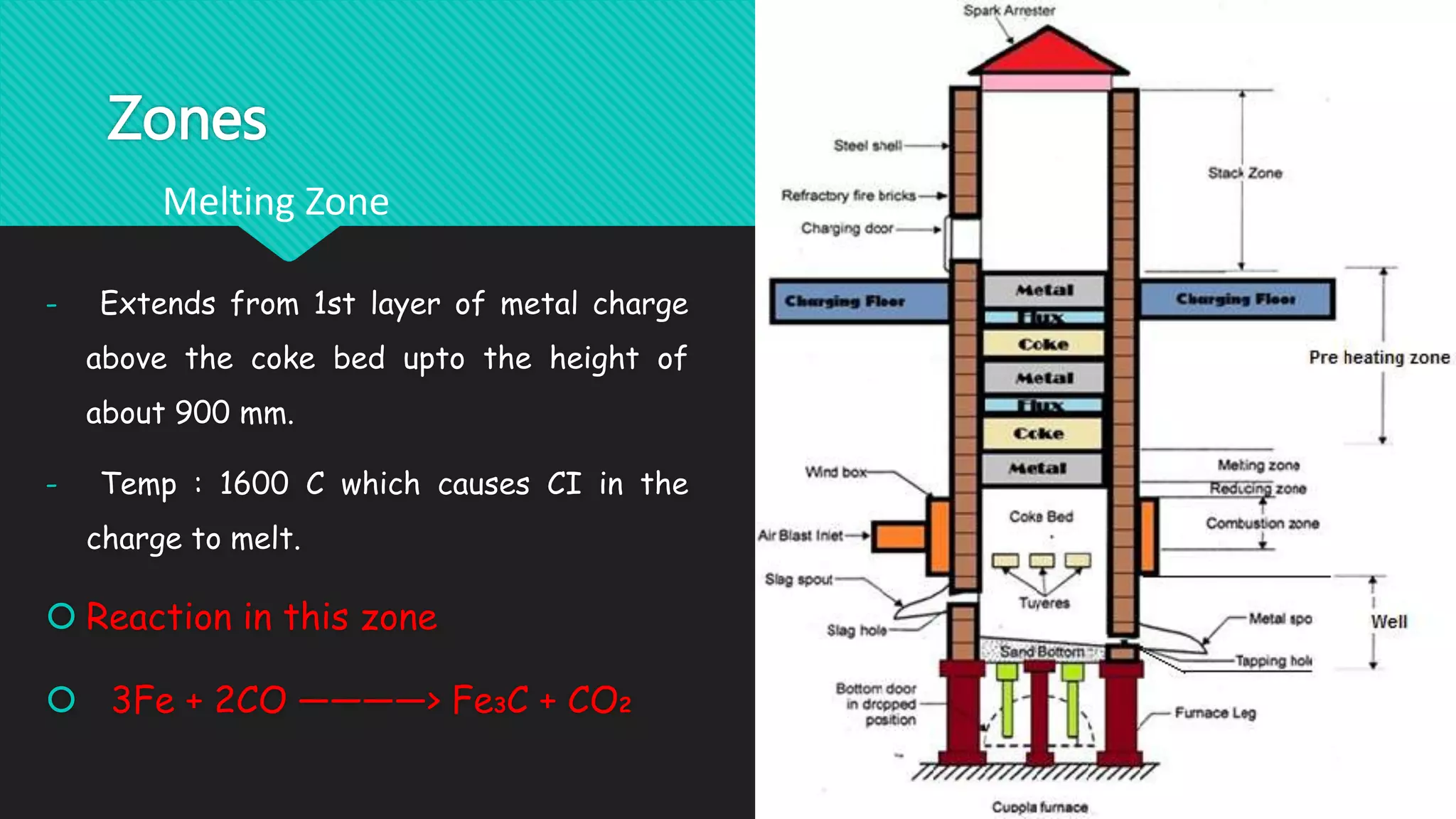
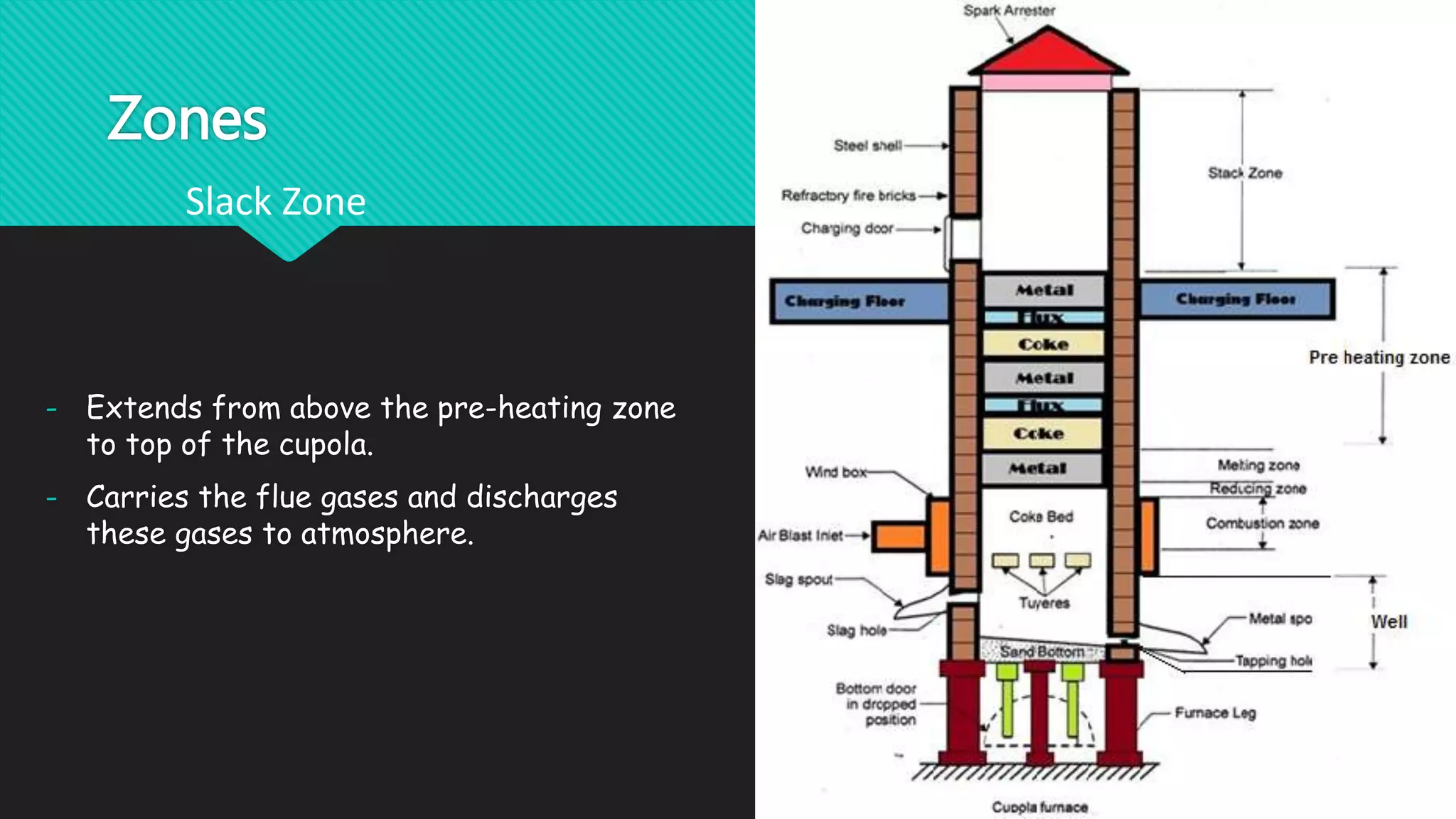
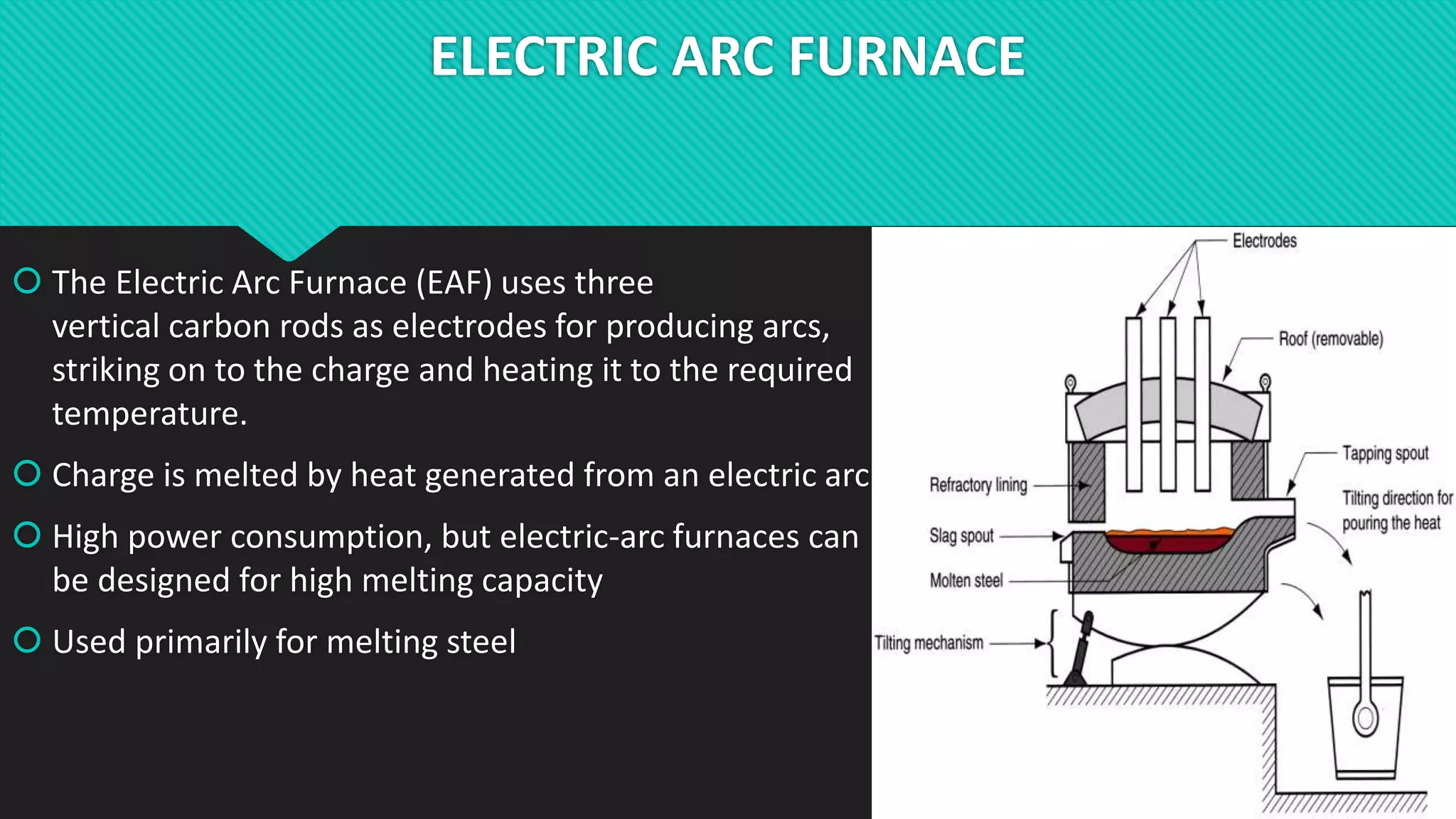
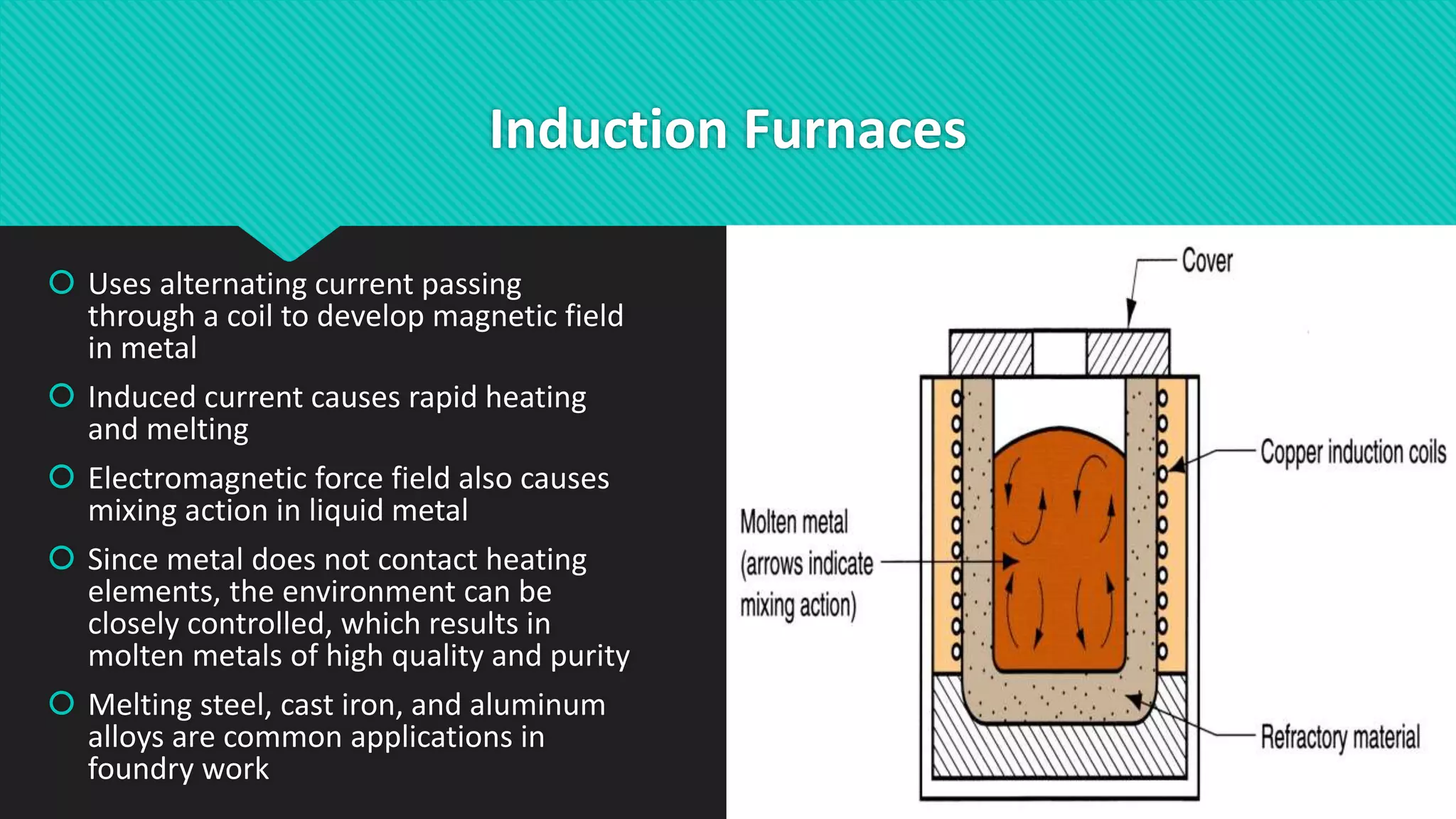
The document discusses different types of metal melting furnaces used in metal casting. It describes Cupola Furnaces, Electric Arc Furnaces, Induction Furnaces, and Metal Pot Furnaces. Cupola Furnaces use layers of metal, coke and limestone fed into the top to melt iron and ferrous alloys through combustion. Electric Arc Furnaces use carbon electrodes to generate arcs and melt metal through heat. Induction Furnaces use electromagnetic induction to rapidly heat and melt metals. Metal Pot Furnaces are used for low melting point alloys like aluminum and are heated by gas or oil without direct contact between flames and metal.