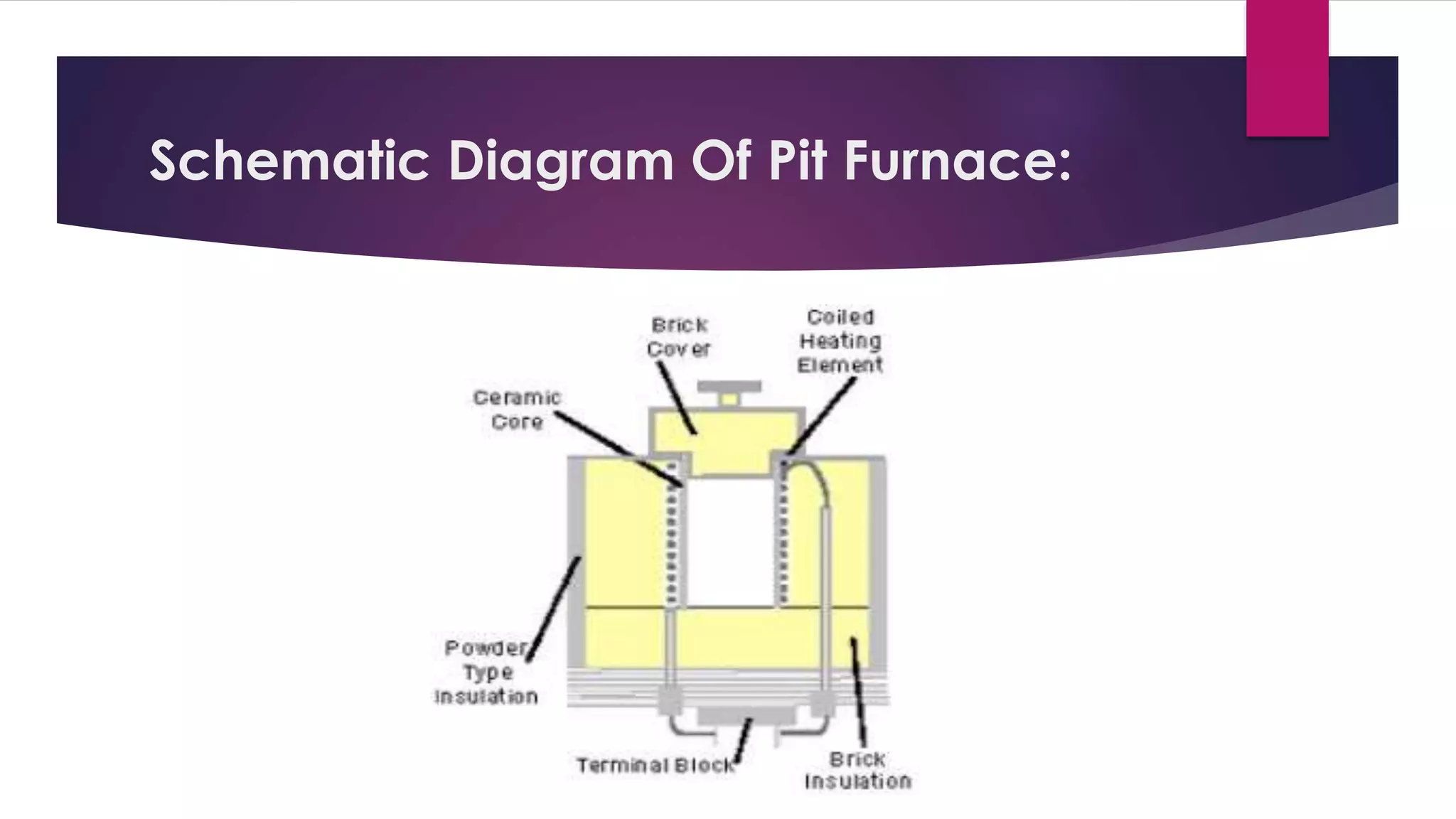
A pit furnace is constructed by digging a pit and building a furnace structure within it. The furnace body is made of steel plates lined with ceramic fiber insulation. It has a lid with a central fan for circulating gases. Pit furnaces can be used to melt metals by placing crucibles containing metal inside. Coke fuel is burned to heat the furnace to the desired temperature for processes like carburizing, hardening, annealing, and nitriding steel parts. Pit furnaces provide flexibility, economic operation, and precision for heat treating large loads.