The document provides an overview of the Internet and how it works:
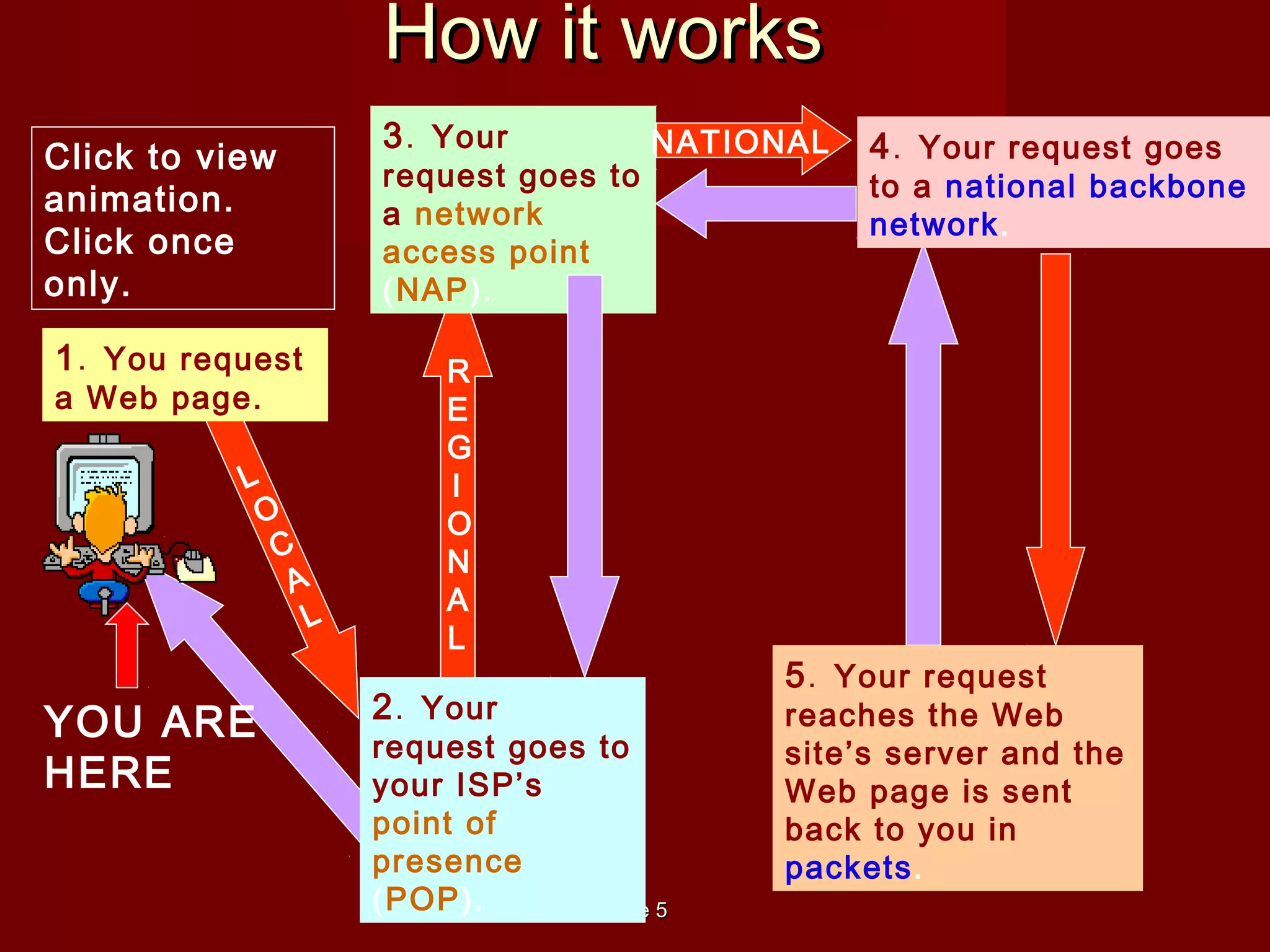
- The Internet is a global network that allows computers to share information electronically. It can be accessed from anywhere through an Internet connection.
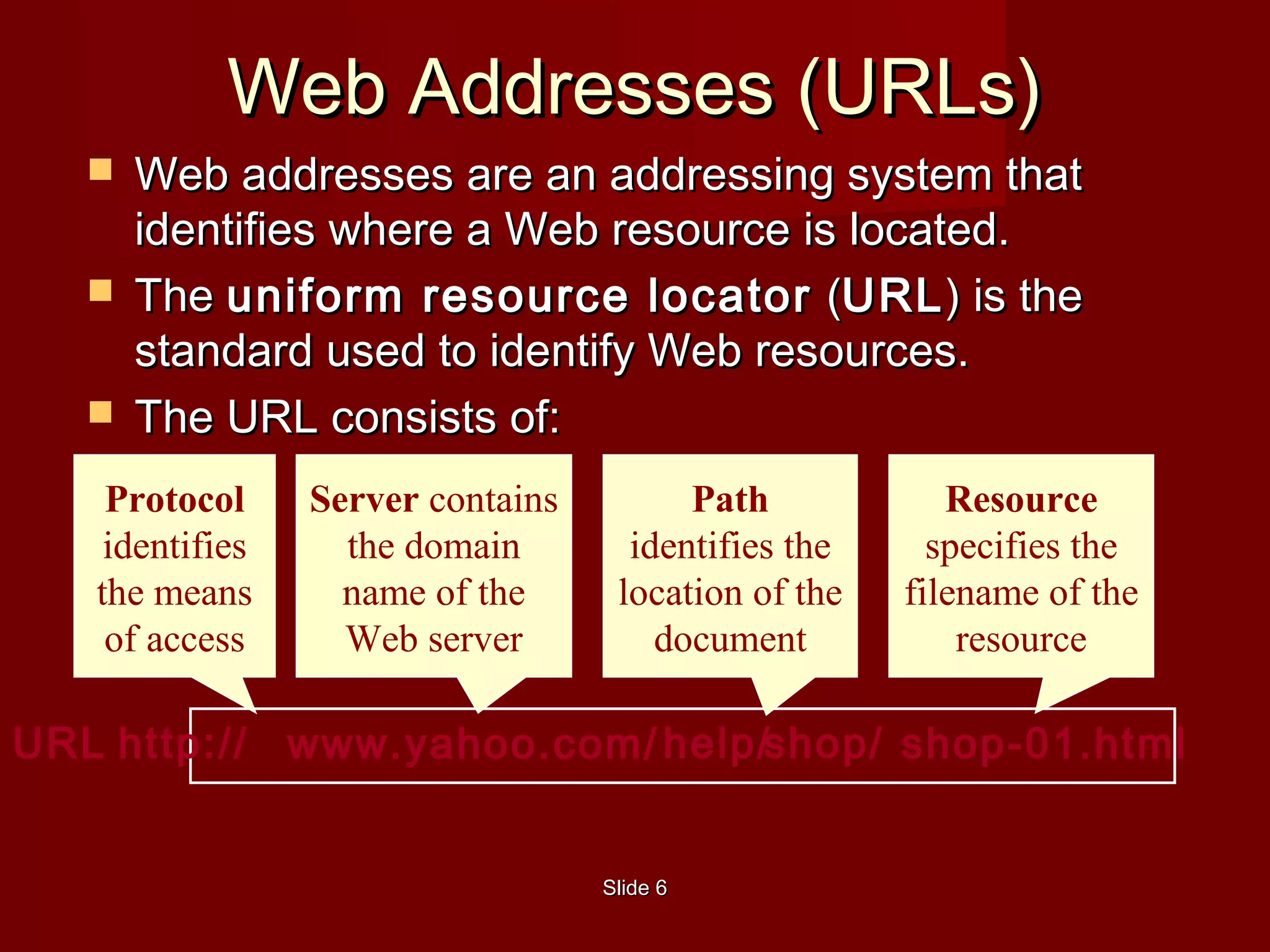
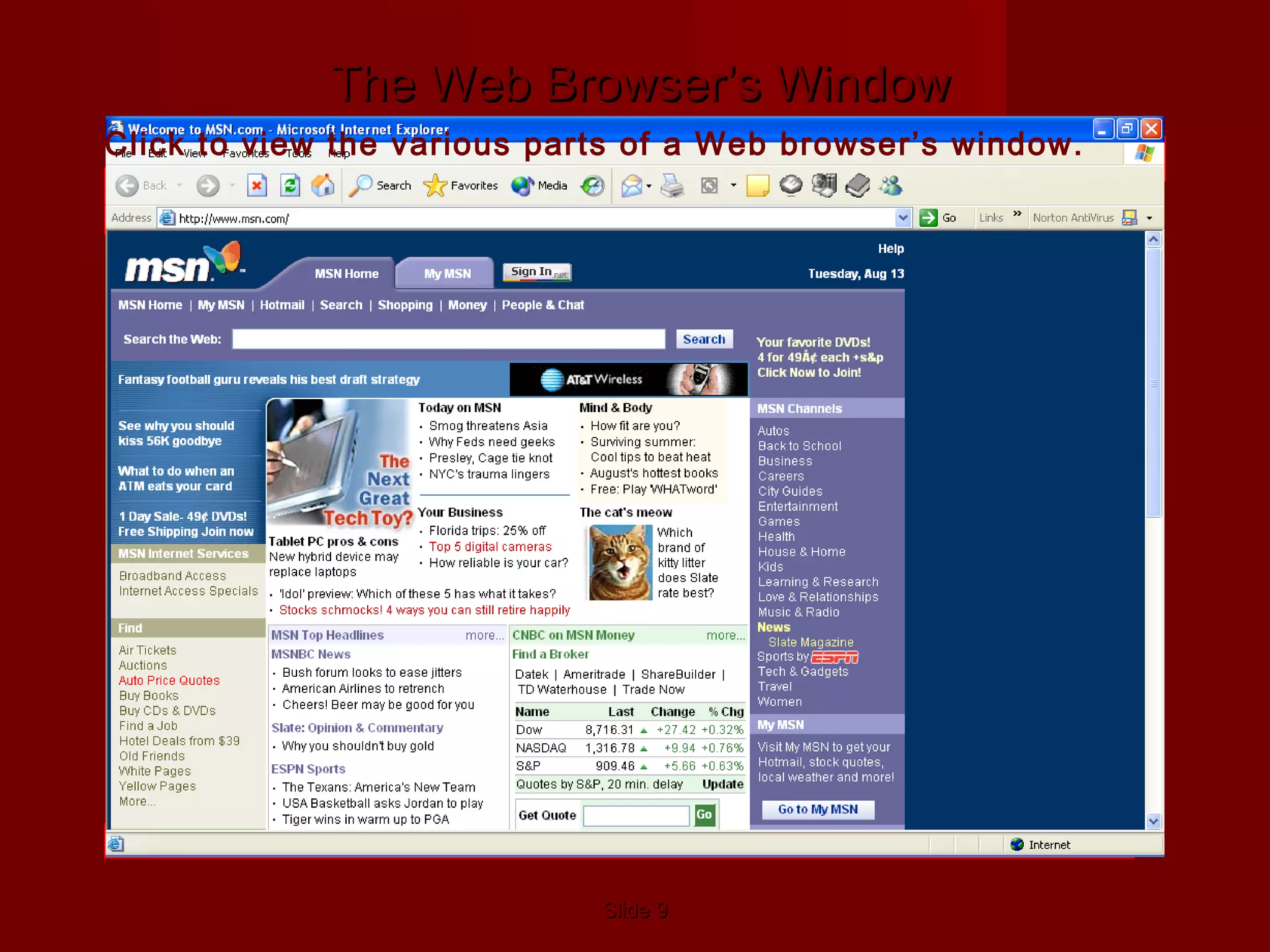
- Web pages are identified by URLs and displayed in web browsers like Safari, Internet Explorer, Google Chrome, and Mozilla Firefox. A URL includes the protocol, server, path, and resource name.
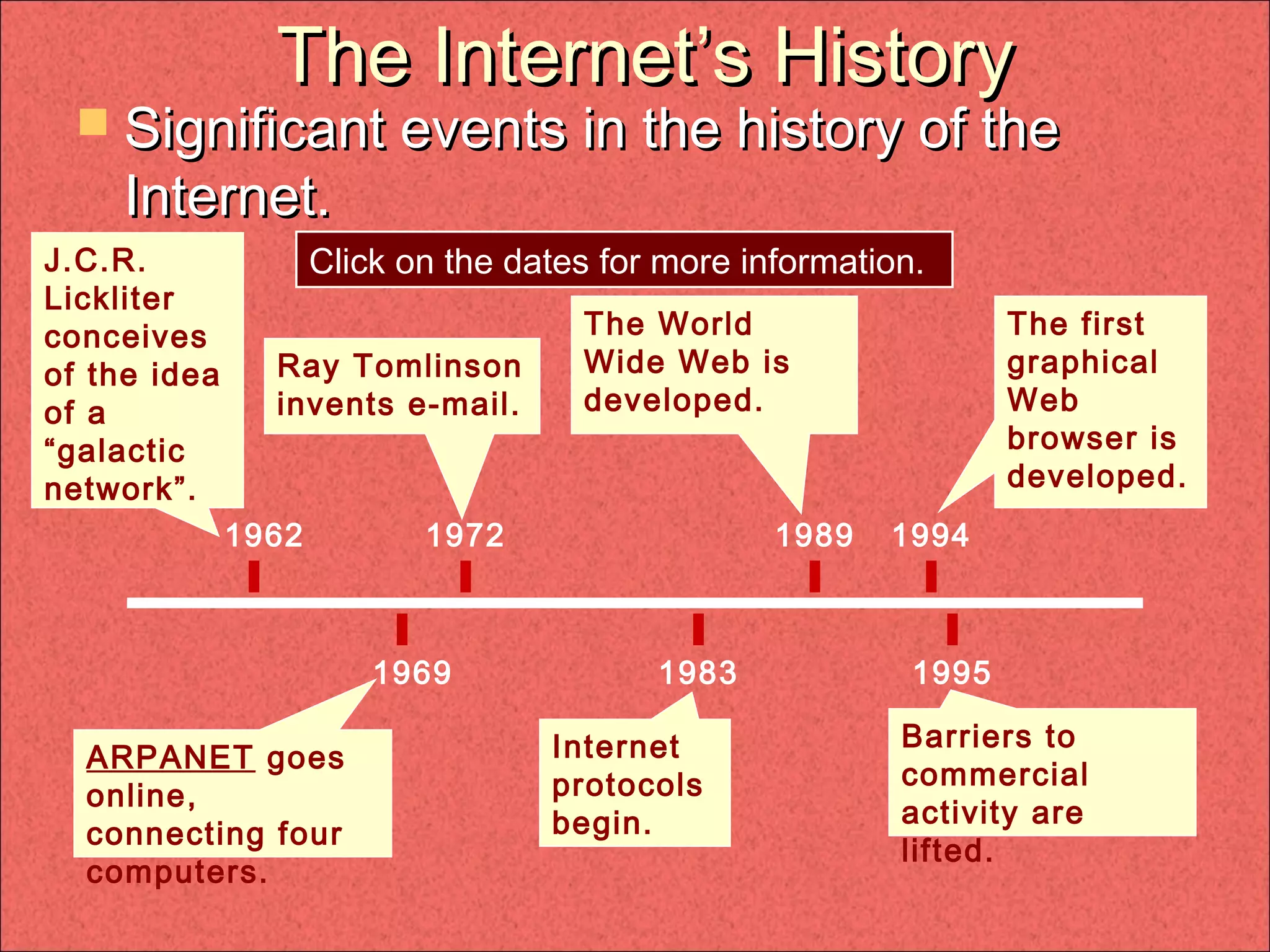
- The Internet has grown from ARPANET in the 1960s and key developments like the introduction of email, the World Wide Web, and graphical web browsers. It enables access to information through various services like web pages, email, file transfers, messaging, and voice calls.