Embed presentation
Downloaded 191 times


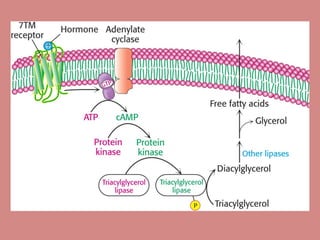
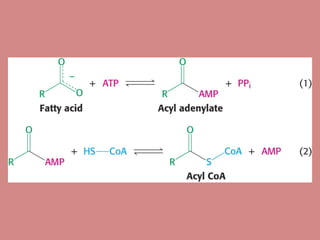
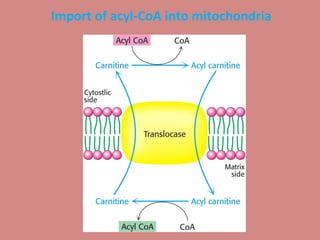
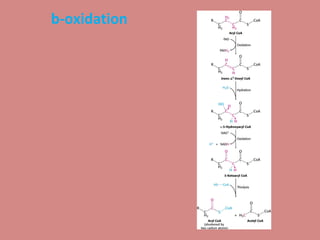


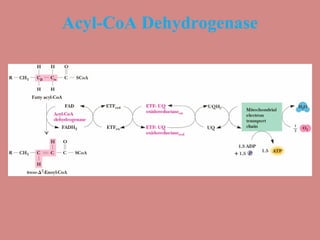
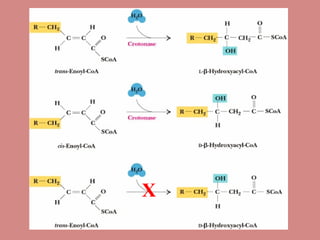
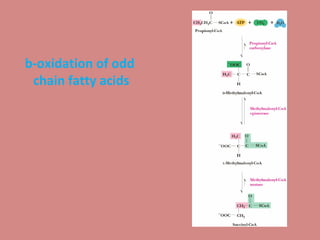
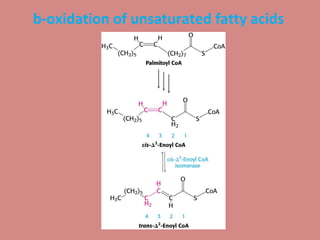
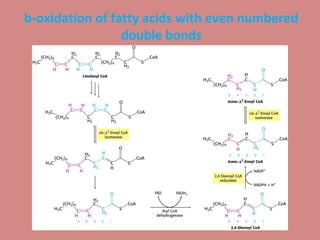
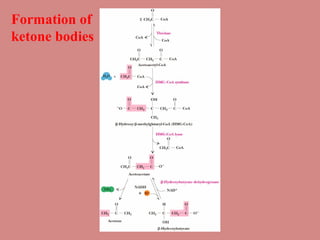
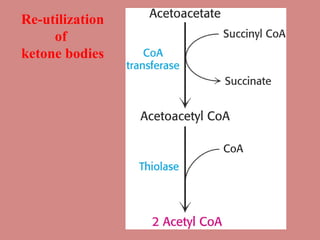
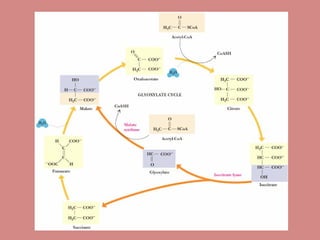
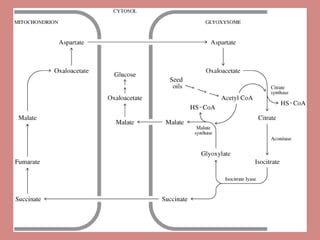

Fatty acid catabolism, or beta-oxidation, is the process by which fatty acids are broken down in the mitochondria to generate energy. The document outlines that beta-oxidation of palmitate, a 16-carbon fatty acid, yields 106 molecules of ATP through multiple steps where acetyl-CoA molecules are produced, generating 80 ATP equivalents total. NADH and FADH2 are also produced, contributing another 17.5 and 10.5 ATP equivalents respectively.
















